Listen to this article
In recent developments regarding US childhood vaccine recommendations, a significant reduction in the list of mandated vaccinations has stirred debate among health officials and parents alike. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has revised their vaccine guidelines, cutting the required immunizations from 17 to 11, focusing now on diseases such as polio and measles while leaving others, including hepatitis and COVID vaccines, up to parental discretion. This decision aligns with recent vaccine schedule changes under the Trump administration, which has been praised by some, including President Trump himself, while receiving sharp criticism from the American Academy of Pediatrics. Many are now concerned about the implications of these childhood immunization updates on public health and the long-term effects of the new vaccine recommendations. As this policy unfolds, the topic of childhood vaccinations has never been more critical, raising questions on how these changes will shape the health environment for American children in the years ahead.
The recent changes to childhood immunization standards in the United States represent a pivotal shift in public health policy, drawing attention to the broader implications for pediatric healthcare. With the recent decision by the CDC to modify the vaccine schedule, fewer diseases are now included in the mandatory immunization list for young children. This trend mirrors an era of evolving vaccine policies, impacted notably by the Trump vaccine policy, which has prompted discussions about the necessity and effectiveness of certain vaccines. Parents and healthcare professionals must now navigate these complex childhood health updates, balancing risks and benefits based on the new recommendations. As society debates potential long-term effects of these adjustments, the conversation on childhood vaccinations remains at the forefront of public health discourse.
Overview of the New US Childhood Vaccine Recommendations
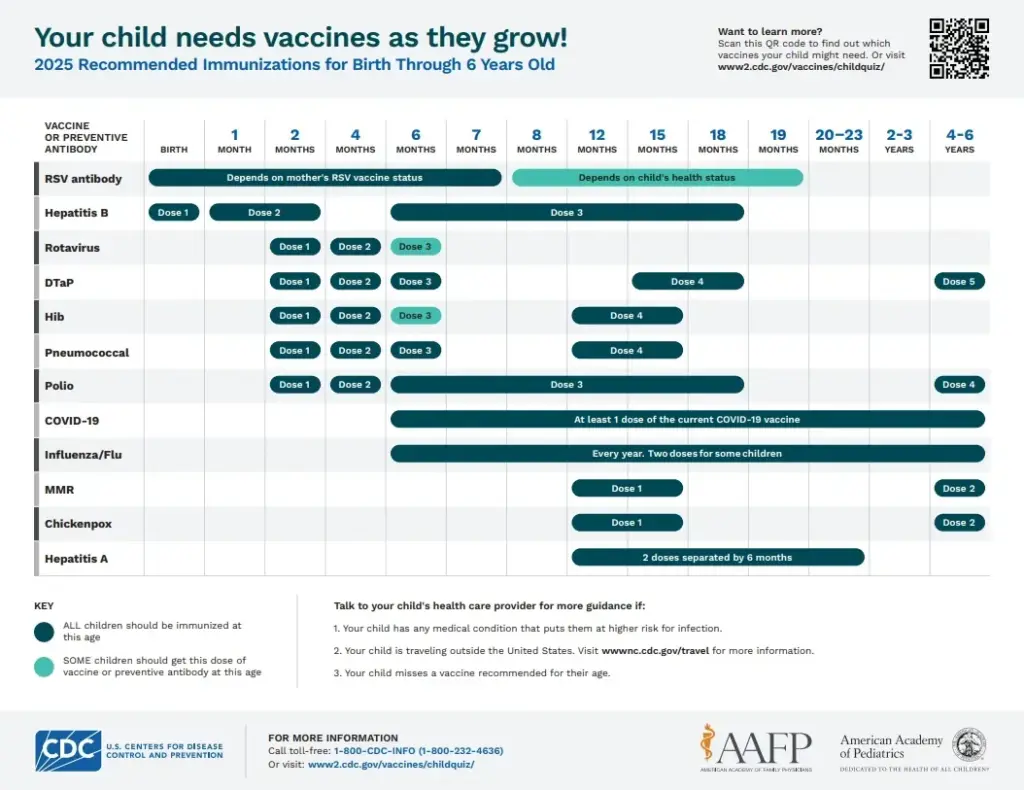
The recent changes to the US childhood vaccine recommendations have stirred considerable debate and concern among health professionals and parents alike. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has significantly reduced the number of diseases for which children are universally vaccinated, dropping the total from 17 to 11. This revision is intended to align the United States’ immunization practices with international standards, reducing the disparity in vaccination policies that existed prior to this change. However, the CDC’s new recommendations have raised questions about the safety and health implications for American children.
As experts analyze the modified vaccine schedule, they assert that while some vaccinations remain mandatory, others, such as those for COVID-19 and hepatitis B, are now relegated to optional status, depending on the child’s risk profile and parental decisions. This nuanced approach attempts to balance public health recommendations with individual family circumstances, yet it creates a landscape where vaccination decision-making is inherently more complex. Critics warn that such changes can lead to lower herd immunity and increased susceptibility to outbreaks of preventable diseases.
Importance of Adhering to CDC Vaccine Guidelines
Following CDC vaccine guidelines is crucial for maintaining public health and safeguarding children against numerous diseases. Vaccinations protect both individual children and the community by preventing the spread of infectious diseases. The recent reduction in the childhood vaccine schedule has raised alarms among healthcare professionals, including those from the American Academy of Pediatrics, who argue that limiting vaccine recommendations could leave children vulnerable. In essence, adherence to established guidelines helps ensure that rates of vaccination remain high, thus preventing outbreaks of diseases like measles and polio.
Health professionals emphasize that adherence to these guidelines not only protects children but also contributes to the broader goal of public health safety. Increased vaccination rates lead to herd immunity, which is essential for protecting those who are unable to be vaccinated for medical reasons. The recent changes to the vaccination recommendations highlight the importance of consulting healthcare providers to understand the implications of an altered vaccine schedule. Parents must navigate these changes carefully to ensure their children are adequately protected.
Effects of Vaccine Recommendations on Public Health
The changes in vaccine recommendations have direct implications for public health in the United States. Reducing the number of mandatory vaccinations could potentially lead to a rise in vaccine-preventable diseases, particularly as misinformation about vaccines continues to proliferate. Concerns have been raised regarding the public’s trust in the healthcare system, especially given the controversial nature of some political figures involved in these policy changes. Health experts warn that these shifts may inadvertently encourage vaccine hesitancy among parents, casting doubts on the effectiveness of vaccines that have historically contributed to significant reductions in disease prevalence.
Additionally, the alignment of US vaccine recommendations with those of other countries, as mentioned by the CDC, still requires careful consideration of the unique demographic and health infrastructure of the US. The comprehensive nature of public health policies should consider various sociocultural factors affecting vaccination uptake. The effects of these recommendations could vary greatly, and extensive monitoring will be necessary to assess the impact on public health outcomes over time.
The Role of Political Influence in Vaccine Policy
Political influence inevitably impacts health policy, and the recent revision of vaccine guidelines in the US is no exception. With former President Trump openly supporting these changes and framing them as rooted in scientific rigor, the political implications cannot be overlooked. This influence has led some to express concern that vaccine recommendations may be swayed by political agendas rather than public health evidence. The role of political figures like Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. complicates the vaccine discourse, particularly given his skeptical views on vaccine safety.
Healthcare providers and public health officials emphasize the need for policy decisions to prioritize scientific evidence above political considerations. The perception that vaccine policies are influenced by political motives can undermine public trust in immunization programs. Stakeholders urge that any vaccine recommendations be created through collaborations among healthcare professionals, public health agencies, and community representatives, ensuring that they are both scientifically sound and accepted by the broader population.
Implications of Vaccine Schedule Changes for Healthcare Providers
The recent amendments to the US childhood vaccine schedule present significant challenges for healthcare providers. With the decrease in the number of vaccinations recommended outright, pediatricians and family doctors must now navigate a complex landscape where vaccine recommendations depend on shared clinical decision-making between parents and providers. This shift necessitates that healthcare professionals are well-informed and prepared to discuss these changes comprehensively with parents, helping them make informed choices about their children’s health.
Moreover, the lack of a clear directive regarding certain vaccinations may contribute to confusion among families. It is essential that healthcare providers take the initiative to educate patients about which vaccinations are critical and which remain optional based on individual health evaluations. Establishing trust through effective communication will be key as providers balance their role as educators with the latest recommendations.
Understanding the Complexity of Informed Consent in Vaccinations
Informed consent is crucial in the context of childhood vaccination, particularly following the adjustments made to the CDC’s recommendations. With the shift away from mandatory vaccines for certain diseases, parents are now tasked with understanding the risks and benefits of optional vaccines. This underscores the necessity for healthcare professionals to provide thorough information, enabling parents to make educated decisions regarding their child’s immunization. Transparency within conversations about these changes can foster a collaborative healthcare environment.
Furthermore, informed consent becomes vital as parents weigh the benefits of vaccinations against potential risks. Each family may have unique considerations based on their health history and societal factors, making personalized discussions with healthcare providers essential. Implementing truly informed consent processes involves not only presenting information but also engaging with parents to address their concerns and preferences openly.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy Among Parents
Vaccine hesitancy poses a pressing challenge, especially following significant revisions to childhood immunization guidelines. As the CDC eases certain vaccination mandates, parents may be more apprehensive about vaccinating their children, resulting in lower vaccination rates and increased disease risks. Addressing these concerns requires healthcare providers to engage effectively with families, validating their worries while providing evidence-based information to alleviate fears about vaccine safety and efficacy.
Strategies to build trust are essential in combating vaccine hesitancy. Community outreach programs, educational campaigns, and transparent discussions about the rationale behind changing vaccine guidelines can help increase understanding and acceptance. By fostering an environment of trust and clear communication, healthcare professionals can play a critical role in encouraging parents to adhere to recommended immunizations, ultimately benefiting public health at large.
The Future of US Childhood Immunization Practices
Looking ahead, the future of childhood immunization practices in the United States hinges on the outcomes of current policy changes and their reception by the public. As the CDC continues to monitor vaccine uptake and disease prevalence, adaptations to the recommended schedule may be necessary. Ongoing research into the effectiveness and safety of vaccines will guide future recommendations, emphasizing the need for an evidence-driven approach in the framing of public health policies.
In addition, it will be critical to foster an environment where transparency and scientific discourse are prioritized. Continuous engagement with healthcare professionals, legislators, and communities can ensure that immunization policies reflect both the health needs of the population and the scientific evidence available. Establishing a responsive and adaptive vaccination strategy is vital to safeguarding the health of future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest US childhood vaccine recommendations from the CDC?
The latest US childhood vaccine recommendations from the CDC have reduced the number of mandatory vaccines from 17 to 11. The updated schedule includes vaccines against diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella, polio, and pertussis, with hepatitis A and B, and COVID-19 vaccines suggested based on individual risk factors and shared decision-making between healthcare providers and parents.
How have the CDC vaccine guidelines changed recently?
Recently, the CDC vaccine guidelines have undergone significant changes, reflecting a reduction in required vaccinations for children from 17 to 11. This change emphasizes a distinction between mandatory vaccines and those recommended based on risk, ostensibly aimed at aligning US recommendations more closely with international practices.
What are the implications of the recent vaccine schedule changes for parents?
The recent vaccine schedule changes mean that parents now have more discretion over certain vaccines, such as COVID-19 and hepatitis vaccines, which can be decided in consultation with healthcare providers. This shift may create uncertainty for some families, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making regarding childhood immunizations.
What effects do the new childhood immunization updates have on public health?
The new childhood immunization updates may lead to confusion and concern among parents and healthcare providers, potentially undermining confidence in vaccines. Critics, including the American Academy of Pediatrics, warn that these changes could compromise public health by reducing vaccination rates for critical diseases.
What stance did President Trump take regarding the new vaccine recommendations?
President Trump endorsed the new US childhood vaccine recommendations, describing them as scientifically sound and necessary reforms. His administration’s changes to the CDC vaccine guidelines are seen as part of a broader effort to streamline immunization practices and rebuild trust in the US healthcare system.
How do the CDC vaccine guidelines compare with international practices?
The CDC vaccine guidelines are now proposed to align more closely with international practices, reducing the diseases covered to match models like Denmark, which recommends vaccinations against 10 diseases. However, critics argue that such comparisons are inappropriate given the vastly different public health landscapes between countries.
What criticisms have been raised concerning the new childhood vaccine schedule?
Critics, including pediatricians and public health officials, have raised concerns that the new childhood vaccine schedule lacks scientific support, could instill fear among parents, and may threaten the health of children by reducing vaccination coverage for serious diseases like hepatitis and COVID-19.
Why are some vaccines now recommended based on risk rather than universally mandated?
The recent changes in US childhood vaccine recommendations reflect a move towards personalized medicine, where vaccines like hepatitis A and B, and COVID-19 can be advised based on individual health risks and circumstances, allowing for shared decision-making between parents and healthcare providers.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Reduction in Recommended Vaccines | The number of vaccines recommended for children has decreased from 17 to 11. |
| New Vaccination Guidelines | The CDC now recommends vaccines for measles, mumps, rubella, polio, pertussis, tetanus, diphtheria, Hib, pneumococcal disease, HPV, and chickenpox. |
| Vaccines Based on Risk | Certain vaccines like hepatitis A and B, and COVID vaccines are now suggested based on risk factors and discussion between parents and doctors. |
| Criticism from Medical Community | The American Academy of Pediatrics has criticized the recommendations as ‘dangerous and unnecessary’. |
| Support from Political Figures | President Trump praised the guidelines for being ‘rooted in science’. Health Secretary Kennedy supports the changes based on an extensive review. |
Summary
The recent changes to US Childhood Vaccine Recommendations mark a significant shift in immunization policy, calling for vaccinations against only 11 diseases. While some argue that these modifications are based on scientific reviews aimed at protecting children, the response from pediatricians and health experts has been overwhelmingly critical, warning that the new approach could lead to public confusion and diminished trust in vaccinations. Overall, these changes reflect a departure from previous practices and raise concerns about the long-term effects on child health.