Listen to this article
The United Kingdom is set to take a significant leap forward in energy innovation with its first small modular reactor (SMR) nuclear plant, slated to be built at the historic Wylfa site on Anglesey, North Wales. This groundbreaking project, supported by a £2.5 billion investment from the government, marks a pivotal moment in the UK’s nuclear power landscape as it aims to generate cleaner energy while creating thousands of local jobs. The small modular reactor technology promises quicker construction timelines compared to traditional nuclear facilities, offering an efficient solution to energy needs in a time of rising costs. Great British Energy-Nuclear is leading the charge, revitalizing the former Anglesey nuclear plant site into a hub of modern nuclear energy. As the UK aims to reclaim its status in nuclear power, the success of the Wylfa reactor could pave the way for more nuclear developments across the country, underscoring the critical role of nuclear energy in achieving energy sovereignty and abundance.
In the sphere of nuclear energy, the introduction of compact nuclear systems known as small modular reactors (SMRs) is reshaping the landscape of power generation in the UK. These innovative and smaller-scale nuclear facilities are designed for on-site assembly and rapid deployment, making them a potentially faster alternative to traditional large-scale reactors. At Wylfa, the former site of a larger nuclear facility, the UK’s commitment to advance its energy infrastructure is evident with the backing of substantial government funds and the involvement of Great British Energy-Nuclear. This initiative is not only about providing sustainable energy but also revitalizing local economies through job creation and technological investment in Anglesey. The progress at Wylfa signals a broader movement towards enhancing the UK’s nuclear capabilities, helping to meet the nation’s growing energy demands while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Understanding Small Modular Reactors: A New Era in Nuclear Power
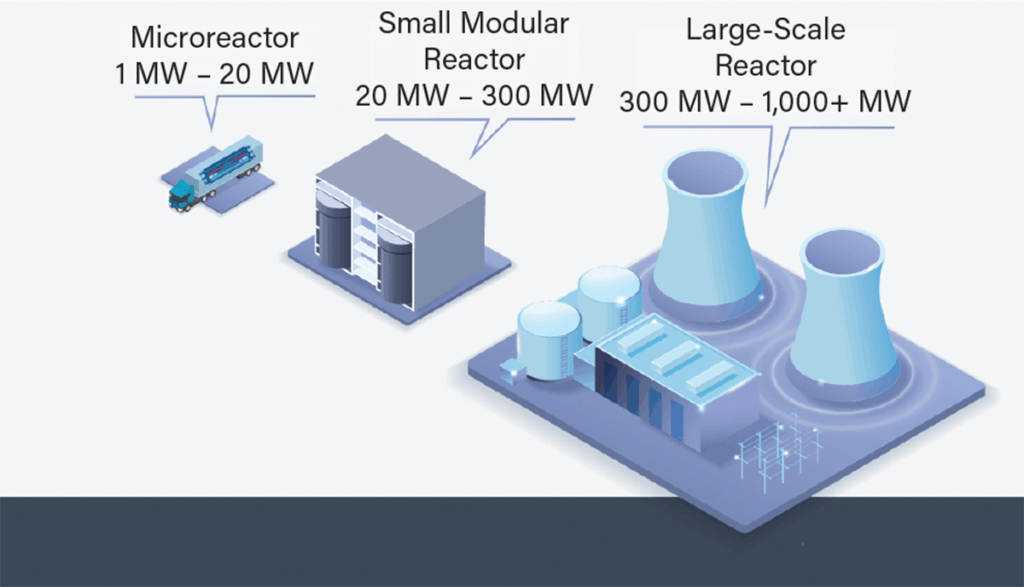
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) represent a groundbreaking approach to nuclear power, emphasizing safety, efficiency, and scalability. Designed with prefabricated components, these compact reactors can be manufactured and assembled on-site, making them quicker to deploy than traditional nuclear facilities like Hinkley Point C. The UK’s first SMR is set to be constructed at the Wylfa site in Anglesey after significant governmental support, demonstrating a commitment to revitalizing the nation’s nuclear capabilities. As the UK continues to navigate energy challenges, the potential for SMRs to supply power to millions of homes while creating jobs in the local economy is paramount.
The revolution in nuclear energy brought about by SMRs can significantly contribute to the UK’s energy strategy. By utilizing advanced designs, including those from reputable firms like Rolls-Royce SMR, these reactors promise to enhance energy sovereignty by diversifying the energy supply mix. The Government’s support highlights its focus on clean energy alternatives, with SMRs expected to generate sufficient electricity to power around three million homes. This aligns with broader initiatives aimed at reducing reliance on fossil fuels, thereby establishing a sustainable energy future for the country.
The Economic Impact of the Wylfa Small Modular Reactor Project
The Wylfa SMR project is set to inject substantial investment and job creation into the local economy of Anglesey. With £2.5 billion in government backing, the initiative aims to create up to 3,000 jobs during peak construction, providing essential economic benefits to a region that has experienced previous setbacks in nuclear development. This investment not only revitalizes the local workforce but also stimulates ancillary industries, driving growth and innovation in and around Anglesey. As such, Wylfa serves as a prime example of how nuclear energy advancements can produce far-reaching benefits beyond just electricity generation.
Moreover, the economic benefits extend beyond immediate job creation, as the introduction of SMRs is projected to lower energy bills in the long run. By focusing on smaller, modular designs, the Government is positioning the UK to harness a more cost-effective route to energy generation. As outlined by Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer, this initiative is part of a broader strategy to reverse decades of decline in the nuclear sector, ensuring that communities like Anglesey receive the attention and resources they deserve to thrive in a competitive energy market.
Government’s Role in Nuclear Energy Development
The UK Government has taken a proactive stance in promoting nuclear energy development, particularly through support for the small modular reactor initiative at Wylfa. By investing significantly in the capabilities of Great British Energy-Nuclear (GBE-N), the Government aims to restore the UK’s leadership in nuclear technology. The push towards SMRs showcases a shift in focus towards innovative solutions that promise quicker deployment and enhanced safety, crucial for meeting the UK’s energy needs amidst rising demand.
In addition to the Wylfa project, the Government has also mandated GBE-N to explore additional nuclear sites across the UK, potentially paving the way for further large-scale installations similar to those at Hinkley Point and Sizewell. This strategic approach underlines the importance of establishing a comprehensive nuclear power framework, not only to secure energy supply but also to position the UK as a sustainable energy leader in the global arena.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding the Wylfa SMR Project
While the introduction of small modular reactors at Wylfa symbolizes hope for a renewed nuclear sector, it has not been without its challenges. Notably, the plans have drawn criticism from international parties, including the US government, which expressed disappointment over the decision to prioritize SMRs over larger reactors. This contention raises questions about the UK’s strategic energy partnerships, particularly with major players in the nuclear industry, and calls into question the potential for earlier and larger scales of power generation.
Furthermore, debates surrounding the viability and efficiency of SMRs compared to traditional nuclear plants have emerged. Critics argue that while SMRs promise safety and quicker build times, they may not necessarily deliver the best economic outcomes or energy efficiency compared to larger reactors. These discussions highlight the importance of balancing innovation in nuclear technology with practical considerations regarding investment, construction timelines, and the overall impact on energy pricing for consumers.
The Future of Nuclear Power in the UK: Looking Beyond Wylfa
The Wylfa project not only marks the introduction of small modular reactors but also represents a pivotal moment in the UK’s nuclear journey. With plans to continue expanding the nuclear landscape across the nation, including potential sites for larger facilities, the Government aims to revitalize its energy independence. This is crucial in addressing concerns surrounding energy security and climate change, as nuclear power is a key player in reducing carbon emissions while providing consistent energy supply.
Looking ahead, the UK must capitalize on the synergies between nuclear and renewable energy sources to create a sustainable, robust energy future. Integrating SMR technology with existing infrastructure offers not only a diversity of energy sources but also positions the UK as a frontrunner in the global transition to clean energy. As highlighted by Energy Secretary Ed Miliband, the pursuit of energy sovereignty through a mix of nuclear and renewables is essential for the well-being of the nation, ensuring that both current and future generations have access to reliable and affordable energy.
Community Involvement in Nuclear Projects: Ensuring Local Buy-in
For the successful implementation of the Wylfa small modular reactor project, community involvement is crucial. The Government and GBE-N have recognized the importance of engaging with local residents to garner support and address potential concerns. Public consultations and transparency in decision-making processes can help mitigate apprehensions regarding safety and environmental impacts. By fostering a collaborative relationship with the Anglesey community, stakeholders can work together towards a common goal of sustainable energy and economic regeneration.
Moreover, cultivating local support for nuclear initiatives like Wylfa can create a sense of ownership among residents, further enhancing the benefits of the project. This includes facilitating discussions about job opportunities, training programs, and overall economic impacts, ensuring that the community reaps the rewards of this significant investment. As plans for additional nuclear sites are considered across the UK, the importance of maintaining community dialogue will be key in securing the long-term success of nuclear energy in the nation.
Advancements in Nuclear Technology and Their Global Implications
The advancements in nuclear technology represented by projects like the Wylfa small modular reactor bring potential not only for the UK but also for the global energy landscape. The development of SMR technology signifies a move towards more adaptable and scalable solutions that can be deployed in a variety of settings worldwide. As nations grapple with the need for clean and sustainable energy sources, the UK’s leadership in SMR technology could set a precedent for future nuclear endeavors globally, reinforcing the role of nuclear power in energy transitions.
Furthermore, the focus on small modular reactors aligns with international efforts to combat climate change by providing lower carbon alternatives to fossil fuel dependency. With the ability to produce significant amounts of energy with reduced environmental impact, organizations around the globe may look to the UK’s initiatives as models for their nuclear strategies. As energy demands continue to rise, exploring innovative nuclear solutions like SMRs could play a vital role in meeting these challenges effectively while ensuring a sustainable and clean energy future.
Nuclear Policy and Its Role in Climate Change Mitigation
The role of nuclear policy in addressing climate change cannot be overstated, especially as the UK advances projects like the Wylfa small modular reactor. By committing to nuclear energy as part of the broader climate change strategy, the UK government sends a strong message about the importance of low-carbon energy solutions in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. With the UK targeting ambitious climate goals, integrating nuclear power into the energy mix is essential for achieving these targets while ensuring energy reliability.
Moreover, as nuclear energy becomes an integral part of national and international climate frameworks, the UK has the opportunity to collaborate with other nations to share knowledge and innovation in nuclear technology. The commitment to small modular reactors signifies a willingness to adapt and lead the conversation on sustainable energy practices. By pursuing rigorous nuclear policies centered on safety, efficiency, and environmental responsibility, the UK can truly position itself as a leader in the global effort to combat climate change.
Comparing Small Modular Reactors to Traditional Nuclear Power Plants
Small modular reactors (SMRs) present several advantages when compared to traditional nuclear power plants, such as those at Hinkley Point and Sizewell. One of the most notable benefits is the reduced physical footprint and enhanced safety features of SMRs, allowing for easier integration into existing energy systems. The modular design enables quicker construction times, which can lead to faster energy generation and contribute to alleviating energy shortages. Additionally, improved safety measures inherent to SMR design can help assuage public concerns related to nuclear disasters, enhancing community trust in nuclear projects.
On the other hand, traditional large-scale nuclear plants have long been the backbone of the UK’s nuclear power generation. With extensive infrastructure and established operational protocols, these facilities deliver large amounts of energy that are critical for meeting national demands. However, the shift towards SMRs demonstrates a recognition of the need for innovation and adaptability in the energy sector, particularly in light of evolving technology and economic factors. The UK’s approach of diversifying its nuclear strategy, incorporating both SMRs and traditional reactors, showcases a comprehensive effort to modernize its energy landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a small modular reactor (SMR) and how does it differ from traditional nuclear power plants?
A small modular reactor (SMR) is a type of nuclear power plant that is smaller in size and designed for on-site installation using prefabricated modules. Unlike traditional large-scale nuclear power stations, like those at Hinkley Point, SMRs are expected to be quicker to build and more cost-effective. The UK’s first SMR will be developed at Wylfa, Anglesey, paving the way for a new era in nuclear energy.
What investment is being made into the Anglesey nuclear plant for the small modular reactor project?
The Anglesey nuclear plant, where the UK’s first small modular reactor will be located, has received a significant £2.5 billion investment from the UK Government. This funding aims to support the development of the SMR technology at the former Wylfa reactor site.
How will the small modular reactors at Wylfa contribute to the energy needs of the UK?
The small modular reactors (SMRs) at Wylfa are expected to generate enough electricity to power approximately three million homes. This development is part of the UK’s strategy to enhance energy sovereignty and reduce energy costs while promoting sustainable energy solutions.
What role does Great British Energy-Nuclear (GBE-N) play in the small modular reactor project in Anglesey?
Great British Energy-Nuclear (GBE-N) is responsible for overseeing the development of the small modular reactor at Anglesey’s Wylfa site. GBE-N has been tasked with managing the construction process, which is anticipated to boost the local economy by creating jobs and supporting a nuclear renaissance in the UK.
When is construction expected to begin on the small modular reactors at Wylfa?
Construction of the small modular reactors at the Wylfa site is set to commence in 2026. The project plans to initially build three reactors, with the potential for the site to accommodate up to eight SMRs, which are expected to start delivering power to the grid by the mid-2030s.
What advantages do small modular reactors offer over traditional nuclear plants like those being constructed at Hinkley Point?
Small modular reactors (SMRs) offer several advantages over traditional nuclear plants, including faster construction times, lower upfront costs, and enhanced safety features. These characteristics make SMRs an attractive choice for regions like Anglesey, where the UK’s first SMR will be situated, as they can be deployed more efficiently to meet growing energy demands.
What has been the response from the US regarding the small modular reactor plans at Wylfa?
The response from the US has been critical, with the US ambassador expressing disappointment over the UK’s decision to pursue small modular reactors instead of larger plants. The ambassador emphasized that larger reactors could provide cheaper and faster solutions to energy needs, highlighting a preference for alternative plans proposed by US firms.
How many jobs is the small modular reactor project at Wylfa expected to create?
The construction of the small modular reactors at Wylfa is projected to create up to 3,000 jobs in the local economy at the peak of construction. This initiative aims to stimulate economic growth in Anglesey while advancing the UK’s nuclear energy capabilities.
What is the timeline for the small modular reactors to start supplying power from Wylfa?
The small modular reactors (SMRs) at Wylfa are anticipated to begin supplying power to the grid by the mid-2030s. This timeline aligns with the UK’s ambitious plans to enhance its clean energy resources through innovative nuclear technology.
What is the significance of the site selection for the small modular reactor at Wylfa on Anglesey?
The selection of Wylfa on Anglesey for the UK’s first small modular reactor is significant as it represents a new chapter in the UK’s nuclear energy landscape. This site, previously home to a traditional reactor, is being revitalized to become a leading center for SMR technology, reflecting the government’s commitment to nuclear power and sustainable energy solutions.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Anglesey, North Wales – First small modular reactor site in the UK. |
| Investment | £2.5 billion government funding supporting the project. |
| Project Developer | Great British Energy-Nuclear, a publicly owned entity. |
| Employment Impact | Expected to create up to 3,000 jobs at peak construction. |
| Technology | Small modular reactors (SMRs) designed for quicker, onsite prefabricated installation. |
| Production Capacity | Projected to generate enough electricity to power three million homes. |
| Political Response | UK Government support met with criticism from the US regarding alternative large reactor proposals. |
| Future Plans | Initial three reactors planned, with potential for eight at the site. |
| Timeline | Construction commencement in 2026, power expected to start by mid-2030s. |
Summary
The UK is set to lead the world in nuclear energy with the development of its first small modular reactor. This innovative project at Wylfa in Anglesey, supported by significant government investment, aims not only to resurrect the local economy but also to spearhead a new era of clean energy production. As small modular reactors promise to be quicker and easier to build than traditional large plants, this initiative could pave the way for a more sustainable and energy-abundant future.