Listen to this article
The term “shadow fleet” is becoming increasingly relevant in discussions of international maritime law, particularly concerning the recent seizure of the Grinch, a suspected Russian shadow fleet tanker, near Marseille. This oil tanker was intercepted by the French navy, demonstrating efforts to enforce sanctions against Russia amidst its ongoing conflict in Ukraine. As maritime authorities tighten their grip on sanctions evasion, the implications of such actions are critical for global shipping, especially concerning oil tanker sanctions. The Grinch’s journey from the Russian Arctic highlights the lengths to which nations like Russia will go to finance their operations, further challenging international norms. With one in five oil tankers being linked to these clandestine activities, understanding the dynamics of the shadow fleet is more important than ever.
In the realm of international shipping, clandestine vessels often dubbed ‘ghost fleets’ or ‘stealth fleets’ emerge as crucial players in evading regulations. These vessels, including the notorious Russian shadow fleet, represent a significant challenge to global maritime compliance, especially as nations like Russia, Venezuela, and Iran exploit them to circumvent oil embargoes. The recent Marseille tanker seizure underlines the importance of adhering to maritime laws aimed at preventing sanctions evasion. As international enforcement efforts intensify, the implications for global oil trade and security become increasingly complex. Understanding these shadowy operations is vital for nations striving to uphold their sanctions policies.
Understanding the Shadow Fleet Phenomenon
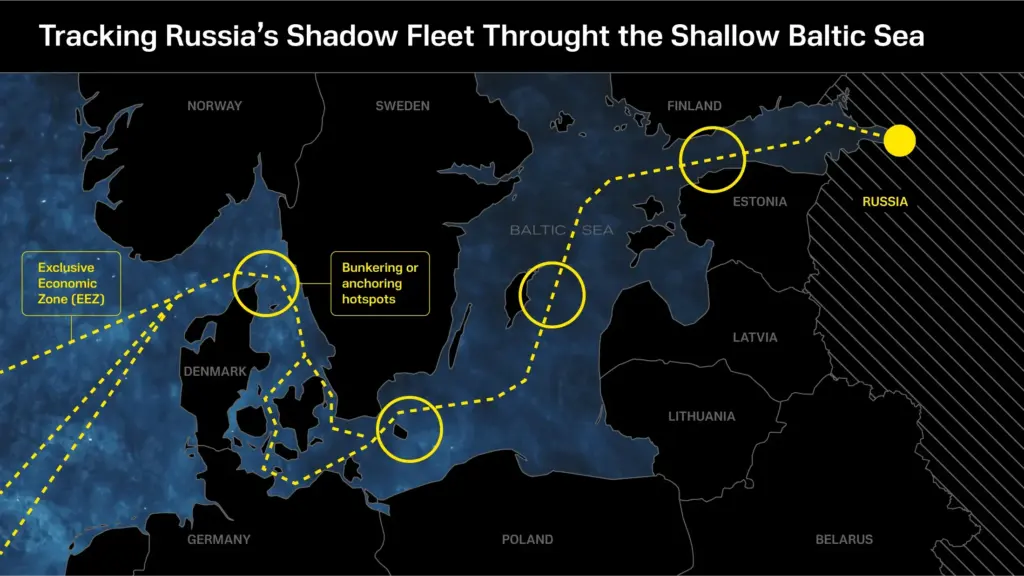
The concept of a shadow fleet has gained considerable attention in recent years, especially as countries have imposed sanctions on nations like Russia, Iran, and Venezuela. Shadow fleets refer to ships that operate clandestinely to transport oil or goods while circumventing international sanctions. These vessels often sail under false flags or less scrutinized registries to hide their true origins. The recent seizure of the Grinch near Marseille illustrates how these clandestine operations operate beneath the radar of international maritime law, complicating enforcement efforts against sanctioned states.
The rise of shadow fleets can be attributed to increased vigilance from Western nations against energy exports from sanctioned countries. As traditional routes become riskier, those who smuggle oil and goods must adapt. Increased demand and high oil prices further incentivize the use of shadow fleets, making it a lucrative endeavor despite the risks involved. This phenomenon highlights the intricate dance of international maritime law where enforcing sanctions requires cooperation across borders and jurisdictions, and it poses significant challenges for law enforcement agencies.
Marseille Tanker Seizure and its Implications
The seizure of the oil tanker Grinch by French authorities serves as a critical moment in the ongoing efforts to enforce sanctions against Russia. By intercepting a ship suspected of being part of a Russian shadow fleet, French officials have acted decisively to uphold international laws that aim to limit Russian oil exports in response to its aggressive actions in Ukraine. The involvement of the French navy and the subsequent investigation into the tanker’s validity and operational license are indicative of a broader strategy to thwart sanctions evasion across the maritime industry.
This event also raises broader questions about global energy security and the compliance of other nations with international trade laws following sanctions. The fact that such a vessel was able to operate under a false flag for a time without detection underscores the increasing challenges in monitoring maritime activities. It emphasizes the need for enhanced cooperation among maritime nations to share intelligence and address the complexities presented by shadow fleets, which could undermine global economic sanctions intended to influence political behavior.
International Maritime Law and Sanction Evasion
International maritime law serves as a framework for regulating shipping activities and enforcing sanctions. The recent encounter involving the Grinch highlights the complexities that arise when vessels purportedly violate these laws. Maritime security experts emphasize that while laws exist to prevent such activities, the enforcement relies heavily on proactive intelligence-gathering and international cooperation. The challenges in identifying and apprehending shadow fleets often lead to situations where violators can escape accountability due to lapses in compliance by flagged countries.
Furthermore, as maritime domains become increasingly looked upon for potential smuggling activities, nations are compelled to keep a vigilant eye on vessel operations, especially those from sanctioned regions. The implications of not enforcing laws adequately can have far-reaching consequences, not only for the offending nations but also for countries that adhere to international regulations. Thus, the pursuit of enforcing sanctions against states like Russia necessitates a robust framework of international maritime collaboration coupled with effective responses to evasion tactics employed by shadow fleets.
The Role of Financial Intelligence in Monitoring Sanctions
The role of financial intelligence is crucial in monitoring and enforcing sanctions against countries that employ shadow fleets for oil trading. Firms like S&P Global provide sharp insights into the movements of tanker fleets, uncovering illicit activities that often go unnoticed. Their analytical frameworks assist governments in identifying patterns and tracking the flow of resources from sanctioned nations like Russia, who use deceptive practices to circumvent established trade restrictions. By utilizing sophisticated data and technology, financial intelligence not only informs maritime operations but also enhances law enforcement strategies.
As financial transactions related to the oil trade become increasingly scrutinized, the need for collaboration between maritime authorities and financial intelligence units becomes paramount. Investigations similar to that of the Grinch will benefit immensely from the data-related insights that financial firms can provide. Such a synergy will aid in exposing concealed ownership structures and funding mechanisms that facilitate sanctions evasion, thereby contributing significantly to global enforcement efforts against shadow fleets.
Venezuela’s Connection to the Shadow Fleet
Venezuela, alongside Russia and Iran, is often linked to shadow fleet operations as part of their efforts to circumvent international oil sanctions. The strategic positioning of these countries, combined with their reliance on oil exports for revenue, pressures them to seek alternative routes for their oil. Activities involving clandestine shipments illustrate how nations can sustain energy production and revenue despite being under severe economic sanctions. The use of shadow fleets allows them to continue operating in the global market, evade restrictions, and finance their domestic and foreign activities.
The complexity of the Venezuela-shadow fleet relationship highlights a significant issue for international maritime law enforcement. For governments seeking to uphold sanctions, the challenge lies in dismantling the networks that enable such operations to flourish. Recent incidents showing the extent of this collaboration have led to a greater urgency in maritime security and heightened vigilance in monitoring tanker routes. As enforcement agencies adapt their strategies, they must consider the geopolitical motivations that drive these nations to engage in illicit operations.
The Global Impact of Oil Tanker Sanctions
The imposition of sanctions on oil tankers, particularly those linked to Russia, has far-reaching global implications. These sanctions not only impact the targeted nations but also affect global oil supply chains, ultimately influencing prices and availability for consumers worldwide. The ripple effects extend to allied countries who are trying to navigate the delicate balance between energy demands and compliance with international sanctions. The tangible pressure on Russia’s economy underscores a larger fight that involves redefining energy dependence and supply routes.
In the wake of sanctions, alternative energy sources and routes are gaining traction as countries seek to reduce reliance on sanctioned oil. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine and Western nations’ response has changed the landscape of energy production and consumption. Consequently, these sanctions are reshaping the oil market, testing long-standing alliances, and giving rise to new energy partnerships. The global community must grapple with the consequences of these shifts while aiming for a more unified stance against unlawful maritime activities involving shadow fleets.
International Cooperation to Combat Smuggling
International cooperation is increasingly essential in combating the growing phenomenon of smuggling through shadow fleets. As vessels like the Grinch exploit gaps in maritime law to evade scrutiny, nations must come together to enhance surveillance, information sharing, and coordinated enforcement actions. Collaborative efforts can lead to more comprehensive responses to sanctions evasion, enabling countries to address these issues more effectively. Initiatives among maritime nations to develop intelligence-sharing networks are now more crucial than ever.
This cooperative spirit is further reflected in joint exercises conducted by naval forces across nations aimed at improving maritime security against illicit activities. By establishing robust frameworks for collaboration, nations can collectively address the challenges posed by shadow fleets. Improved coordination not only leads to a better-prepared enforcement strategy but also fosters accountability within the maritime industry, thus restoring trust in global shipping practices.
Consequences of Non-compliance with International Laws
The consequences of non-compliance with international maritime laws have significant ramifications for countries engaging with shadow fleets. Failure to adhere to sanctions may lead to diplomatic tensions and economic repercussions for nations found to be assisting in sanctions evasion. The recent capture of the Grinch and its crew exemplifies how international law is persistently challenged. Nations must recognize that overlooking non-compliance can undermine their credibility on the global stage.
Moreover, the legal frameworks surrounding these issues highlight the need for continual updates and reforms to adapt to modern challenges. Countries that flout these laws invite scrutiny and may face collective actions from the international community. To safeguard their interests while maintaining a commitment to upholding international maritime law, nations must ensure rigorous enforcement of compliance among their flagged vessels, particularly those suspected of engaging in unauthorized activities in high-risk regions.
Maritime Security Challenges in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea poses unique maritime security challenges, particularly with the rise of shadow fleets involved in illicit oil trading. The region is a strategic intersection for international shipping routes, making it an attractive target for vessels attempting to evade sanctions. Increased activity in these waters calls for enhanced licensing and monitoring protocols to ensure that all operations within the Mediterranean adhere to international laws. The challenges are compounded by the sheer number of vessels that navigate these waters, necessitating focused enforcement efforts.
As highlighted by the recent seizure of the Grinch, maritime security efforts must evolve to meet emerging threats. French authorities’ establishment of exclusion zones demonstrates a proactive approach to securing maritime routes. Meanwhile, collaboration with international maritime organizations and relevant nations can foster a unified response to address these dangers effectively. The Mediterranean remains a critical theater for national security interests, and ongoing efforts to fortify law enforcement and monitoring capabilities will play a crucial role in deterring shadow fleet operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Russian shadow fleet in global oil sanctions?
The Russian shadow fleet plays a crucial role in circumventing international oil sanctions imposed by Western nations. By using tactics like disguising a ship’s true ownership or flying false flags, these tankers evade detection and continue to transport oil, thus financing Russia’s ongoing war efforts.
How does the seizure of the Grinch tanker relate to shadow fleet operations?
The seizure of the Grinch, a suspected shadow fleet tanker, underscores the challenges in enforcing sanctions against Russian oil shipments. Intercepted by the French navy, this incident illustrates the ongoing efforts to tackle ships that violate international maritime law through sanctions evasion.
What actions have been taken against oil tanker sanctions and shadow fleets?
In response to violations, international authorities, including France and the U.S., have intensified maritime enforcement operations against suspected shadow fleet tankers. These include vessel seizures and legal action against crew members to maintain compliance with sanctions on Russian oil.
What is the Marseille tanker seizure and its implications for the shadow fleet?
The Marseille tanker seizure specifically targets vessels like the Grinch that are associated with the Russian shadow fleet. This event highlights the increasing international scrutiny of maritime operations that attempt to bypass sanctions, reinforcing the legal and logistical challenges faced by the shadow fleet.
What are the potential consequences for ships associated with the Russian shadow fleet?
Ships linked to the Russian shadow fleet risk seizure, legal action, and crew detentions under international maritime law. The Grinch incident demonstrates the proactive measures taken by countries to uphold sanctions and prevent vessels from facilitating the Russian oil trade.
How do sanctioned countries like Russia utilize shadow fleets for oil transportation?
Sanctioned nations like Russia employ shadow fleets to covertly transport oil by altering ship registrations and using deceptive practices. This allows them to continue exporting oil despite sanctions aimed at crippling their economy and funding military operations.
Why are shadow fleets a growing concern for international maritime law?
Shadow fleets pose a significant concern because they undermine international maritime law by enabling illegal oil trade and sanctions evasion. The frequent use of such fleets complicates enforcement efforts and hinders the effectiveness of sanctions designed to deter aggression from these nations.
What role do financial intelligence firms play in identifying shadow fleet activities?
Financial intelligence firms like S&P Global monitor and analyze maritime traffic to identify patterns indicative of shadow fleet activities. Their reports, suggesting that one in five oil tankers may be involved in smuggling oil from sanctioned countries, provide critical insights for governments and enforcement agencies.
| Key Points |
|---|
| French authorities have detained an Indian captain of a suspected Russian shadow fleet tanker named ‘Grinch.’ |
| The Grinch was intercepted by the French navy while traveling from Murmansk through the Mediterranean Sea. |
| The tanker is now moored under guard at a southern French port near Marseille. |
| Only the captain, a 58-year-old Indian, was taken into custody while the crew remains on board. |
| The investigation focuses on verifying the legitimacy of the flag under which the tanker was operating. |
| French authorities have established exclusion zones around the anchorage site for security reasons. |
| Shadow fleets help finance Russia’s aggression against Ukraine and are used by countries like Venezuela and Iran to evade sanctions. |
| An estimated one in five oil tankers globally are involved in smuggling oil from sanctioned nations, per S&P Global. |
Summary
The concept of a shadow fleet emerges as a significant issue given the recent seizure of the oil tanker Grinch. Shadow fleets, which include vessels that operate under false flags to evade international sanctions, play a crucial role in financing unjust warfare, such as Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. It’s imperative for international authorities to maintain vigilance against these operations to curb illicit oil trafficking and uphold sanctions. The ongoing investigation into the Grinch and similar vessels emphasizes the importance of monitoring maritime activities tied to sanctioned nations.