Listen to this article
Seagrass restoration is gaining momentum as a vital strategy in the fight against climate change, particularly within the Humber Estuary. This innovative project aims to revive extensive saltwater plant meadows that are crucial for maintaining marine habitats. Experts recognize that these underwater meadows can help combat climate change while providing significant benefits such as carbon sequestration and protecting coastlines from erosion. With trial plantings yielding promising results, the restoration efforts are set to enhance the ecological balance of the area. By adopting effective seagrass planting methods, the Humber Estuary’s restoration initiatives are proving to be a beacon of hope for both local wildlife and coastal communities seeking climate change solutions.
The rehabilitation of aquatic grasslands, commonly referred to as seagrass meadows, is emerging as an essential component of environmental restoration efforts. Within the Humber Estuary, schemes focused on reviving these marine ecosystems are not only addressing ecological degradation but also contributing to sustainable coastal management. These grassy habitats enhance biodiversity, empower local fisheries, and play a crucial role in carbon capture, all while improving water quality. Employing varied seagrass planting techniques has shown promise, demonstrating that large-scale recovery of these ecosystems is possible even in challenging environments. Overall, the work being done reflects a commitment to harnessing nature’s potential for climate action and creating healthier marine landscapes.
Understanding the Importance of Seagrass Restoration
Seagrass restoration has emerged as a vital strategy for addressing the pressing challenges of climate change and its impact on marine ecosystems. These underwater plant meadows play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, a process that helps mitigate the effects of global warming. By restoring seagrass in areas like the Humber Estuary, we not only combat climate change but also provide essential habitat for various marine species, enhancing biodiversity within these crucial ecosystems.
In the Humber Estuary, the historical significance of seagrass is notable, as these meadows once flourished over 1,100 acres. Unfortunately, due to anthropogenic activities such as pollution and coastal development, there has been a dramatic decline in seagrass coverage. By focusing on seagrass restoration, we are not only reviving these vital marine habitats but also contributing to more resilient coastal communities. Initiatives like Wilder Humber demonstrate that sustainable practices can successfully restore these ecosystems and promote environmental health.
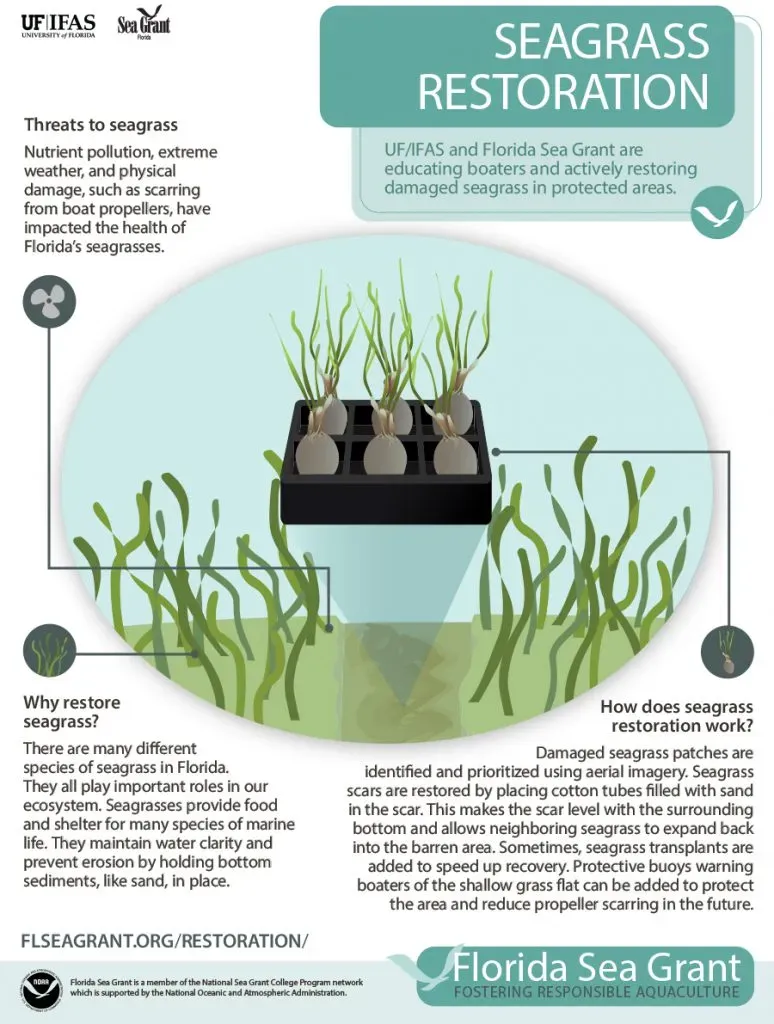
Innovative Seagrass Planting Methods
Research conducted on different seagrass planting methods has revealed promising results that could revolutionize restoration efforts. Recent trials in the Humber Estuary explored three distinct techniques, including direct seed injection and the transplantation of intact patches. These innovative approaches aimed to assess their effectiveness in ensuring the survival and growth of seagrass populations in dynamic estuarine environments, which often face challenges due to shifting currents and changing water quality.
The findings indicate that the method of directly injecting seeds into the seabed, coupled with the transplantation of small patches, significantly enhances the chances of successful seagrass restoration. This is particularly important for regions like the Humber Estuary, where historical degradation has led to stark reductions in seagrass coverage. By utilizing these scientific advancements, conservationists can create more effective strategies for rejuvenating marine habitats and, in doing so, bolster the environmental resilience of coastlines experiencing climate change.
Seagrass and Its Role in Carbon Sequestration
Seagrass meadows are vital ecological assets in the fight against climate change due to their remarkable ability to sequester carbon at rates substantially higher than tropical rainforests. In fact, studies show that seagrass can sequester carbon up to 35 times faster, making its restoration crucial for carbon management strategies. The ability of seagrass to capture and store carbon dioxide illustrates its essential role in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing the overall health of marine ecosystems.
As we witness the growing impact of climate change, initiatives focused on seagrass restoration, particularly in coastal areas like the Humber Estuary, are becoming increasingly imperative. Not only does seagrass contribute to carbon sequestration, but it also improves water quality by filtering pollutants, providing a range of ecosystem services that benefit both marine life and coastal communities. By fostering the recovery of seagrass, we are taking significant steps toward addressing climate change solutions and preserving the integrity of marine habitats.
Biodiversity and Marine Habitats Enriched by Seagrass
Seagrass meadows provide critical habitats for numerous marine species, including fish, eels, and birds, making them indispensable for maintaining oceanic biodiversity. The complex root systems and dense foliage of seagrass create shelter and breeding grounds for juvenile fish, while also serving as a foraging area for various aquatic organisms. This biodiverse environment is essential for sustaining fish populations, which, in turn, supports local fisheries and economies.
The restoration of seagrass habitats in areas like the Humber Estuary is vital for fostering a balance between marine ecosystems and protecting coastal biodiversity. Effective seagrass planting initiatives increase the abundance of these vital habitats, offering refuge to countless marine species and contributing to the overall productivity of the marine environment. As we enhance these meadows, we support not only wildlife but also the livelihoods dependent on healthy marine ecosystems.
Collaborative Efforts in Seagrass Restoration
Restoring seagrass meadows requires a collaborative approach that brings together various stakeholders, including environmental organizations, local authorities, and renewable energy companies. In the Humber Estuary, collaborative initiatives like Wilder Humber exemplify how different entities can unite to achieve common ecological goals. By sharing expert knowledge and resources, these groups work towards developing effective restoration techniques and raising awareness about the importance of seagrass meadows.
Partnerships are crucial for driving successful seagrass restoration projects. Support from companies like Orsted not only provides necessary funding but also highlights the role of green technology in fostering environmental resilience. By leveraging collective expertise and community engagement, these collaborative efforts can effectively restore seagrass habitats, ensuring our coastlines are better equipped to handle the challenges brought by climate change.
Impact of Pollutants on Seagrass Meadows
Pollution poses a significant threat to seagrass meadows, impacting their health and ability to thrive. Nutrient runoff, chemicals, and plastic debris can degrade water quality, leading to negative effects on the growth and survival of seagrass. As highlighted in the decline of seagrass coverage in the Humber Estuary, addressing pollution sources is essential for meaningful restoration efforts.
Efforts to mitigate pollutants can enhance the effectiveness of seagrass restoration initiatives. By advocating for stricter regulations on agricultural runoff and promoting community awareness about reducing waste, we can contribute significantly to the health of these important marine habitats. Restoration projects not only focus on planting but also encompass broader environmental stewardship aimed at safeguarding seagrass meadows from ongoing pollution.
Long-Term Benefits of Seagrass Restoration
The long-term benefits of seagrass restoration extend beyond immediate ecological impacts, influencing climate change mitigation, coastal protection, and community resilience. These meadows act as natural buffers against storm surges and erosion, safeguarding coastal areas from the adverse effects of climate change. By re-establishing seagrass populations, we invest in the physical protection of coastlines, enhancing the safety and sustainability of local communities.
Additionally, restored seagrass meadows contribute to improved water quality, which aids in the recovery of marine ecosystems. Cleaner water not only benefits marine life but also enhances recreational opportunities and supports local economies dependent on fishing and tourism. By recognizing and harnessing the long-term benefits of seagrass restoration, we can foster healthier coastal environments that support both nature and human well-being.
Seagrass Restoration as a Climate Change Solution
Amidst the growing challenge of climate change, seagrass restoration has positioned itself as a viable and effective solution. By sequestering significant amounts of carbon and enhancing coastal resilience, seagrass meadows represent a natural approach to mitigating climate impacts. Projects aimed at revitalizing these habitats provide a dual benefit—combating climate change while restoring critical marine ecosystems.
The successes seen in recent trials in the Humber Estuary serve as a testament to the promise of seagrass restoration. Enhanced planting techniques and community engagement in restoration efforts can collectively work towards mitigating climate change effects. By prioritizing seagrass restoration, we can not only improve coastal health but also adopt proactive climate change solutions that foster long-term environmental sustainability.
Community Involvement in Seagrass Restoration Projects
Community involvement plays a pivotal role in the success and sustainability of seagrass restoration initiatives. Engaging local populations fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards marine habitats, motivating individuals to participate in restoration efforts. Educational programs and stewardship activities can inspire community members to become advocates for seagrass protection and contribute to ongoing conservation efforts.
Moreover, public participation enhances knowledge dissemination regarding the importance of seagrass in combating climate change and improving coastal resilience. By mobilizing community support and collaboration with local organizations, seagrass restoration projects can leverage grassroots advocacy to bring attention to the critical state of marine habitats. This collective action not only amplifies restoration efforts but also cultivates a culture of environmental stewardship.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is seagrass restoration and why is it important for marine habitats in the Humber Estuary?
Seagrass restoration refers to the process of reviving and expanding seagrass meadows, which are crucial marine habitats in the Humber Estuary. These meadows provide habitat for a wide range of marine life, sequester carbon at impressive rates, and help protect coastlines from erosion and storm damage. Restoring seagrass is vital to combat climate change and enhance biodiversity.
How does seagrass restoration contribute to climate change solutions in the Humber Estuary?
Seagrass restoration acts as a powerful climate change solution by sequestering carbon at rates up to 35 times faster than tropical rainforests. This function helps mitigate climate change impacts while improving water quality. The restoration of seagrass meadows in the Humber Estuary is a strategic effort to enhance carbon sequestration and create healthier ecosystems.
What methods are used for seagrass planting in restoration projects?
Seagrass planting methods used in restoration projects, especially in the Humber Estuary, include directly injecting seeds into the seabed and transplanting small intact patches of existing seagrass. Recent trials have shown that these methods yield the best outcomes for restoring seagrass habitats effectively.
What challenges have hindered seagrass restoration efforts in the Humber Estuary?
Seagrass restoration efforts in the Humber Estuary have faced challenges due to pollution, disease, and the loss of natural coastal habitats, particularly during the 20th century. These factors led to the dramatic decline of seagrass coverage, necessitating extensive restoration measures to revive these essential marine habitats.
What ecological benefits do restored seagrass meadows provide to coastal communities?
Restored seagrass meadows in the Humber Estuary provide significant ecological benefits for coastal communities, including enhanced biodiversity, improved water quality through pollutant absorption, and protection against coastal erosion and storm surges. They also serve as essential habitats for fish, eels, and birds, supporting local fisheries and wildlife.
Why is the Humber Estuary a focus area for seagrass restoration projects?
The Humber Estuary is a focus area for seagrass restoration projects due to its historical significance as a rich marine habitat, which has suffered severe decline. Current restoration efforts aim to revitalize this important ecosystem, promote climate change solutions, and enhance biodiversity, making it a critical site for seagrass planting initiatives.
What role does carbon sequestration play in seagrass restoration efforts?
Carbon sequestration plays a crucial role in seagrass restoration efforts, as seagrass meadows absorb and store carbon dioxide at rates much higher than other ecosystems. By enhancing carbon capture, restored seagrass habitats in the Humber Estuary contribute to climate change mitigation while maintaining healthier marine environments.
How successful have recent trials been in restoring seagrass in the Humber Estuary?
Recent trials in the Humber Estuary have been notably successful, with experts reporting encouraging outcomes from various seagrass planting methods. The best results came from directly injecting seeds and transplanting small patches, demonstrating the potential for large-scale seagrass restoration when the right techniques are employed.
What partnerships support seagrass restoration initiatives in the Humber Estuary?
Seagrass restoration initiatives in the Humber Estuary are supported by various partnerships, including Wilder Humber, a collaboration between wildlife trusts, and renewable energy company Orsted. These partnerships leverage expertise and resources to effectively restore marine habitats and combat climate change.
| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| Seagrass Restoration Project | Restoring saltwater plant meadows in the Humber Estuary. |
| Importance of Seagrass | Effective in combating climate change, protects coastlines. |
| Historical Coverage | Covered 1,100 acres (445 hectares) but declined in the 20th century. |
| Recent Successes | Trial plantings have shown encouraging results for restoration. |
| Restoration Techniques | Direct injection of seeds and transplanting small patches have proven effective. |
| Environmental Significance | Seagrass sequesters carbon 35 times faster than tropical rainforests and improves water quality. |
| Support and Funding | The project is supported by Wilder Humber and renewable energy company Orsted. |
Summary
Seagrass restoration is crucial for combating climate change and enhancing coastal resilience. The recent project in the Humber Estuary highlights the effectiveness of seagrass in providing natural solutions to environmental challenges. Through innovative planting techniques, the restoration efforts aim to recover and expand seagrass meadows, which play a vital role in carbon sequestration and habitat provision for numerous marine species. Continued support and research are needed to ensure the success and sustainability of these invaluable ecosystems.