Listen to this article
Nuclear power plants UK are at the forefront of a critical evolution in the nation’s energy landscape, particularly as the country grapples with complex regulations and escalating construction costs. Recent reports indicate that the UK has become the “most expensive place in the world” to build these facilities, largely due to an overly convoluted bureaucratic framework. In response to this challenge, the Prime Minister has initiated a call for a radical overhaul of nuclear energy regulation, which could pave the way for substantial nuclear capacity expansion while reaffirming the country’s commitment to stringent nuclear safety standards. As the government aims to bolster its energy policy to meet net-zero targets, the cost of nuclear power remains a contentious issue, necessitating a careful balance between affordability, safety, and the environment. The impending changes could not only enhance efficiency in nuclear development but also align with a global trend towards a nuclear renaissance, positioning the UK to play a pivotal role in the future of clean energy generation.
As the discourse surrounding atomic energy intensifies, the strategic role of nuclear facilities in the UK’s energy matrix is becoming increasingly pivotal. These power-generating installations, which harness heat from atomic fission, are seen as essential components in combating climate change and ensuring energy security. With new directives on energy management and public sentiment shifting towards accepting advanced nuclear technology, the challenge remains to navigate the regulatory complexities. Meanwhile, innovative safety protocols and a focused energy strategy may offer viable paths forward for expanding the nation’s existing energy infrastructure. The implications for future energy production, economic investment, and environmental impact are substantial, positioning nuclear technology as a cornerstone of the UK’s sustainable energy transition.
Challenges Facing Nuclear Power Plants in the UK
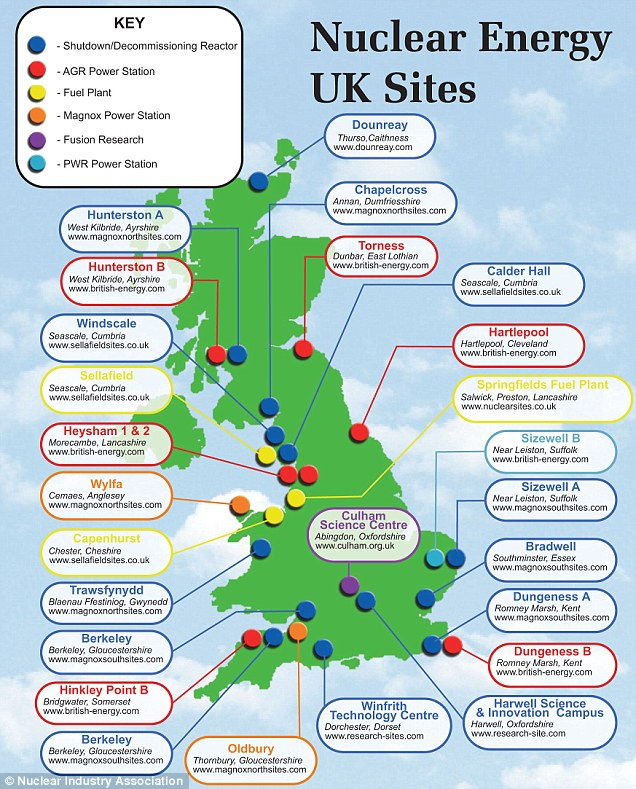
The challenges surrounding the construction of nuclear power plants in the UK have become increasingly evident, with the country now identified as the “most expensive place in the world” for such developments. A recent government review pointed out the overly complex regulatory framework that governs the nuclear energy sector. This bureaucracy not only inflates costs but also slows down project timelines, making it difficult for new nuclear plants to be built efficiently. Furthermore, the lack of cohesion in regulatory oversight has led to a system that is viewed as fragmented, perpetuating inefficiencies that could otherwise be avoided. Such complexities are detrimental to the UK’s ambitions to expand its nuclear capacity and ensure a sustainable energy future.
In the face of these hurdles, many experts are calling for a comprehensive reevaluation of the UK’s nuclear energy regulation. Kicking off a ‘radical reset’ of the nuclear strategy, recommendations from the Nuclear Regulatory Taskforce suggest simplifying regulations while upholding nuclear safety standards. By addressing these challenges head-on, the UK can not only reduce costs and delays but also re-establish itself as a leader in nuclear energy, aligning with broader UK energy policy goals. Such a shift is crucial as the country strives to meet its net-zero targets while accommodating growing energy demands.
The Future of Nuclear Energy and Capacity Expansion
As the UK aims to bolster its energy infrastructure, the future of nuclear power is increasingly seen as pivotal to achieving sustainability and carbon reduction goals. The government is actively working to expand nuclear capacity, with initiatives like the development of Hinkley Point C and Sizewell C set to commence operations in the early 2030s. These plants are expected to provide significant energy contributions—enough to power millions of homes—thereby playing a vital role in the UK’s commitment to tripling nuclear capacity by 2050. This ambitious expansion aligns with the global nuclear renaissance, as numerous countries reassess their energy strategies to incorporate more nuclear solutions.
However, the growth trajectory of nuclear power in the UK also brings forth concerns regarding safety and public perception. The Nuclear Regulatory Taskforce highlights a need for a cohesive approach to ensure that any expansion respects stringent nuclear safety standards while addressing public apprehensions about past incidents like Fukushima and Chernobyl. Moving forward, success will hinge on balancing the drive for energy capacity expansion with the need for transparency and safety in operations. Only then can the UK take full advantage of the benefits offered by nuclear energy, particularly in light of shifting dynamics in global power generation.
Cost Implications of Nuclear Power Generation
The financial implications of nuclear power generation in the UK have drawn scrutiny, especially given recent evaluations that label the country as the most expensive location for building nuclear power plants. Cost overruns and delays associated with existing projects underscore the challenges in managing nuclear construction expenses. According to reports, streamlining regulation could yield significant savings—potentially “tens of billions”—thus making nuclear projects more financially viable. It’s essential for future nuclear endeavors to incorporate cost-effective measures within the established framework while also adhering to rigorous safety standards.
Moreover, evaluating the cost of nuclear power must also consider the long-term benefits associated with clean energy production. Despite high initial investment requirements, nuclear plants offer a low-carbon energy source that can contribute significantly to the UK’s energy mix as fossil fuel alternatives become less viable. The pressing need for a transition to green energy sources aligns with nuclear power’s potential to mitigate climate change impacts, thereby justifying its costs in a broader context of energy sustainability and economic stability. By addressing both short-term expenditures and long-term ecological goals, the UK can reshape its energy landscape effectively.
Strengthening Nuclear Safety Standards
Safety standards in the nuclear industry are more crucial now than ever, particularly as the UK prepares for a new wave of nuclear capacity expansion. The Nuclear Regulatory Taskforce’s findings indicate a need for enhanced safety oversight amidst concerns of a fragmented regulatory system. Striking a balance between maintaining rigorous nuclear safety standards while promoting the rapid construction of new facilities is critical to overcoming public trepidation and building trust in nuclear energy. Establishing a ‘one-stop’ commission with unified decision-making capabilities may streamline oversight processes while ensuring that safety remains paramount.
Additionally, the UK must confront its ‘risk-averse’ policies regarding radiation exposure levels for workers. While it is essential to keep workers safe, overly conservative regulations could hinder the pace of necessary advancements in nuclear technology and infrastructure. A re-evaluation of existing safety parameters in light of contemporary understanding can help the UK align its nuclear safety standards with best practices observed internationally. Through this dual approach—streamlining bureaucracy and reinforcing safety—the UK can foster a revitalized nuclear sector that meets both regulatory demands and public expectations.
Public Perception and Nuclear Energy in the UK
Public perception plays a significant role in the future of nuclear energy in the UK, especially in light of historical incidents like the Fukushima disaster. While nuclear power offers a low-carbon alternative to conventional fossil fuels, its acceptance is often undermined by a lingering fear of catastrophic accidents and radioactive waste management. Surveys show that effective communication about the safety measures and advancements in nuclear technology is essential to change negative public sentiment. By fostering transparency and engaging communities, the government can help build a supportive environment for future nuclear projects.
Moreover, education about the advancements in nuclear technology and its role in addressing climate change is critical for reshaping public opinion. As the UK government reiterates its commitment to meeting net-zero targets, it is imperative to highlight how nuclear energy can be a cornerstone in achieving these objectives. Initiatives aimed at educating the public about the benefits of incorporating nuclear power into a diversified energy portfolio can foster more trust in the sector and help guide the narrative towards a more favorable outlook on nuclear energy.
International Nuclear Strategies and Their Impact
The landscape of nuclear energy is rapidly evolving, with several nations reevaluating their strategies to increase nuclear capacity in response to climate change goals. Countries like France and China are leading the charge, proposing a significant number of new reactors to meet their energy demands sustainably. The UK must consider these international developments as it formulates its own nuclear energy roadmap. Engaging with global best practices could improve safety standards and efficiency in project delivery, ultimately enhancing the UK’s competitiveness in the nuclear sphere.
Additionally, learning from the successes and challenges faced by other countries in their nuclear endeavors can provide valuable insights. For instance, Japan’s recent pivot back to nuclear power after a hiatus demonstrates a shift in energy strategy that prioritizes sustainability. As global energy dependencies evolve, the UK has the opportunity to leverage international partnerships and technologies, thus positioning itself favorably in the race for nuclear energy enhancement. By adapting to these global influences, the UK can ensure its nuclear sector thrives on a foundation of resilience and innovation.
The Role of Small Nuclear Reactors in the UK
The emergence of small nuclear reactors presents a promising opportunity for the UK to expedite its nuclear capacity expansion. These modular facilities can be constructed more rapidly than traditional large-scale reactors, making them a viable solution for meeting growing energy demands in the near term. The UK government is exploring the feasibility and applicability of small modular reactors (SMRs) as part of its broader nuclear strategy, which could revolutionize how energy is produced and consumed across the nation. Ultimately, the incorporation of SMRs could play a pivotal role in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and fulfilling its net-zero commitments.
In addition to speed and efficiency, small nuclear reactors also provide an avenue for enhancing safety. With lower output and a simplified design, SMRs are inherently designed to be safer, offering built-in safety features that can mitigate risks associated with nuclear energy production. As the UK continues to develop its energy policy framework, focusing on SMRs could help overcome public reservations while demonstrating a commitment to adopting cutting-edge technologies that prioritize nuclear safety and environmental stewardship.
The Impact of Nuclear Energy Regulation
Nuclear energy regulation forms the backbone of the industry’s operational integrity, ensuring that safety standards are met while encouraging innovation. However, the current regulatory framework in the UK has been criticized for its complexity and inefficiency. Overlapping authorities often lead to delays in project approvals, hampering the timely development of new nuclear facilities. The Nuclear Regulatory Taskforce emphasizes the urgent need for reform to enhance efficiency while maintaining high safety standards. Streamlining regulations would not only accelerate the approval process but also bolster the UK’s nuclear reputation on the international stage.
Moreover, the impact of nuclear energy regulation extends beyond project management; it plays a crucial role in shaping public confidence in the industry. Clarity and consistency in regulatory frameworks can help address public concerns regarding safety and environmental impact. The UK must prioritize building an effective regulatory environment that is responsive to contemporary challenges in nuclear energy while upholding stringent safety measures. By fostering a supportive regulatory landscape, the UK can attract investment in nuclear projects, enhancing its position as a leader in low-carbon energy production.
Nuclear Power’s Contribution to Achieving Net-Zero Goals
With growing urgency to combat climate change, nuclear power has been identified as a key player in achieving net-zero carbon goals. In the UK’s energy mix, existing nuclear power stations currently contribute about 15% to electricity generation, underscoring the potential of expanding this further. As traditional fossil fuel sources face declining viability, nuclear energy stands out for its ability to provide stable, large-scale power generation without emitting greenhouse gases. The pathway to net-zero will increasingly rely on the integration of nuclear energy alongside renewables to ensure a balanced and resilient energy supply.
The UK government has recognized this potential, launching initiatives aimed at increasing nuclear capacity to meet anticipated energy demands while striving for sustainability. Plans for new reactors and the adoption of small modular reactors provide pathways to enhancing the nuclear contribution to the energy network. This multifaceted approach not only supports the immediate de-carbonization agenda but also helps secure energy independence amidst fluctuating global energy markets. As the UK charts its course towards a low-carbon future, investing in nuclear power becomes essential in laying the groundwork for a sustainable energy landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the current state of nuclear power plants in the UK affect nuclear energy regulation?
The current state of nuclear power plants in the UK has put pressure on nuclear energy regulation due to complex bureaucracies and safety oversight gaps, which have led to increased costs and delays in plant construction. A government report emphasizes the need for simplified regulatory processes to enhance safety while improving efficiency in nuclear projects.
What challenges does the UK’s nuclear capacity expansion face?
The UK’s nuclear capacity expansion faces challenges such as outdated infrastructure, a fragmented regulatory system, and the complexities of nuclear energy regulation. The recent recommendations call for a radical rethinking of strategies to safely and efficiently enable capacity expansion to meet future energy needs.
How is UK energy policy influencing the future of nuclear power plants?
UK energy policy is central to the future of nuclear power plants, as the government aims to establish new facilities to meet energy demands and net-zero targets. The push for a streamlined regulatory framework reflects a commitment to making nuclear energy an essential part of the UK’s energy mix.
What are the current nuclear safety standards for existing plants in the UK?
Current nuclear safety standards in the UK have been criticized as overly conservative, contributing to high costs and delays in projects. The government review suggests that these standards need to be balanced with practical risk assessments to ensure that regulatory measures do not hinder timely nuclear power plant development.
What is the projected cost of nuclear power and its impact on future projects in the UK?
The projected cost of nuclear power in the UK is among the highest globally, attributed to overly complex regulations and inefficiencies. If the recommendations from the Nuclear Regulatory Taskforce are implemented, it could significantly reduce costs and encourage investment in future nuclear projects.
How do new nuclear projects contribute to UK energy security?
New nuclear projects are vital for UK energy security as existing facilities are aging and scheduled for closure. The development of new plants like Hinkley Point C and Sizewell C is expected to provide stable, low-carbon energy, crucial for UK’s net-zero ambitions and overall energy independence.
What role does public opinion play in the development of nuclear power plants in the UK?
Public opinion significantly influences the development of nuclear power plants in the UK, particularly due to concerns following events like Fukushima and Chernobyl. Ongoing efforts to improve safety standards and transparency in decision-making are essential to gaining public support for future nuclear projects.
How does the UK compare to other countries in expanding nuclear capacity?
The UK is part of a growing trend, with plans to triple nuclear capacity by 2050, similar to efforts in countries like France and China. However, compared to these nations, the UK faces unique regulatory challenges that could slow its progress unless addressed.
What are the main findings of the government review on nuclear power plants in the UK?
The government review highlights that the UK is the most expensive place to build nuclear power plants due to complex regulations. It recommends a streamlined regulatory process and better safety oversight to enhance efficiency and reduce costs in future nuclear projects.
When can we expect new nuclear plants to be operational in the UK?
New nuclear plants in the UK, such as Hinkley Point C, are projected to become operational in the early 2030s, with Sizewell C following later in the decade. While these timelines reflect significant future contributions to energy, the existing plants will need to be managed effectively until then.
| Key Area | Details |
|---|---|
| Cost of Building Nuclear Plants | UK is the most expensive place in the world for nuclear construction due to complex bureaucracy. |
| Government Review | Commissioned by PM Sir Keir Starmer, recommending a radical reset in the nuclear strategy. |
| Savings Potential | Changes could save tens of billions in costs and reverse recent industry decline. |
| Regulatory System Issues | Fragmented regulations lead to conservative, costly decisions without adequate safety oversight. |
| Industry Monopolization | Characterized as near-monopolistic, causing budget overruns and delays. |
| Nuclear Plant Importance | Essential for meeting future energy needs and carbon reduction targets. |
| Planned Developments | New plants like Hinkley Point C and Sizewell C will take several years to operate. |
| Public Opinion | Contentious issue influenced by historical safety incidents such as Fukushima. |
Summary
Nuclear power plants in the UK are critical to addressing future energy demands while assisting in carbon reduction goals. The recent review by the Nuclear Regulatory Taskforce highlights the dire need for reform in how the UK manages its nuclear projects, aiming to simplify the bureaucratic landscape to reduce costs significantly. As the country moves forward, developing a unified regulatory approach and investing in new nuclear capacity will help ensure the UK’s energy security and participation in the anticipated global nuclear renaissance.