Listen to this article
Large heat pumps are making a significant impact on our transition to renewable energy, revolutionizing how districts generate and distribute heating. These powerful systems utilize heat pump technology to extract thermal energy from various sources, including water bodies, to efficiently warm up entire communities. With advancements in decarbonization efforts, large heat pumps are increasingly integrated with district heating systems, providing a sustainable solution to reduce carbon footprints. Projects like those developed by MVV Energie not only showcase the biggest heat pump systems in the world but also exemplify the potential these technologies hold for the future of energy production. As cities shift away from fossil fuels, the role of large heat pumps in creating a sustainable urban ecosystem cannot be overstated.
The emergence of massive thermal management units, commonly known as large heat pumps, is reshaping the energy landscape. These substantial heating solutions harness heat from the environment, utilizing innovative technologies to facilitate efficient heat distribution across urban areas. With a focus on harnessing renewable sources, such systems are pivotal in district heating implementations where communal heating demands are met more sustainably. As mining and industrial sites transition towards cleaner technologies, many are realizing the benefits of deploying powerful heat extraction systems that bolster decarbonization initiatives. Consequently, large thermal units stand at the forefront of integrating green energy solutions into our everyday lives.
The Role of Large Heat Pumps in Decarbonization Efforts
Large heat pumps play a crucial role in the global effort to decarbonize energy systems and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. As cities and towns transition from coal and gas-fired heating systems to renewable energy sources, the adoption of large heat pumps becomes integral to this shift. These systems harness heat from various sources, such as the air, ground, or water, thereby delivering a sustainable and efficient heating solution. This not only aids in minimizing carbon emissions but also supports the broader agenda of achieving climate targets. So, as the push for renewable energy intensifies, the importance of large heat pumps within district heating systems cannot be overstated.
In addition to their environmental benefits, large heat pumps enhance energy security by diversifying energy sources and stabilizing heating supply amidst fluctuations in renewable energy output. As noted in recent projects, such as the ones by MVV Energie and Everllence, these powerful heat pumps can provide heating to thousands of homes while connecting seamlessly to existing district heating networks. This integration is critical, especially for urban areas facing increasing heating demands. Therefore, large heat pumps not only contribute to decarbonization but also bolster the resilience and reliability of modern energy systems.
Innovations in Heat Pump Technology for Urban Environments
Recent advancements in heat pump technology have transformed the landscape of urban heating solutions. Innovations such as improved refrigerants, advanced compressor designs, and energy management systems allow large heat pumps to operate at higher efficiencies and under a wider range of conditions. For instance, the largest heat pumps being constructed in places like Mannheim serve as a prime example of how these innovations are being applied to tackle urban heating challenges. By leveraging heat from bodies of water, such as the River Rhine, these systems illustrate the potential of heat pump technology in demanding settings.
Furthermore, partnerships between private companies and municipalities fuel the exploration of these technologies. In cities like Helsinki, the integration of heat pumps within a vast district heating network demonstrates a strategic approach to utilizing resources efficiently. With collaborations aimed at sharing knowledge and overcoming logistical barriers, innovative heat pump systems can optimize energy output while minimizing operational costs. As urban populations grow and energy demands increase, continued investment in heat pump technology will be paramount in ensuring sustainable heating solutions for the future.
District Heating Systems: The Backbone of Heat Distribution
District heating systems serve as an effective and efficient means of distributing heat generated from centralized sources, including large heat pumps. These integrated networks allow for the delivery of hot water or steam across vast distances to various buildings, effectively consolidating energy use and reducing overall carbon footprints. As demonstrated by projects in Germany and Denmark, district heating systems can incorporate diverse energy sources, including renewable forms, to create a robust heating infrastructure. This means that as new heat pump systems come online, they will seamlessly fit into existing networks designed to maximize efficiency.
The key advantage of district heating systems lies in their ability to provide consistent heat supply while reducing energy waste. For example, in Aalborg, the planned implementation of large heat pumps is set to cover a significant portion of the city’s heating demand, ensuring that even during peak times, sufficient energy is available. This centralized approach also allows for seasonal storage methods, enabling heat to be stored when demand is low and utilized when necessary. By linking buildings to a communal heating system, district heating significantly optimizes resource management and paves the way for a more sustainable energy future.
The Economics of Large Heat Pump Installations
Investment in large heat pumps represents a significant upfront cost but is often justified by the long-term savings and environmental benefits. In projects like the one undertaken by MVV Energie in Mannheim, the total setup cost is estimated at €200 million. While this may appear substantial, the ongoing operational savings—due to reduced reliance on fossil fuels and lesser maintenance needs—can result in a strong return on investment over time. These economic considerations are critical for cities and companies considering the shift towards renewable energy and sustainable heating technologies.
Moreover, as the energy landscape evolves, the expenses associated with heat pump installations are becoming easier to manage. The decreasing costs of renewable energy technologies, coupled with supportive government policies, incentivize the adoption of large heat pumps. The transition away from traditional heating methods to innovative solutions like district heating powered by large heat pumps not only addresses environmental concerns but also promotes economic growth through job creation and investment in clean energy infrastructure.
Benefits of Heat Pumps in Urban Decarbonization
Heat pumps are integral to urban decarbonization strategies, as they significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to conventional heating methods. By utilizing renewable energy sources and waste heat, heat pumps can efficiently provide heating and cooling throughout seasons. Cities implementing large heat pumps within district heating systems can enhance their sustainability strategies, targeting net-zero goals and promoting energy efficiency on a large scale. The capability of heat pumps to deliver substantial heat outputs—often exceeding traditional methods—makes them a viable solution in dense urban settings where space and resources may be limited.
Additionally, their ability to harness energy from various sources contributes to the diversification of energy portfolios in cities pursuing decarbonization. As seen in adoptions across Europe, heat pumps complement other renewable technologies, such as solar and wind, thereby maximizing energy use while minimizing waste. The strategic use of large heat pumps in urban areas not only aids in climate mitigation efforts but also enhances the energy independence and resilience that cities need in an ever-changing energy landscape.
Large Heat Pumps and Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating large heat pumps with renewable energy sources is at the forefront of sustainable energy strategies. These systems can produce heat efficiently while facilitating the use of renewable electricity from sources like wind and solar. As renewable energy generation fluctuates, large heat pumps offer a flexible solution by providing much-needed heat during periods of high electricity supply. This balancing act enhances the stability of energy grids while further promoting the transition to clean energy technologies. Various municipalities are already exploring these synergies to optimize heat generation continuously.
The collaboration between power generation and thermal energy use creates a robust and renewable-centric energy ecosystem. By utilizing surplus renewable energy for heat production, cities can reduce dependency on fossil fuel sources, effectively contributing to their decarbonization efforts. Projects in Denmark and Germany exemplify the seamless integration of heat pumps into broader renewable energy portfolios, resulting in a win-win: affordable heating solutions and a sustainable energy future. This alignment presents a promising pathway for other urban centers looking to modernize their heating systems and address climate change.
Emerging Trends in Heat Pump Systems
As energy needs evolve, emerging trends in heat pump technology reflect the changing landscape of urban heating solutions. More municipalities are recognizing the value of large heat pumps that connect to district heating systems. This transition is indicative of a significant trend towards sustainability and efficiency, driving cities to explore diverse heat sources. The ongoing development of modular systems allows for more flexibility, enabling cities to customize their heat pump installations according to specific energy requirements and infrastructure capabilities.
Moreover, the use of advanced technologies such as smart monitoring systems and digital controls further enhances the efficiency of heat pump operations. These innovations allow for real-time adjustments based on heating demands, ultimately optimizing energy consumption. As cities aim for renewable energy targets, the integration of emerging trends in heat pump technology is essential to creating a resilient and efficient future for urban heating.
Challenges Facing Large Heat Pump Deployments
Despite the advantages of large heat pumps, various challenges hamper widespread adoption. One primary concern relates to the installation costs associated with these systems, which can be substantial. Cities often need significant upfront investment to develop the necessary infrastructure, impacting their willingness to adopt these technologies. Regulatory frameworks and grid capacity also pose additional challenges, especially in densely populated urban environments where space is limited and logistics may complicate installations.
Moreover, public acceptance plays a crucial role in the deployment of large heat pump systems. As urban areas transition from traditional heating methods to more sustainable solutions, ensuring that communities understand the benefits and practicality of these systems is vital. Educational initiatives and open dialogue with residents can mitigate concerns and underscore the importance of large heat pumps in achieving climate and energy goals. Addressing these challenges head-on is essential to refining heat pump technology and fostering a broader adoption across cities globally.
Future Prospects for Large Heat Pumps in Urban Heating
The future of large heat pumps in urban heating looks promising, as global awareness of climate change and sustainability continues to grow. The demand for efficient heating solutions presents significant opportunities for the expansion of large heat pump systems that can cater to the changing energy landscape. With advancements in heat pump technology leading to greater efficiencies and lower costs, many cities are keen to invest in these innovative systems as part of their long-term energy strategies. As illustrated by ongoing projects in Europe, long-term planning and investment are key to unlocking the potential of large heat pumps.
Furthermore, collaboration among stakeholders—including governments, energy providers, and communities—will drive the successful integration of large heat pumps into urban infrastructure. As more municipalities commit to sustainability initiatives, the selection of large heat pumps can lead to cleaner heating networks while supporting the transition towards renewable energy sources. As the world strives to meet climate goals, the implementation of large heat pumps as part of a comprehensive urban energy strategy will undoubtedly play a pivotal role.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of large heat pumps in district heating systems?
Large heat pumps play a crucial role in district heating systems by providing a renewable and efficient source of heat. They utilize heat pump technology to extract energy from available natural resources like water or air, making them essential for decarbonization efforts. These systems help lower carbon emissions by replacing fossil fuel sources, thereby contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
How do the biggest heat pump systems work?
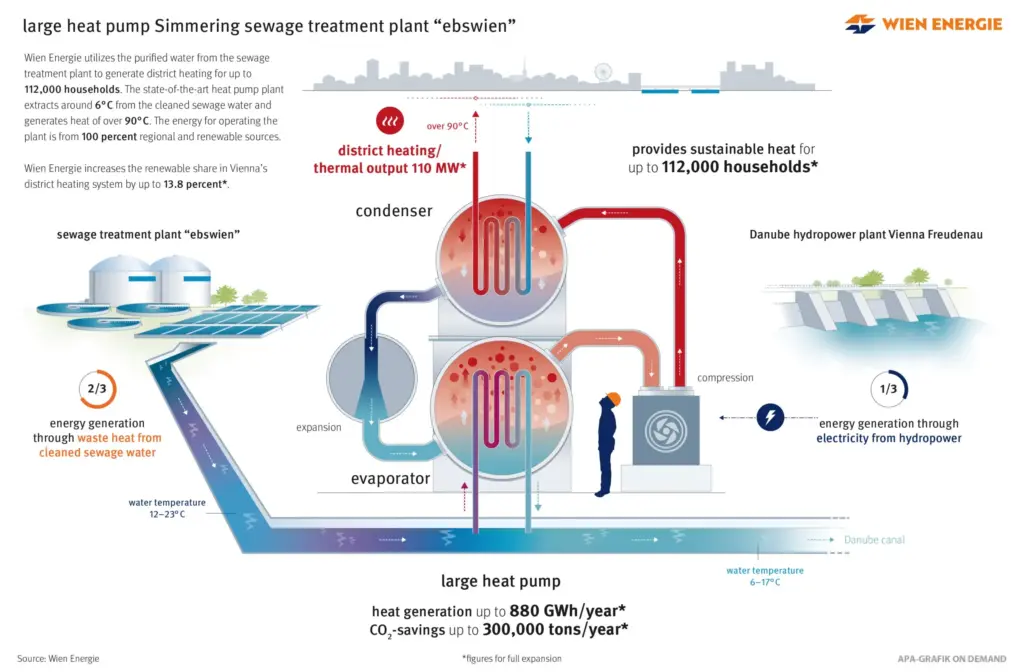
The biggest heat pump systems work by drawing heat from the air, ground, or bodies of water. For instance, MVV Energie’s project in Mannheim uses large pipes to extract water from the River Rhine, heating it through compression. This heat is then distributed via district heating networks to multiple buildings, making it a highly efficient way to provide thermal energy at scale.
What role do large heat pumps play in renewable energy initiatives?
Large heat pumps play a vital role in renewable energy initiatives by enabling the use of renewable sources for heating, such as excess electricity from solar or wind. By connecting to district heating systems, they can transform renewable energy into usable heat, supporting wider decarbonization goals and enhancing the sustainability of energy grids.
Can large heat pumps be used in colder climates?
Yes, large heat pumps can be effectively utilized in colder climates. For example, cities like Helsinki are implementing systems that harness heat from relatively shallow coastal waters despite lower temperatures. By using advanced heat pump technology, they can extract heat even in harsh environmental conditions, ensuring consistent energy supply.
What challenges do large heat pump systems face during implementation?
One of the primary challenges facing large heat pump systems is the high initial investment cost associated with their installation and infrastructure. Additionally, logistical concerns, such as transporting large equipment and connecting to existing district heating networks, can complicate implementation. However, the long-term benefits of energy efficiency and lower operational costs often outweigh these challenges.
What is the future of large heat pumps in urban energy solutions?
The future of large heat pumps in urban energy solutions looks promising as cities increasingly turn to decarbonization strategies. The development of ambitious projects like those in Mannheim and Aalborg indicates a trend toward larger, more efficient heat pump systems. As technology advances and becomes more affordable, it is expected that the integration of large heat pumps with district heating systems will expand significantly.
How do large heat pumps aid in the decarbonization of energy systems?
Large heat pumps aid in the decarbonization of energy systems by providing a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels for heating. By capturing heat from renewable sources and distributing it through district heating networks, these systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance energy efficiency. This transition is crucial as cities and countries commit to lower carbon footprints.
What are some examples of current large heat pump projects worldwide?
Current examples of significant large heat pump projects include MVV Energie’s system in Mannheim, Germany, with a capacity of 162 MW and Everllence’s project in Aalborg, Denmark, exceeding 176 MW. These projects are designed to serve extensive district heating networks, offering an excellent demonstration of how large heat pump technology can effectively meet urban heating demand.
What are the economic implications of large heat pump installations?
The economic implications of large heat pump installations include substantial upfront costs estimated at around €500,000 per megawatt of capacity. However, the long-term savings in energy costs and benefits from increased energy efficiency can lead to favorable economic outcomes. Additionally, large heat pumps can stabilize energy prices by integrating renewable resources, facilitating energy source diversification.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Largest Heat Pump Systems | MVV Energie is building the world’s most powerful heat pump modules with a total capacity of 162 megawatts. |
| Water Source | Heat is harvested from the River Rhine, using pipes with a diameter of 2 meters to take in 10,000 liters of water per second. |
| Capacity and Homes Supported | The heat pumps will supply heat for about 40,000 homes through a district heating system. |
| Environmental Impact | The installation is designed to minimize environmental impact, affecting river temperature by less than 0.1°C. |
| Cost | The setup’s cost is estimated at €200 million ($235 million; £176 million), with equipment costing about €500,000 per megawatt. |
| Future Projects | Another project in Aalborg, Denmark, will have a capacity of 176MW from four units, set to be operational in 2027. |
| District Heating Synergy | Heat pumps can efficiently connect to district heating networks, benefiting from flexibility in operation. |
| Alternative Heating Sources | Heat pumps can also utilize air as a heat source, although city conditions may limit effectiveness. |
| Advancements in the UK | The UK is beginning to explore large heat pump technology with new projects like the Exeter Energy Network. |
Summary
Large heat pumps are revolutionizing the way cities generate heat, providing powerful solutions for district heating systems. With ongoing projects like those in Mannheim, Germany, and Aalborg, Denmark, these massive systems are designed to supply heating for thousands of homes while integrating renewable energy sources. The transition from coal to more sustainable options through the installation of large heat pumps is crucial for decarbonizing urban environments and achieving long-term energy efficiency goals.