Listen to this article
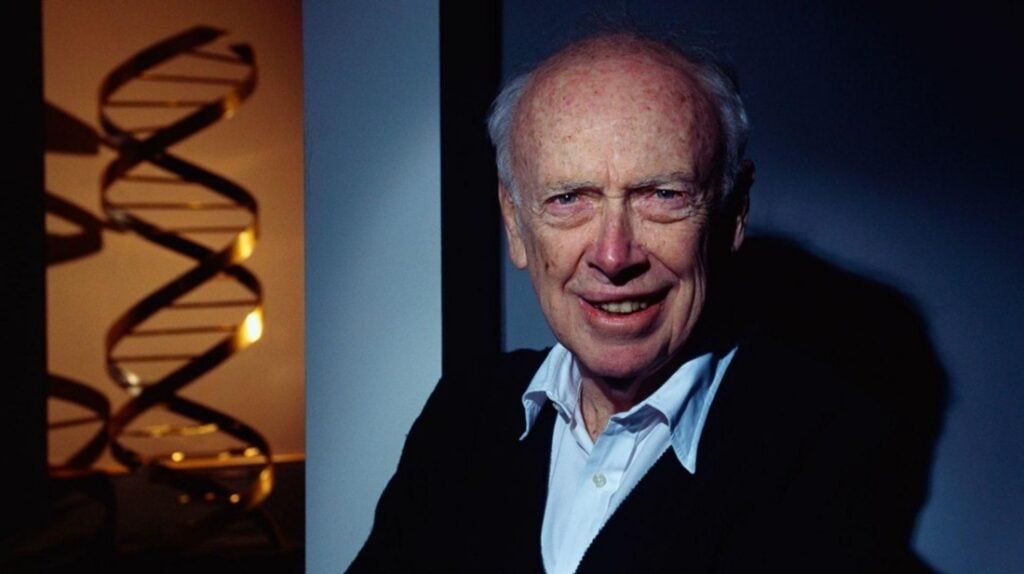
James Watson, the celebrated American biologist, and co-discoverer of DNA’s double-helix structure alongside Francis Crick, passed away at 97, leaving a mixed legacy in the scientific community. His monumental achievement in 1953 not only revolutionized our understanding of genetics but also earned Watson and Crick the esteemed Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962, cementing their role in history alongside giants like Mendel and Darwin. However, Watson’s career was not without controversy; his provocative remarks on race and intelligence have drawn significant backlash, leading many to examine his contributions critically. As retrospectives unfold, the James Watson obituary reveals both the brilliance of his scientific breakthroughs and the complexities of his public persona. His story intertwines with debates over genetics, making him a polarizing figure in the realm of modern science.
James Watson, an influential figure in biological research, is widely known for his pivotal discovery regarding the double-helix structure of DNA. His collaborative work with fellow scientist Francis Crick during the early 1950s set the stage for revolutionary advancements in the field of human genetics. The Nobel Prize awarded to Watson and Crick in 1962 symbolized a significant achievement in understanding hereditary information, although their journey was complemented by the essential contributions of Rosalind Franklin. Despite his scientific accolades, Watson’s later years were clouded by controversy due to his contentious views on race and intelligence, which sparked fierce debates and raised questions about the ethical implications of his research. The narrative surrounding Watson serves as a lens through which the intricate relationship between scientific discovery and societal values can be explored.
James Watson: A Pioneering Force in Genetics
James Watson, an American biologist, is best remembered for his pivotal role in the discovery of the structure of DNA. In 1953, alongside British scientist Francis Crick, he unveiled the double-helix model that would become foundational in genetics. This groundbreaking work provided essential insights into how genetic information is stored and transmitted across generations. Their partnership ignited a scientific revolution that not only changed biology but also altered our understanding of heredity, making them integral figures in the annals of science.
Moreover, their achievement garnered them the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962, solidifying their positions as leaders in the field. However, it is important to note that their discovery was built upon the contributions of other scientists, such as Rosalind Franklin, whose X-ray diffraction images were crucial in elucidating the DNA structure. Watson’s recognition and accolades, including the Nobel Prize, highlight how pivotal moments in science often involve multiple contributors, even as certain figures garner the most public attention.
The Controversies Surrounding James Watson
Despite his monumental contributions to science, James Watson’s legacy is not without controversy. Throughout his career, he made numerous provocative statements regarding race and intelligence that sparked significant backlash. These comments not only affected his standing within the scientific community but also fueled debates about the ethical responsibilities of scientists when discussing sensitive topics like genetics and human behavior. The controversy surrounding his views has cast a long shadow over his scientific achievements, raising questions about the intersection of science and social responsibility.
Watson’s remarks led to a notable decline in his reputation and resulted in losing many professional affiliations and honors. Many institutions chose to distance themselves from him, illustrating the consequences of intertwining scientific discourse with personal beliefs. Nonetheless, Watson continued to engage with the scientific community, maintaining his influence and relevance despite the turbulence of his later years. His journey underscores the complex relationship between scientific innovation and personal accountability in the public eye.
Celebrating the Legacy of Discovery: Watson and Crick’s Impact on Science and Society
The collaborative effort of James Watson and Francis Crick in elucidating the structure of DNA heralded a new era in molecular biology. Their work provided the blueprint for modern genetics, influencing countless areas of research, from evolutionary biology to medical genetics. The double-helix model became not only a scientific achievement but also a symbol of scientific progress and the pursuit of knowledge, inspiring future generations of scientists to delve deeper into the mysteries of life.
The societal implications of their discovery have been vast, impacting education, healthcare, and ethical debates surrounding genetic research. The ability to understand DNA has paved the way for advancements in genetic engineering, gene therapy, and personalized medicine. As discussions about genetic editing and biotechnology continue to evolve, Watson and Crick’s legacy serves as a reminder of the immense potential and responsibility that comes with scientific discovery.
Celebrating the Structure of DNA and Its Discoverers
The discovery of DNA’s double-helix structure was more than just an academic milestone; it was a leap into a new understanding of life itself. James Watson’s collaboration with Francis Crick represents a high point in scientific achievement, celebrating the power of teamwork and intellectual curiosity. Their investigation not only brought clarity to the intricacies of genetic material but also stirred public interest in genetics, reflecting a broader societal engagement with scientific issues.
In recent years, the applications of their discovery have transformed various fields, including medicine and forensics. The ability to analyze DNA has revolutionized how we understand genetic diseases, inheritance patterns, and even criminal justice. Watson and Crick’s work continues to reverberate through contemporary science, underscoring the profound influence that a single discovery can have on both academia and society as a whole.
James Watson’s Contributions to Genetic Research
James Watson’s legacy extends beyond the discovery of the DNA structure; his work has had a lasting impact on the field of genetics. As a scientist, Watson has contributed to various research areas including molecular biology and genetics, shaping the way future generations approach the study of heredity and genetic variation. His early research projects laid the groundwork for understanding complex genetic phenomena, which have been essential in modern biology.
Furthermore, Watson’s involvement in scientific leadership roles and his ability to communicate scientific ideas to the public also established him as an advocate for genetic research. His contributions helped promote the significance of genetics in explaining biological processes, which has become increasingly relevant in contemporary discussions on biotechnology and genetic ethics.
The Context of Watson’s Controversy in Modern Science
In recent decades, science has made remarkable strides in understanding genetics, and James Watson’s contributions sit at the center of this evolution. However, the controversies that have surrounded his public statements highlight a crucial debate in science: the role of scientists as public figures. Watson’s views have ignited discussions about the ethics of scientific discourse and the responsibility that comes with a prominent role in the scientific community.
The scrutiny of Watson’s comments has led to a broader examination of the intersection between genetics and societal issues such as race and intelligence. Modern genetics operates under the framework of ethical considerations, raising the question of how scientists should navigate complex societal topics while remaining grounded in research evidence. Watson’s legacy thus serves as a cautionary tale about the importance of maintaining ethical integrity in scientific conversations.
The Legacy of Watson and Crick in Genetic Research
The journey of James Watson and Francis Crick in unveiling the structure of DNA has changed the landscape of genetic research forever. Their collaborative efforts are often regarded as a quintessential example of how teamwork can lead to monumental discoveries. The double helix is not just a scientific model; it symbolizes the beginning of modern genetics, where understanding the blueprint of life has profound implications in medicine, biology, and beyond.
Their work laid the foundation for the Human Genome Project and continues to inform ongoing research in genetics. As science advances, the partnership between Watson and Crick serves as a reminder of the collaborative nature inherent in scientific inquiry, showcasing that significant discoveries stem from shared knowledge and dedication to understanding the fundamental aspects of life.
A Tribute to Watson’s Dedication to Science
In reflecting on James Watson’s life, it is essential to honor his unwavering dedication to science. From an early age, Watson exhibited a fervent curiosity about the natural world, which eventually guided him toward the groundbreaking discovery of the DNA structure. His relentless pursuit of knowledge, even in the face of controversy, underscores the commitment of many scientists to their work and the pursuit of scientific truth.
Watson’s contributions to science, despite his controversial views, remain a testament to the dynamism of scientific inquiry. While his statements may have sparked debate, they also reflect the complexity of human thought and the challenges of communicating scientific ideas in a societal context. The legacy he leaves behind is one of remarkable scientific achievement coupled with the lessons learned about the responsibilities of scientists in closely-knit communities.
Understanding the Double Helix: A Milestone in Biology
The double-helix structure of DNA, proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick, represents a major milestone in biology that fundamentally altered our comprehension of heredity and genetics. This model illustrates how genetic information is stored, replicated, and passed on through generations, thereby becoming a cornerstone of genetic research. The implications of this discovery are far-reaching, influencing practical applications in medicine, agriculture, and beyond.
Moreover, the moment of unveiling the double helix was a testament to rigorous scientific endeavor. The collaboration of Watson and Crick, alongside Rosalind Franklin’s pivotal contributions, exemplifies how scientific progress often necessitates the pooling of diverse expertise and perspectives. This collaborative spirit continues to inspire new generations of scientists to think creatively and work collaboratively to solve complex biological puzzles.
The Nobel Prize Legacy and Its Significance in Genetics
Winning the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962 was a crowning achievement for both James Watson and Francis Crick, recognizing their groundbreaking discovery of the DNA structure. The award not only acknowledged their scientific contributions but also elevated the field of genetics to new heights in public esteem. Receiving such a prestigious accolade has vast implications for a scientist’s career, often providing opportunities for continued research funding and collaboration.
The Nobel recognition also highlights the importance of collaborative scientific efforts in achieving significant milestones. While Watson and Crick are often the most celebrated figures, it is essential to remember the contributions of others like Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins, whose work was crucial to understanding the DNA structure. Their collective efforts serve as a compelling reminder of the collaborative nature that is often essential in the path towards scientific discovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is James Watson best known for in the field of genetics?
James Watson is best known for his pivotal role in the discovery of the DNA structure in 1953, alongside British scientist Francis Crick. Their groundbreaking work identified the double-helix model of DNA, which has been crucial for the understanding of genetics and inheritance.
How did James Watson contribute to the Nobel Prize in genetics?
James Watson, along with Francis Crick, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962 for their discovery of the DNA double helix. This monumental achievement not only advanced the field of genetics but also established Watson as a key figure in scientific history.
What controversies surrounded James Watson during his career?
James Watson faced significant controversy during his career due to his provocative statements regarding race, intelligence, and genetics. These comments resulted in backlash from the scientific community, leading to loss of positions and honors.
Who were the co-researchers of James Watson in the DNA structure discovery?
In the race to uncover the structure of DNA, James Watson collaborated with Francis Crick at Cambridge. They were also in competition with Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins, whose crucial research played a significant role in their eventual success.
What impact did James Watson’s work have on the scientific community?
James Watson’s work in revealing the DNA structure has had a profound impact on the scientific community, providing fundamental insights into the mechanics of genetics and inheritance. This discovery has paved the way for advancements in molecular biology, genetics, and medicine.
What was James Watson’s early life and education like?
James Watson was born on April 6, 1928, in Chicago and grew up in a politically active family. He showed an early interest in science, earning a scholarship to the University of Chicago at just 15 years old. Initially studying ornithology, he eventually shifted his focus to genetics, driven by his fascination with DNA.
What role did Rosalind Franklin play in the DNA structure discovery alongside James Watson?
Rosalind Franklin’s research was crucial to the DNA structure discovery made by James Watson and Francis Crick. Although she did not receive the Nobel Prize due to her passing prior to the award announcement, her X-ray diffraction images of DNA significantly aided in confirming the double-helix model.
Did James Watson continue his scientific contributions after the controversies?
Despite facing personal and professional repercussions due to controversies surrounding his views on race and intelligence, James Watson continued to engage in scientific research and discussions throughout his later years until his death.
What legacy did James Watson leave in the field of genetics?
James Watson’s legacy in genetics is defined by his groundbreaking discovery of the DNA double helix structure with Francis Crick. His contributions have fundamentally shaped our understanding of genetics, influencing multiple fields, including biochemistry and biotechnology.
What are some of the honors James Watson received during his lifetime?
During his illustrious career, James Watson received numerous honors, including the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962. However, these honors were also accompanied by challenges due to his controversial statements later in life.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| James Watson’s Birth | April 6, 1928, in Chicago. |
| DNA Discovery | Co-discovered the structure of DNA with Francis Crick in 1953. |
| Nobel Prize | Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962. |
| Controversies | Known for controversial statements regarding race and intelligence. |
| Education | Received a scholarship to the University of Chicago at 15, initially studied ornithology before focusing on genetics. |
| Scientific Race | Competed with Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins to decode DNA. |
Summary
James Watson, who recently passed away at the age of 97, leaves behind a complex legacy in the field of biology. His discovery of the DNA structure, achieved alongside Francis Crick, was pivotal in understanding the blueprint of life. Despite his groundbreaking scientific contributions, Watson’s career was shadowed by controversies regarding his opinions on race and genetics, which led to significant debates within the scientific community. Overall, Watson’s life epitomizes the duality of scientific endeavor: extraordinary achievement intertwined with contentious views. His story will continue to provoke thought and discussion.