Listen to this article
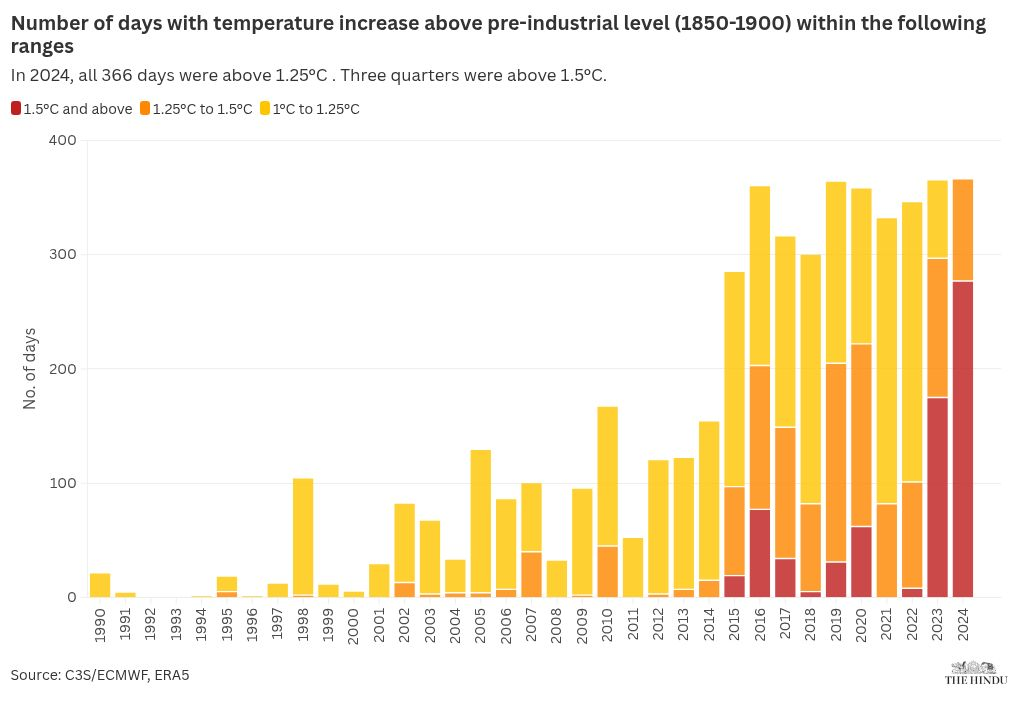
The concept of global warming limits is critical as scientists warn that humanity is nearing the brink of exceeding these boundaries. Recent studies indicate that our carbon budget is rapidly dwindling, with the 1.5°C global warming limit nearly exhausted due to escalating fossil fuel emissions. As carbon dioxide emissions continue to rise, it becomes increasingly clear that urgent action is needed to address the dire implications of climate change. With projections showing record high emissions this year, the window for mitigating catastrophic global warming is closing fast. As we approach COP30, the focus on reducing wildfire risk and averting further damage to our planet becomes more pressing than ever.
Addressing the pressing issue of climate thresholds demands our immediate attention as researchers highlight the alarming reality of reaching critical warming thresholds. Current assessments of the allowable atmospheric carbon levels reveal that our capacity to increase global temperatures without disastrous consequences is significantly compromised. With fossil fuel consumption still rampant, the urgency for comprehensive climate action has never been greater. The ongoing discussions at the UN-led climate summit aim to redefine our approach to emissions reduction and sustainable practices, underlining the urgent need to tackle rising risks, including wildfires and extreme weather events. In this context, prioritizing collaborative efforts to preserve planetary health and keep warming in check is of utmost importance.
Understanding Global Warming Limits
The concept of global warming limits is crucial to understanding the current state of our climate. At the forefront is the 1.5°C threshold, which represents the maximum increase in global temperatures that scientists warn must not be exceeded to avoid the most catastrophic impacts of climate change. This limit is significantly tied to our remaining carbon budget, which refers to the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions that can still be emitted without surpassing the 1.5°C increase. Research from the University of Exeter has highlighted that this budget is nearly exhausted, placing urgent pressure on nations worldwide to drastically reduce fossil fuel emissions in the coming years.
As we stand on the brink of surpassing critical global warming limits, the implications are profound. The report indicates that if current emission rates continue, we could exhaust our carbon budget within the next few years. This scenario not only threatens future generations with volatile weather patterns and rising sea levels but also increases the risk of extreme climate events. We are already witnessing these risks materialize through more frequent and severe wildfires, as seen in London this past summer, further emphasizing the pressing need for global action.
The Escalating Threat of Fossil Fuel Emissions
Fossil fuel emissions remain a significant contributor to climate change, accounting for the majority of the anthropogenic CO2 released into the atmosphere. Despite some advancements in the transition to renewable energy, the world still heavily relies on oil, coal, and natural gas. In fact, global carbon emissions are projected to hit record highs, rising by 1.1% in the current year, demonstrating a concerning trend of continued fossil fuel dependency. As nations brace for COP30 in Brazil, discussions surrounding emissions reduction strategies and carbon budgets are more critical than ever to curb this escalating threat.
The increasing carbon footprint from fossil fuels not only challenges the 1.5°C goal but also amplifies other climate-related issues, such as the surge in wildfire incidents. For example, the summer of 2025 was marked by excessive heat and a spike in wildfires in London, underscoring the intersection of rising temperatures and fossil fuel emissions. World leaders must prioritize actionable commitments to drastically lower emissions and foster a swift transition to cleaner, sustainable energy sources to mitigate these pressing concerns.
COP30 and Climate Change Commitments
The upcoming COP30 conference represents a vital forum for world leaders to re-evaluate their commitments to combating climate change. As countries gather to discuss strategies for reducing carbon emissions and preserving the remaining carbon budget, the stark reality of their obligations is clearer than ever. Current trends indicate several nations are hesitant to enforce stricter climate commitments, even in the face of escalating climate crises such as severe storms and droughts. The actions taken or neglected during COP30 will significantly shape global responses to climate challenges moving forward.
The urgency surrounding COP30 is exemplified by the recent research indicating that the carbon budget necessary to keep global warming below the 1.5°C limit is dwindling. This juncture presents a critical opportunity for participating nations to recommit to ambitious climate action, focusing on reducing fossil fuel use and increasing investments in renewable energy technologies. The encouraging progress made by a select number of countries in decreasing their emissions while supporting economic growth serves as a powerful model for the transformative policies needed to combat climate change effectively.
The Impact of Climate Change on Wildfire Risk
Climate change is increasingly linked to heightened wildfire risk, as shown by the dramatic rise in incidents over recent years. The scorching heatwaves experienced in urban areas like London have led to an alarming increase in wildfires, with the capital reporting multiple, severe fire events in just one season. Notably, the Dagenham wildfire in July required extensive firefighting resources and is a stark reminder of how climate instability exacerbates the risks associated with wildfires. This situation underscores the urgency for communities to adopt proactive measures to engage with climate challenges.
As temperatures continue to rise, the factors contributing to wildfire susceptibility become more pronounced. This requires a two-fold approach where not only are immediate firefighting resources needed, but also systemic changes must be implemented to tackle the root causes of climate change. Reducing fossil fuel emissions and enhancing land management practices can contribute to lowering wildfire risks. Through dedicated efforts, cities can better prepare for the growing threat of wildfires, all while striving toward broader climate goals.
The Role of Deforestation in Climate Change
Deforestation plays a pivotal role in exacerbating climate change and depleting our carbon budget. As forests are cleared for agriculture, urban development, and other human activities, the CO2 that would have otherwise been stored in trees is released into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse gas emissions that drive global warming. Recent reports hint at slight improvements in deforestation rates, which could lead to modest reductions in overall carbon emissions. However, the ongoing challenge of high deforestation levels remains significant.
To combat climate change effectively, global efforts must include strategies to protect and restore forests. Deforestation not only hinders our ability to meet the 1.5°C global warming limit but also reduces biodiversity and increases vulnerability to climate-related disasters. Collaborative international efforts must emphasize sustainable land-use practices while fostering reforestation initiatives. By prioritizing the preservation of our forests, we can enhance our resilience against climate impacts and support a healthier planet for future generations.
Collective Action Needed Against Climate Change
Addressing climate change effectively requires unprecedented collective action from individuals, governments, and organizations around the globe. The interconnected nature of climate challenges means that local efforts can have a significant global impact. Initiatives aimed at reducing carbon footprints, such as adopting sustainable energy sources and advocating for climate-friendly policies, are crucial. Public awareness campaigns can drive community engagement, encouraging citizens to take part in activities that reduce fossil fuel consumption and promote environmental stewardship.
As we grapple with the reality of our dwindling carbon budget, it is apparent that time is of the essence. Countries need to unite their efforts to commit to actionable plans that transcend political and economic differences. Collaboration in technology transfer, sharing best practices, and providing financial support to developing nations can lay the groundwork for a united front against climate change. Collectively, we must reinforce our commitment to safeguarding the environment and adhering to the global warming limits necessary for a sustainable future.
Innovations in Renewable Energy Solutions
Innovations in renewable energy solutions are essential for achieving meaningful reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and working toward sustainable development. Renewable sources such as solar, wind, and hydro offer viable alternatives to fossil fuels, enabling us to transition toward a cleaner energy landscape. The recent progress demonstrated by 35 countries in reducing emissions while growing their economies indicates that it is indeed possible to harmonize economic growth with environmental responsibility through strategic investments in clean technologies.
Moreover, advancements in energy storage and efficiency are pivotal in making renewable energy more accessible and reliable. These innovations can mitigate the challenges associated with intermittent energy generation from sources like solar and wind. By investing in research and development, countries can create energy systems that are resilient, affordable, and capable of meeting future demands without exceeding global warming limits. This transition not only enhances energy independence but also plays a critical role in addressing the threats posed by climate change.
The Future of Climate Policy Frameworks
The future of climate policy frameworks is being shaped by the recognition of the urgent need to adhere to global warming limits and reduce fossil fuel dependency. Policymakers are now tasked with developing comprehensive strategies that integrate environmental sustainability into all aspects of governance and economic planning. The passing of new regulations aimed at curbing emissions and encouraging renewable energy adoption signifies a progressive approach to tackling climate change.
Furthermore, as countries participate in vital conferences like COP30, there is a growing emphasis on international collaboration and commitment. Policies that foster transparency, accountability, and cooperation are essential for creating a unified response to climate change threats. The evolution of climate policy frameworks must consider the interlinked nature of ecosystem health and economic viability, reinforcing the message that environmental action is not just a moral imperative, but also beneficial for long-term economic stability.
Community Engagement in Climate Action
Community engagement is crucial to climate action, as local efforts can have far-reaching effects on global environmental issues. Grassroots movements and localized initiatives empower communities to take ownership of their climate goals, inspiring individuals to adopt behaviors that contribute to emission reductions. Education and awareness programs can play a significant role in mobilizing populations to recognize their impact on climate change and encouraging collective efforts toward sustainability.
As communities come together to advocate for climate-friendly practices, collaborative projects and partnerships can enhance their effectiveness. Sponsoring events focused on sustainability, like tree planting and clean energy workshops, nurtures a culture of environmental responsibility. By fostering community engagement in climate action, we can build resilient societies ready to face the challenges of climate change while working to stay within global warming limits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the global warming limit in relation to climate change?
The global warming limit is critical as it represents the maximum increase in temperature that is deemed safe for human life and ecosystems. Specifically, the 1.5°C limit serves as a threshold to avert severe climate impacts, including extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and heightened wildfire risks. Scientists warn that we are nearing the exhaustion of our carbon budget to maintain this limit due to ongoing fossil fuel emissions.
How does the carbon budget relate to global warming limits?
The carbon budget is the total amount of carbon dioxide emissions that can be released while still keeping global warming within a specific limit, such as 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. Recent research indicates that the remaining carbon budget is nearly exhausted, meaning that we have limited time to reduce emissions significantly to prevent catastrophic climate outcomes.
What role do fossil fuel emissions play in reaching global warming limits?
Fossil fuel emissions are the primary contributors to global warming, significantly impacting our ability to stay within the 1.5°C limit. As emissions continue to rise, projected to reach record highs this year, they deplete our carbon budget, pushing us closer to irreversible climate change. Reducing fossil fuel reliance is essential to maintaining global warming limits and safeguarding future generations.
What can we expect from COP30 in terms of global warming limits?
COP30 is crucial as world leaders will discuss and potentially strengthen commitments to maintain global warming limits. Given the urgency highlighted by scientists, including the depletion of our carbon budget, this conference represents an opportunity for nations to collaborate on innovative solutions and reinforce climate action, despite some countries reconsidering their climate commitments.
How do increasing wildfires relate to global warming limits?
Increasing wildfires are a direct consequence of climate change, which is exacerbated by exceeding global warming limits. Higher temperatures and altered weather patterns heighten the risk of wildfires, as evidenced by a rise in wildfire incidents during exceptionally hot summers. Addressing global warming limits is imperative to reduce the severity and frequency of such natural disasters.
What actions need to be taken to meet global warming limits?
To meet global warming limits, significant and immediate actions are required, including reducing fossil fuel emissions, transitioning rapidly to renewable energy sources, and enhancing energy efficiency. Additionally, collective global efforts to implement policies that promote sustainability and protect carbon sinks, like forests, are crucial for remaining within our carbon budget and mitigating climate change.
Why is the term ‘climate change’ critical in discussions about global warming limits?
The term ‘climate change’ encapsulates the broader impacts and consequences of overshooting global warming limits. It highlights the urgent need for action against the increasing occurrence of extreme weather events, such as storms and droughts, which are becoming more frequent as we approach critical warming thresholds. Understanding climate change is essential for fostering public awareness and driving policy change to secure our future.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Global Warming Limit | The 1.5°C limit is nearly exhausted, leaving only 170 billion tonnes of CO2 before exceeding this threshold. |
| Current Emissions | Fossil fuel carbon emissions are projected to reach record highs, with a 1.1% global increase this year. |
| Consequences for Futurity | At the current rate, the 1.5°C limit could be fully utilized within four years, leading to severe climate impacts. |
| Recent Climate Events | London experienced four intense heatwaves this summer, resulting in 83 wildfires. |
| Global Response | World leaders are gathering in Brazil for COP30 to discuss climate action amidst rising emissions. |
| Improvement in Deforestation | Deforestation rates have decreased slightly, yet they remain high, requiring more effort. |
Summary
Global warming limits are nearing exhaustion, as indicated by recent scientific studies highlighting the critical state of our climate. With only 170 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide left in the carbon budget before exceeding the 1.5°C threshold, immediate and decisive action is imperative. The alarming rise in fossil fuel emissions, alongside record-breaking heatwaves and increased wildfire incidences, underscores the pressing need for global leaders to unite and reinforce their climate commitments. As we face an uncertain future, the emphasis on reducing emissions and transitioning to sustainable energy sources has never been more crucial.