Listen to this article
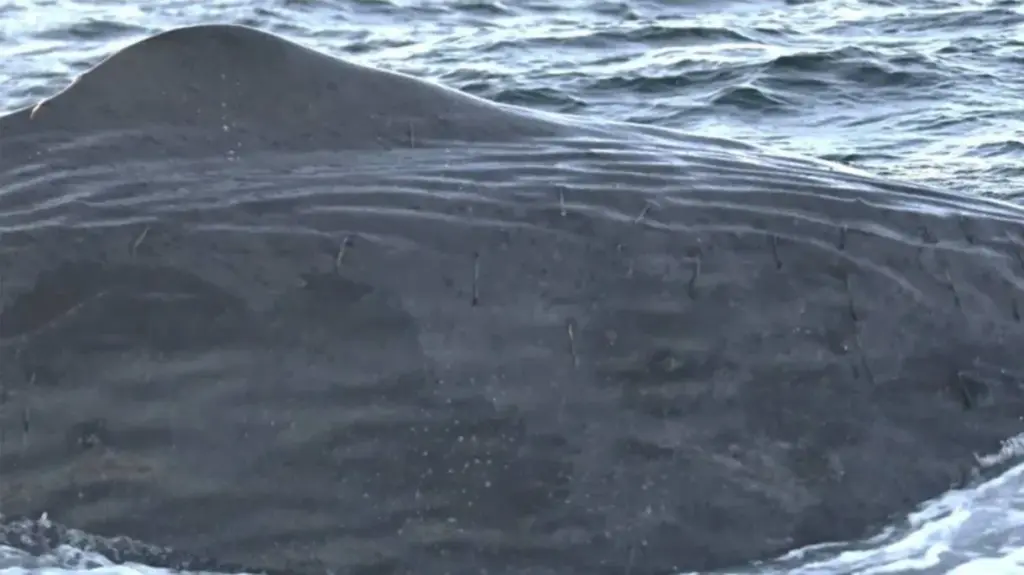
In a groundbreaking development, drones detect whale virus through innovative techniques that enhance whale health monitoring. Equipped with advanced technology, researchers can now obtain vital health data from the breath of humpbacks and other cetaceans, all while minimizing stress to these magnificent creatures. This method is particularly crucial in studying diseases like cetacean morbillivirus, which poses significant threats to marine life populations. As Arctic marine ecosystems face rapid changes, the application of drone technology in marine research provides an essential tool in understanding and safeguarding whale health amidst evolving environmental pressures. The implications are profound, paving the way for proactive measures in wildlife conservation and disease management.
In recent years, aerial surveillance utilizing unmanned vehicles has emerged as a revolutionary approach in studying marine mammal health. These remarkable devices collect exhaled breath from whales, enabling scientists to monitor critical health indicators without intruding on the animals’ natural behaviors. A particular concern among researchers is the cetacean morbillivirus, recognized for its devastating impact on whale populations. By leveraging drone capabilities, scientists can track and respond to potential outbreaks swiftly, which is essential given the precarious state of Arctic marine ecosystems. This progressive method illustrates the synergy between drone technology and wildlife research, transforming how we understand and protect vulnerable species at sea.
The Role of Drones in Whale Health Monitoring
Drones are revolutionizing the field of whale health monitoring by offering a non-invasive method to collect vital biological data. These unmanned aerial vehicles are equipped with advanced sensors and sterile collection devices that can safely gather exhaled breath from whales without causing any disturbance to their natural behaviors. This technological advancement allows researchers to analyze whale health conditions in real-time, making it possible to detect potential diseases such as cetacean morbillivirus before they can escalate into larger outbreaks.
The implementation of drone technology in marine research represents a paradigm shift in understanding the health of cetaceans. Researchers are able to harvest samples from various species, including humpback and fin whales, while minimizing human contact. This innovative technique not only aids in whale health assessments but also provides critical insights into the impacts of climate change and anthropogenic stressors on Arctic marine ecosystems. By studying these interactions, scientists can develop strategies for protecting these majestic marine mammals.
Understanding Cetacean Morbillivirus and Its Impact
Cetacean morbillivirus (CeMV) poses a significant threat to whale populations across the globe, particularly in vulnerable Arctic regions. This contagious virus can lead to severe health issues and mass strandings among affected species. Identifying and monitoring the presence of CeMV through drone-collected whale breath is crucial for managing whale health and ensuring the sustainability of marine ecosystems. Researchers are now able to track the virus’s prevalence in real-time, providing essential data that can inform conservation strategies.
Mass strandings linked to cetacean morbillivirus highlight the urgency of addressing this viral threat. The ability to detect the virus early through innovative drone techniques empowers marine biologists to intervene and protect at-risk populations. Ongoing surveillance using drones facilitates a clearer understanding of the disease’s spread and its impact on whale health. With this knowledge, conservationists can formulate targeted responses and resource allocations to mitigate the effects of this and other emerging pathogens.
Advancements in Drone Technology for Marine Research
The advancements in drone technology are yielding remarkable benefits for wildlife research, particularly in marine environments. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and specialized sampling apparatus are capable of capturing crucial data without physically interacting with the creatures they study. This non-invasive approach allows scientists to gather biological markers, track movement patterns, and assess environmental stressors impacting whale health.
In marine research, drones serve as an invaluable tool for studying animal behavior and health across vast and often inaccessible oceanic regions. The capability of drones to collect genetic material and biological samples from whales not only enhances the database of existing knowledge but also contributes to a more dynamic understanding of the intricacies of life in the Arctic. As drone technology continues to evolve, its application in wildlife research will likely expand, fostering new insights into the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Drones and Their Role in Monitoring Arctic Marine Ecosystems
Arctic marine ecosystems are under increasing pressure from climate change and human activities. Drones play a critical role in monitoring these ecosystems by providing researchers with the tools needed to conduct real-time assessments of marine life health. The use of drones allows for the evaluation of whale populations, as well as the broader marine habitat, in a way that traditional methods cannot match. This aerial perspective offers vital insights into animal behavior and environmental changes, enhancing our understanding of the interconnectedness of marine life.
By integrating drone technology into marine research, scientists can create a comprehensive overview of ecosystem dynamics in the Arctic. These aerial observations can reveal patterns of whale movement and feeding habits, informing conservation efforts that aim to protect marine biodiversity. Moreover, the ability to monitor the health of key species like whales provides a gateway to understanding larger environmental issues that may be impacting these fragile ecosystems.
Future Directions for Drone-Based Wildlife Research
Looking ahead, the future of drone-based wildlife research appears promising, particularly in the realm of whale conservation. The insights gained from utilizing drones to detect diseases like cetacean morbillivirus are paving the way for innovative approaches to wildlife management. With continuous development in drone technology, future studies may include improved sampling methods, data analytics, and the integration of artificial intelligence to forecast health outcomes for marine mammals.
Moreover, the ongoing collaboration between research institutions is integral to advancing these technologies. Collaborative efforts enhance the breadth of research while ensuring that findings effectively contribute to both conservation policies and public awareness initiatives. As strategies evolve, drones will become even more crucial in providing data that support the health and sustainability of not just whales but entire marine ecosystems.
The Importance of Disease Surveillance in Marine Mammals
Disease surveillance in marine mammals is essential for early detection of potential health threats, and drones are now integral to this process. By analyzing whale breath samples collected via drones, scientists can monitor respiratory pathogens that could indicate broader health issues within populations. Understanding the prevalence and impact of diseases like cetacean morbillivirus allows for timely intervention, which is crucial for preventing mortality events that could devastate populations.
Effective disease management not only supports the health of individual whales but also protects the integrity of marine ecosystems. Drones have made it possible to conduct large-scale health assessments that were previously impractical. These important surveillance efforts provide a foundation for enhancing marine conservation initiatives and ensuring that future generations can enjoy thriving whale populations and healthy oceans.
Conservation Implications of Drone Technology
The implications of integrating drone technology into whale research extend well beyond immediate health monitoring. Conservation organizations can utilize data gathered from drone flights to influence policy decisions aimed at protecting marine mammals. By demonstrating the health statuses of key species through empirical evidence, advocates can push for critical environmental protections and address threats posed by climate change and habitat degradation.
Furthermore, the non-invasive nature of drone sampling can be a powerful tool in garnering public support for marine conservation. As stakeholders witness the ongoing research facilitated by drones, there may be an increased awareness of the importance of preserving biodiversity. This growing public interest can drive funding and resources towards conservation efforts, fostering a more informed and engaged community advocating for the protection of marine life.
Potential Challenges in Using Drones for Whale Health Monitoring
Despite the advantages of drone technologies in monitoring whale health, researchers must navigate potential challenges associated with their use. For instance, ensuring the accuracy of the samples collected from whale breath is critical, as various external factors can influence the results. To combat this, scientists are continuously refining their drone equipment and sampling methodologies to uphold the integrity of the data.
Moreover, regulatory frameworks surrounding the use of drones in wildlife research can present obstacles. Navigating the legal landscape requires researchers to maintain compliance with aviation regulations and wildlife protection laws. Building relationships with regulatory bodies and advocating for supportive legislation will be crucial in ensuring that drone use can expand and effectively contribute to the study and conservation of marine mammals.
The Future of Drones in Marine Conservation Efforts
As drone technology continues to advance, its potential application in marine conservation efforts will likely grow. Future developments may include enhanced imaging capabilities, automated data collection processes, and improved flight endurance, which would allow drones to cover larger areas and gather more comprehensive datasets. This evolution will undoubtedly provide researchers with better tools to gauge the health of whale populations and assess environmental impacts more effectively.
Furthermore, as public and scientific interest in marine conservation increases, the integration of drone technology will become essential for driving effective conservation strategies. Collaborations among research institutions, environmental organizations, and technology developers will be pivotal in harnessing the full potential of drones for protecting marine ecosystems. As a result, the ongoing evolution of this innovative technology stands to significantly benefit whale health monitoring initiatives and promote the long-term sustainability of our oceans.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do drones detect whale virus in marine research?
Drones equipped with advanced technology are used to collect exhaled droplets, known as ‘blows’, from whales. This method allows scientists to detect pathogens such as the cetacean morbillivirus while monitoring whale health without distressing the animals.
What is the significance of using drones for whale health monitoring?
Utilizing drones for whale health monitoring represents a major advancement in marine research. It enables researchers to gather important health data from live whales, including identifying infectious diseases like cetacean morbillivirus, without causing stress to the animals.
What role does cetacean morbillivirus play in whale populations?
Cetacean morbillivirus is a highly contagious virus that poses a severe threat to whale populations, causing mass strandings and fatalities among affected marine mammals, including dolphins and porpoises. Drones that detect this virus help researchers understand its impact on whale health.
How does drone technology enhance research in Arctic marine ecosystems?
In Arctic marine ecosystems, drone technology allows for non-invasive collection of biological samples from whales, facilitating the study of their health and the presence of viruses like cetacean morbillivirus, which is crucial given the changing environmental conditions in these regions.
Can drones aid in early detection of whale viruses?
Yes, drones can significantly aid in the early detection of whale viruses. By analyzing the exhaled breath droplets of whales, researchers can identify the presence of viruses such as cetacean morbillivirus, allowing for proactive measures to safeguard whale populations.
What are the advantages of using drones in wildlife research?
Drones offer numerous advantages in wildlife research, including minimal disturbance to the animals, the ability to cover large areas efficiently, and the capability to collect critical data on whale health and the presence of pathogens like cetacean morbillivirus in their habitats.
How might drone technology impact the study of marine mammal diseases?
Drone technology could revolutionize the study of marine mammal diseases by providing a non-invasive method to monitor whale health and track viral outbreaks, such as cetacean morbillivirus, which is increasingly important in preserving biodiversity in changing Arctic ecosystems.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Drones were used to collect whale breath in the Arctic, providing a non-invasive method to monitor whale health. |
| Scientists identified a highly infectious virus, cetacean morbillivirus, linked to mass whale and dolphin strandings. |
| The study enables researchers to analyze pathogens without stressing the whales, offering crucial insights into Arctic ecosystems. |
| Drones collected droplets using sterile petri dishes while biopsy samples were taken from boats. |
| Cetacean morbillivirus has a contagious nature and poses serious threats to marine mammals across species. |
| The research aims to facilitate early detection of marine disease threats for better management of ocean ecosystems. |
| This study is a collaboration between King’s College London, The Royal (Dick) School of Veterinary Studies, and Nord University. |
Summary
Drones detect whale virus through innovative methods that allow researchers to monitor the health of whales non-invasively. By analyzing the breath of whales in the Arctic, scientists have confirmed the presence of the dangerous cetacean morbillivirus, which poses a severe threat to marine mammal populations. This breakthrough research not only enhances our understanding of diseases affecting whale species but also serves as a vital tool for preserving marine ecosystems in the face of rapid climate change. The continued use of drones for long-term monitoring will ensure that threats to ocean health are recognized early, leading to more effective conservation strategies.