Listen to this article
Japan is facing a dementia crisis that demands urgent attention and innovative solutions. With over 18,000 elderly individuals living with this condition wandering off last year alone, the risks to their safety are alarmingly high, and nearly 500 were tragically found dead as a result. As the elderly population in Japan swells to nearly 30%, the nation is striving to integrate advanced technologies, such as Japan dementia technology and AI in dementia care, to provide effective elderly care. The government is keenly aware that the support of robotics, like robot caregivers in Japan, can help bridge the gaps created by a shrinking workforce and contribute to the development of dementia support technologies. By harnessing these tools, Japan seeks not only to monitor and assist those affected but also to enhance their quality of life as the nation navigates this profound challenge.
The urgent need for effective responses to cognitive decline among the elderly is of paramount importance in Japan’s rapidly aging society. As the nation grapples with increasing cases of memory-related illness, innovative care strategies leveraging automation and artificial intelligence are emerging. Enhanced resilience in elderly assistance now relies on sophisticated solutions, encompassing smart robotic aides and cutting-edge monitoring systems aimed at safeguarding those affected. Additionally, community-based initiatives and supportive technologies are coming to the forefront, creating a framework for integrated care that balances human connection with technological advancements. Through these dynamic approaches, Japan aims to sustain a dignified living experience for its aging population suffering from dementia.
The Dementia Crisis in Japan: An Overview
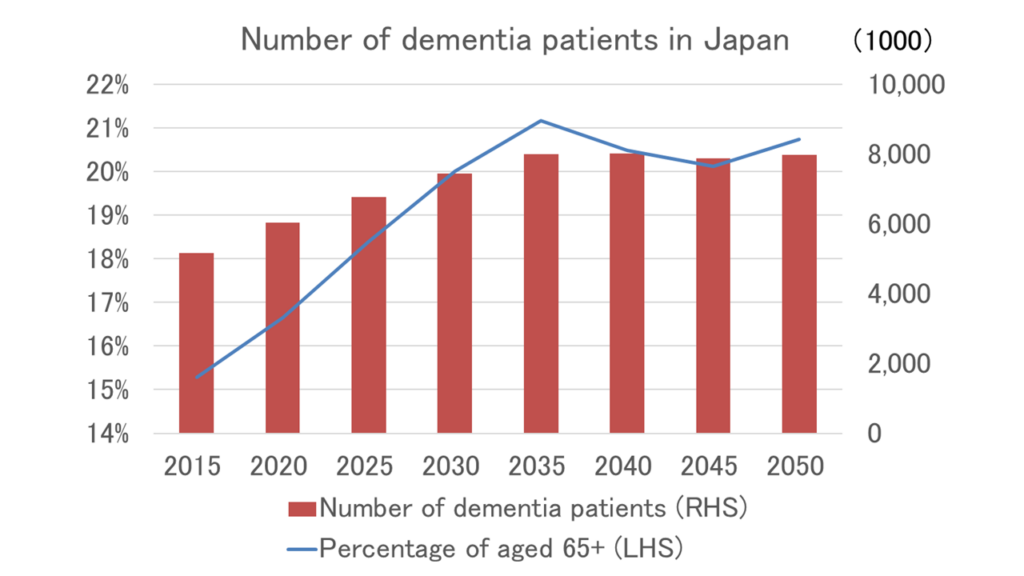
Japan is currently grappling with a significant dementia crisis, illustrating the urgent need for enhanced support and care systems for the elderly population. With nearly 30% of its citizens being 65 years or older—the second highest in the world—Japan’s health care system is increasingly burdened. The alarming statistic of over 18,000 individuals with dementia wandering away from home in the past year, leading to almost 500 fatalities, highlights the profound challenges faced. As the Japanese government project that dementia-related costs will balloon to 14 trillion yen by 2030, a multi-faceted solution is essential to address this pressing epidemic.
Technologically driven initiatives are emerging as viable approaches to mitigate the effects of this crisis. Individuals are advocating for systems that utilize GPS tracking to enhance the safety of those suffering from dementia. These measures not only alert authorities and caregivers when an individual wanders outside a safe zone but also foster a community approach to safeguarding the vulnerable. The urgency is palpable: Japan must integrate innovative solutions into its healthcare model to effectively counter the growing dementia challenge.
Leveraging Technology for Elderly Care in Japan
In response to the dementia crisis, Japan is increasingly prioritizing technological solutions to bolster elderly care. Initiatives involving GPS-based tracking systems, practical wearables, and AI-driven health monitoring are gaining traction. Such technologies enhance the quality of life by providing immediate alerts to caregivers when someone with dementia wanders off, fostering a sense of security for families. The introduction of these innovations has prompted discussions about the fusion of technology and traditional healthcare methods, creating a holistic approach to dementia care in Japan.
Moreover, these advanced technologies address not only immediate concerns but also long-term health management. The implementation of AI in detecting symptoms early through posture analysis, as seen with Fujitsu’s aiGait system, reflects a paradigm shift towards preventive care. By identifying potential signs of dementia early, healthcare providers can offer interventions that enhance life quality and prolong independence for the elderly, thereby minimizing long-term care costs.
AI and Robot Caregivers: The Future of Dementia Support
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics are transforming the landscape of dementia support in Japan. Research institutions, such as Waseda University, are at the forefront of this change, developing humanoid robots like AIREC to assist in daily activities for the elderly. These technologies aim to enhance the quality of life for those with dementia by providing physical assistance and companionship. Such innovations exemplify Japan’s commitment to integrating technology into elderly care, aligning with the pressing need as the population ages.
While robot caregivers like AIREC are still in development, the need for effective solutions is urgent. Current applications include simpler robots in care facilities that help with tasks such as music therapy or gentle physical exercises, proving beneficial in managing dementia symptoms. The balance between human interaction and robotic assistance is key, as many experts assert that robots should complement rather than replace human caregivers, ensuring emotional intelligence and connection remain paramount in dementia care.
The Role of Community and Social Support in Dementia Care
Community engagement is a crucial component in addressing the dementia crisis in Japan. Initiatives like the Restaurant of Mistaken Orders not only provide employment for those with dementia but also create a valuable social environment. By allowing individuals to engage with patrons, these initiatives counteract social isolation, showcasing the significance of human connection in fostering a sense of purpose and belonging among the elderly.
Such community-driven projects emphasize the necessity of integrating social support with technological advancements. While technology offers tools to manage care and track health, the emotional well-being of individuals with dementia is paramount. The interactions facilitated in supportive environments help bridge the gap between technology and human connection, offering a more rounded approach to elderly care.
AI in Dementia Care: Enhancing Early Detection and Intervention
The introduction of AI technologies in dementia care represents a groundbreaking advancement in early detection and intervention strategies. Systems like Fujitsu’s aiGait function on motion-sensing technologies to analyze walking patterns, enabling clinicians to identify probable signs of dementia long before the condition progresses significantly. Such early detection is crucial as it opens avenues for timely care interventions that can improve a patient’s quality of life.
Additionally, the application of AI extends beyond physical monitoring; it also supports personalized care plans that cater to individual needs and conditions. By utilizing data analytics and machine learning, AI can provide insights into the cognitive and emotional requirements of dementia patients, allowing caretakers to adapt their approaches and enhance the level of care provided. This integration of AI into dementia care exemplifies the potential for technology to not only transform healthcare delivery but also revolutionize patient outcomes in Japan.
Robotic Innovations in Elderly Care: A Promising Outlook
Advancements in robotics are playing an increasingly pivotal role in the realm of elderly care within Japan. Robots designed to assist with daily activities, such as AIREC, are transforming the caregiving landscape by providing physical support and contributing to the safety of dementia patients. These robots can potentially relieve the burden on human caregivers, allowing them to focus on more complex tasks that require emotional and cognitive engagement.
However, the journey towards seamless integration of robotic caregivers into everyday life is accompanied by cautious optimism. Research indicates that while robots exhibit capabilities in monitoring and assisting, there remain hurdles in achieving the emotional intelligence required for meaningful interactions with patients. As engineers and scientists continue to iterate on design and functionality, it is vital to ensure that the primary aim of robotic technologies complements human care rather than substituting it.
Japan’s Innovations in Dementia Support Technologies
Japan is a burgeoning leader in the development of innovative dementia support technologies, ranging from tracking devices to robotic caregivers. These advancements are not only reflective of the nation’s commitment to addressing the current crisis but also demonstrate the proactive measures taken to ensure that individuals with dementia can lead fulfilling lives. Technologies such as GPS systems and motion-sensing devices are pivotal in tracking and safeguarding those at risk of wandering, effectively serving as safeguards for their wellbeing.
Moreover, Japanese companies are continuously investing in research and development to create cutting-edge solutions that address various aspects of dementia care, including early detection and daily support. The integration of technology into the elderly care framework not only enhances efficiency but allows families to remain connected with their loved ones, ensuring they receive the best possible care tailored to their specific needs.
The Integration of Human Touch and Technology in Dementia Care
While technological innovations are essential in battling dementia, the irreplaceable human touch must not be overlooked. Experts emphasize that technology should enhance rather than replace the fundamental human empathetic connection necessary for effective elderly care. Interactions between caregivers and patients bring comfort and an emotional foundation that technology alone cannot replicate.
This synergy between human care and technological assistance represents the future of dementia support in Japan. By embracing both elements—technology to monitor and manage care, and human insight to foster emotional wellbeing—Japan can create a more effective, holistic care model. Ultimately, the goal is to ensure dignity and quality of life for those affected by dementia.
Addressing the Shrinking Workforce for Elderly Care in Japan
Japan’s aging population and shrinking workforce present significant challenges in providing adequate care for its elderly, especially those living with dementia. With fewer hands to support an exponentially growing demographic, reliance on technology becomes imperative. The inability to supplement the healthcare workforce with foreign caregivers due to stringent immigration policies further complicates this issue, necessitating innovation in how care is delivered.
As Japan pivots towards technology, initiatives aimed at training existing caregivers to utilize these advanced tools effectively are essential. Not only does technological implementation streamline care processes, but it also alleviates some of the pressures on caregivers, allowing them to manage larger caseloads without sacrificing quality of care. The country’s approach reflects an understanding that, while technology is a vital part of the solution, investing in training and adapting to this changing landscape is equally crucial.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current dementia crisis in Japan?
Japan is currently facing a significant dementia crisis, with over 18,000 older individuals with dementia reported to have wandered off last year alone. The situation is exacerbated by an aging population, where nearly 30% of citizens are over 65. As dementia prevalence rises, the government acknowledges the urgent health and social care costs related to dementia, projected to reach 14 trillion yen ($90 billion) by 2030.
How is Japan leveraging technology to address the dementia crisis?
In response to the dementia crisis, Japan is increasingly integrating technology into elderly care, such as GPS tracking systems to monitor individuals at risk of wandering. Wearable GPS tags that alert authorities when a person strays from designated areas are becoming common, enhancing community safety indirectly through local businesses, like convenience stores.
What role does AI play in dementia care in Japan?
AI is playing a crucial role in dementia care in Japan through innovations like Fujitsu’s aiGait, which analyzes walking patterns to detect early signs of dementia. By identifying these signs through motion-capture technology, healthcare providers can intervene sooner, promoting longer active lifestyles for elderly individuals.
Are robot caregivers being used in Japanese dementia care facilities?
Yes, robot caregivers are increasingly being employed in Japanese dementia care facilities. These robots, such as those being developed by Waseda University, assist with tasks like folding laundry and providing emotional support, contributing significantly to the overall care experience for patients while allowing human staff to focus on critical interactions.
What are some examples of dementia support technologies being developed in Japan?
Recent developments in dementia support technologies in Japan include AIREC, a humanoid robot designed to assist with daily tasks, and Poketomo, a pocket-sized robot that helps individuals remember medications and reduces social isolation through interaction. These technologies aim to enhance the quality of care for individuals living with dementia.
How does Japan’s elderly care system address social isolation among dementia patients?
Japan’s elderly care system incorporates social interventions to combat isolation, exemplified by initiatives like the Restaurant of Mistaken Orders, where individuals with dementia work in a supportive environment. This fosters engagement and gives them a sense of purpose while simultaneously offering respite to their families.
What challenges does Japan face in integrating technology into dementia care?
Japan faces challenges in integrating technology into dementia care, including a shrinking workforce and the need for advanced robot caregivers with human-like interaction capabilities. Experts suggest that while technology can assist, it should not replace the fundamental human connections necessary for effective dementia care.
What is the significance of community support in Japan’s dementia care strategy?
Community support plays a vital role in Japan’s dementia care strategy, emphasizing engagement and connection among individuals with dementia. Initiatives like community cafes and local safety networks demonstrate how social interaction complements technological advancements, highlighting that meaningful connections are as critical as technological solutions.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Dementia Crisis | Japan is experiencing a significant dementia crisis with over 18,000 elderly individuals wandering off and almost 500 found dead last year. |
| Aging Population | 30% of Japan’s population is aged 65 and older, the second highest in the world. |
| Economic Impact | Dementia-related costs are anticipated to rise to 14 trillion yen ($90bn) by 2030. |
| Technological Solutions | Emphasis on GPS and AI technology to assist and monitor elderly and detect dementia early. |
| Role of Robotics | Development of robots like AIREC to assist caregivers and interact with patients. |
| Community Support | Restaurants employing individuals with dementia, promoting social engagement. |
| Balance of Technology and Human Interaction | While technology provides solutions, human interaction remains essential in caregiving. |
Summary
The dementia crisis in Japan is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. With a rapidly growing aging population and increasing numbers of dementia cases, the country is exploring technological innovations to aid in care and monitoring. While advancements such as GPS devices and AI-powered robots show promise, the importance of human connection and community support cannot be overlooked. Solutions must combine both technology and compassionate human interaction to effectively address the challenges posed by dementia in Japan.