Listen to this article
COP30 climate change discussions held in Belém, Brazil, have once again brought global leaders together to address the pressing crisis affecting our planet. This pivotal UN climate conference aimed to forge new climate change agreements, particularly as nations face increasing pressure to tackle greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels. Leaders gathered to confront critical issues such as deforestation efforts that compromise vital ecosystems and threaten biodiversity. However, the outcome has faced criticism, with many leaders expressing dissatisfaction over the lack of substantial measures to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. As the world relies on these discussions to guide future actions, the stakes have never been higher.
The 30th Conference of the Parties (COP30) marks a crucial moment in international efforts to combat global warming and protect the environment. Hosted in the vibrant city of Belém, Brazil, this annual gathering of nations seeks to advance climate initiatives and align global strategies against climate change. Stakeholders are particularly focused on enhancing collaboration through climate accords that facilitate investments in renewable energy while combating the destructive practices of deforestation. As nations are called upon to diminish their carbon footprints, the spotlight remains on policies that successfully phase out fossil fuels and foster sustainable development. Ultimately, the outcomes of COP30 will critically shape our collective path towards a resilient future.
Understanding COP30: The Significance of the Meeting
COP30, the 30th annual Conference of the Parties to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, holds immense significance as a platform for global dialogue on climate policies. This year’s conference took place in Belém, Brazil, a region crucial for its proximity to the Amazon rainforest, underscoring the meeting’s focus on environmental issues. As nations convened, their primary goal was to re-evaluate global commitments to combat climate change and to reinforce agreements made in past conferences about reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By bringing together nearly 200 countries, COP30 aimed to build momentum towards meeting the targets set in the Paris Agreement.
The importance of COP30 also reflects the urgency of addressing the ongoing climate crisis. Climate change continues to threaten ecosystems and human livelihoods worldwide, making the discussions held at this conference critical for future policymaking. With the effects of climate change becoming increasingly severe, COP30 was an opportunity for countries to not only reassess their commitments but also to inspire renewed action. The expectation for a robust response to the challenges posed by climate change was palpable among the attendees, who saw this meeting as pivotal for advancing international cooperation.
The Location of COP30: Brazil’s Role in Climate Discussions
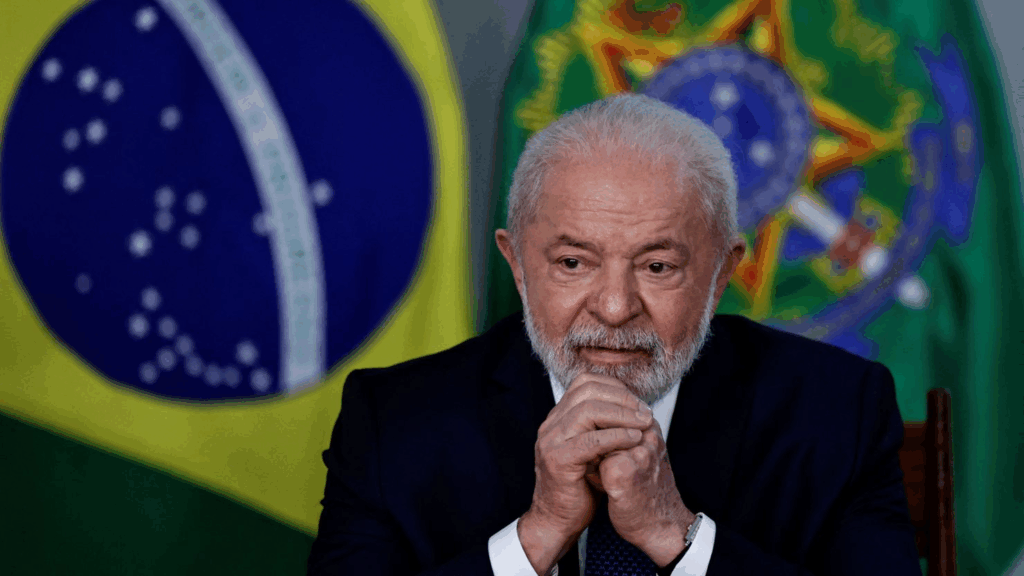
Hosting COP30 in Brazil, specifically in Belém, was a strategic choice that highlighted the connection between environmental preservation and climate negotiations. Brazil, home to a significant portion of the Amazon rainforest, faced the dual challenge of showcasing its natural beauty while grappling with pressing issues like deforestation and fossil fuel extraction. The choice of Belém brought attention to the environmental impacts of such activities and served as a reminder of the importance of preserving natural resources in the face of climate change.
Moreover, the implications of hosting the conference in a region so affected by climate change issues were significant; it enabled the participating nations to witness firsthand the challenges of balancing economic development with environmental sustainability. Despite the logistical challenges faced by delegations seeking accommodation and the criticism surrounding increased fossil fuel licenses issued by Brazil, the conference served as a crucial backdrop for discussions on an equitable transition toward sustainable practices and the preservation of vital ecosystems.
Key Attendees at COP30: Leaders and Their Absence
The participation at COP30 included influential leaders such as UK Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer, French President Emmanuel Macron, and Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva. Their presence symbolized a commitment to addressing climate issues on a global scale, as these leaders engaged in high-stakes discussions aimed at finding solutions to pressing environmental challenges. Additionally, figures like UN Secretary-General António Guterres emphasized collaborative efforts necessary to combat climate change, reinforcing the notion that international cooperation is crucial in this fight.
However, notable absences, including Chinese President Xi Jinping and US President Donald Trump, raised concerns regarding the effectiveness of COP30. As the two largest emitters of greenhouse gases, their lack of representation could hinder progress towards comprehensive climate agreements. Despite a broad representation of over 190 countries, the presence of key players is vital for securing meaningful commitments, as their actions significantly impact global emissions and environmental policies.
The Critical Goals of COP30: Funding and Fossil Fuels
At COP30, a primary focus was the need to address the funding disparities that exist in global climate initiatives. Wealthier nations had previously committed to providing substantial financial support to developing countries, yet significant gaps remain. Brazil presented a comprehensive roadmap intended to guide these financial commitments, aiming for a tripling of funding by 2035 to assist nations disproportionately affected by climate change. The necessity of equitable funding is crucial for ensuring that vulnerable nations can adapt to climate impacts while also making strides toward sustainable energy sources.
Furthermore, the discussions around transitioning away from fossil fuels garnered attention, building on agreements reached at previous COP meetings. Although COP30 sought to clarify the commitments made at COP28 in the UAE regarding fossil fuel dependency, the final outcomes did not put forth strong mandates. This lack of definitive action sparked criticism, indicating that while there is an acknowledgment of the need to shift away from fossil fuels, actual implementation remains a contentious issue on the international agenda.
Deforestation Efforts: What Was Achieved at COP30?
Deforestation was another critical topic at COP30, especially given Brazil’s geographical context and the ongoing challenges posed by illegal logging and land clearing in the Amazon rainforest. Brazil launched the “Tropical Forests Forever Facility,” aiming to raise significant funds to combat deforestation and promote sustainable land use practices. This initiative reflects an urgent recognition of the link between tropical forests and global climate stability, as trees play a vital role in absorbing carbon dioxide.
Despite these efforts, the discussions around deforestation were met with challenges, as the concrete roadmap to address this issue was largely absent from the final agreement. Environmental advocates voiced their concerns over the inadequate measures taken, suggesting that without a decisive plan to curb deforestation, the objectives of COP30 could fall short in addressing the pressing threats posed by habitat loss and climate change.
COP30’s Legacy: Will It Influence Future Climate Action?
The legacy of COP30 remains uncertain, as many observers express skepticism about the tangible outcomes of the conference. Given that negotiations are often bogged down by competing national interests, especially regarding fossil fuel reliance and economic recovery strategies, the agreements reached may not lead to significant advancements in climate action. The urgency of the climate crisis necessitates immediate and bold steps; however, the cautious approaches observed at COP30 raise concerns about the adequacy of commitments made.
Despite the challenges, there is hope that COP30 could serve as a stepping stone for future initiatives. The continued dialogue among nations is vital, as it fosters collaboration and the sharing of best practices. While the outcomes may not have met the expectations of many, the discussions held during the conference pave the way for future negotiations and actions aimed at mitigating the consequences of climate change, emphasizing the necessity for ongoing engagement in the fight for a sustainable planet.
The Impact of Climate Change Agreements from COP30
One of the primary aims of COP30 was to reinforce longstanding climate change agreements and align nations’ commitments with the urgent need for action. The conference underscored the significance of adhering to the goals set out in the Paris Agreement, particularly the ambitious target of limiting global warming to 1.5°C. However, as evidenced by the mixed responses during the negotiations, the actual commitment to these agreements appears tenuous, with many countries falling short on their promises to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The effectiveness of climate change agreements made at COP30 will ultimately depend on the willingness of nations to enforce these commitments domestically. While the conference set the stage for potential collaborative action, the continued reliance on fossil fuels and inadequate support for deforestation efforts highlight the need for stronger action. Going forward, the post-COP30 landscape will require all countries to transform their pledges into concrete actions that can yield measurable progress in combating climate change.
The Role of International Collaboration in Climate Change Mitigation
International collaboration emerges as a crucial element in the dialogue surrounding climate change mitigation, particularly demonstrated in meetings like COP30. As climate impacts transcend national borders, the global nature of environmental challenges necessitates a unified approach to finding solutions. By fostering partnerships among nations, the conference highlighted the importance of sharing knowledge, resources, and technologies vital for addressing climate change.
Strategic alliances established at COP30 could lead to mutual benefits, such as funding collaborations and technology transfer that enhance resilience to climate impacts in developing countries. However, the effectiveness of such collaborations relies on the commitment of all parties to see beyond national interests and prioritize collective action toward sustainable practices. Building robust international partnerships is essential to fostering a concerted response that effectively counters the challenges posed by climate change.
Key Challenges Facing Climate Action Post-COP30
Despite the discussions and initiatives launched at COP30, significant challenges loom over the horizon for climate action. A key obstacle is the need to balance economic growth with environmental sustainability, especially for developing nations reliant on fossil fuel exports. As many nations grapple with the immediate pressures of economic recovery, the urgency to transition to renewable energy sources must be encapsulated within national policies.
Additionally, the inconclusive outcomes of COP30 regarding fossil fuel agreements and deforestation efforts illustrate the complexity surrounding climate negotiations. Moving forward, countries must confront the realities of entrenched practices that contribute to climate change while also fostering innovative solutions that pave the way for a sustainable future. The road ahead will require steadfast commitment and collaboration to surmount these challenges and achieve meaningful global progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main outcomes of COP30 climate change conference?
The COP30 climate change conference, held in Belém, Brazil, aimed to address key climate issues. While discussions included a roadmap for transitioning away from fossil fuels and commitments for climate funding, no substantial new measures were implemented. The agreements failed to include stronger actions on fossil fuels and deforestation efforts, which many countries had hoped for.
How did COP30 address fossil fuels and climate change?
At COP30, while there was a focus on the need to transition away from fossil fuels, the final agreement did not enhance commitments regarding this issue. Brazil proposed a separate fossil fuel roadmap, but the conference ultimately did not introduce new measures aimed at curbing fossil fuel dependence or enhancing climate change agreements.
Why is deforestation a critical topic at COP30 climate change?
Deforestation is a significant contributor to climate change as it increases carbon emissions and reduces biodiversity. At COP30, Brazil attempted to address deforestation efforts by launching the ‘Tropical Forests Forever Facility’ aimed at preventing tropical forest loss. However, definitive actions on deforestation were notably absent from the final agreements.
What are the responsibilities of countries following COP30 climate change agreements?
Following COP30, countries are expected to align their national policies with the climate change agreements made during the conference. This includes developing plans to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, addressing fossil fuel dependencies, and strategizing funding for climate adaptation, especially for vulnerable nations.
How does COP30 impact future climate conferences?
The outcomes of COP30 will set the stage for future climate negotiations, particularly with respect to global ambitions on fossil fuel transitions and deforestation. The lack of decisive agreements may lead to increased pressure at subsequent COP conferences for stronger commitments and actions on climate change.
What challenges did the COP30 climate change conference face?
COP30 faced several challenges, including logistical issues for delegations, resistance to stronger climate action from fossil fuel-dependent countries, and significant dissatisfactions with the outcomes regarding fossil fuels and deforestation. These factors reflect the competing national interests that often hinder progress in climate change agreements.
What role did Brazil play in COP30 climate change discussions?
As the host country for COP30, Brazil played a central role in discussions surrounding climate finance, fossil fuel transitions, and deforestation efforts. Their leadership included launching initiatives like the ‘Tropical Forests Forever Facility’ and outlining funding roadmaps, though the effectiveness of these measures remains in question due to inadequate agreements.
Why are emissions reductions important in the context of COP30 climate change?
Emissions reductions are critical to limit global warming and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change. COP30 sought renewed commitments from countries to submit updated climate action plans, but the initial responses indicated insufficient progress towards necessary reductions to meet the 1.5°C target.
What is the significance of climate finance pledges made at COP30?
The climate finance pledges made at COP30 are significant as they represent commitments by wealthier nations to support developing countries in adapting to the impacts of climate change. These financial agreements aim to enhance resilience and counteract the negative effects of global warming.
How can COP30’s discussions influence public perception of climate change action?
COP30’s discussions, particularly around fossil fuels and deforestation, can shape public perception by highlighting the urgent need for climate action. However, the lack of robust agreements may lead to disillusionment among advocates and the public, influencing activist agendas and policy discussions at both national and global levels.
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| What is COP30? | The 30th annual UN climate meeting, also known as the Conference of the Parties (COP). |
| When was COP30? | Scheduled from November 10 to November 21, with talks extending to November 22. |
| Location Significance | Held in Belém, Brazil, a location near the Amazon rainforest, highlighting environmental challenges and controversies. |
| Key Attendees | Included UK Prime Minister, French President, Brazilian President, but notable absences from the US and China. |
| Importance of COP30 | Addressed the urgent need to meet climate targets established in Paris 2015, focusing on the 1.5°C limit. |
| Agreements at COP30 | No new major commitments on fossil fuels or deforestation, but funding and nature conservation initiatives were discussed. |
| Outlook | Many experts believe that the outcomes of COP30 will not significantly advance global climate action. |
Summary
COP30 climate change discussions in Belém highlighted the urgent need for actionable commitments to address climate change. While some agreements were reached regarding funding and conservation, the lack of concrete measures on fossil fuels and deforestation left many nations dissatisfied. As the global community continues to grapple with climate challenges, the outcomes of COP30 could be pivotal in shaping future international climate policies. The presence of world leaders underscored the importance of collaboration but also revealed significant gaps that need to be addressed in order to meet the ambitious climate targets set during previous conferences.