Listen to this article
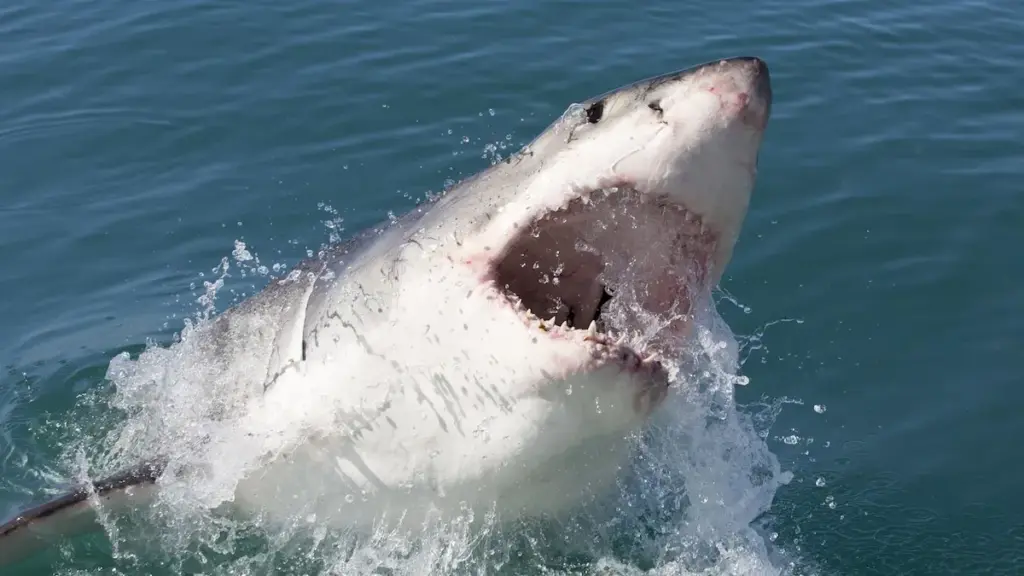
The Mediterranean great white sharks are at the brink of extinction, facing severe threats from illegal fishing practices that devastate their populations. This alarming situation is emphasized by research conducted by scientists and the UK-based Blue Marine Foundation, highlighting the rampant sale of these endangered shark species in North African fish markets. Despite being protected under international law, Mediterranean great white sharks continue to be captured and sold, raising concerns about the effectiveness of shark protection laws and Mediterranean fishing regulations. Conservationists warn that without urgent intervention, these magnificent creatures may vanish from the seas altogether. The plight of the great white is a poignant reminder of the critical need for effective great white shark conservation efforts and stringent enforcement against illegal fishing activities in the region.
Often referred to as the apex predators of the ocean, the Mediterranean white sharks are facing dire circumstances due to unsustainable fishing practices and overexploitation. Recent studies unveil the staggering number of sharks being commercially sold in vulnerable regions of North Africa, which draws attention to the inadequacy of current shark protection regulations. With many of these endangered shark species being fished despite international agreements, the need for improved conservation initiatives is paramount. The situation reflects not only an ecological crisis but also questions the socioeconomic challenges faced by local communities in coastal areas. To ensure the survival of these legendary creatures, a collaborative approach to shark conservation and enforcement of fishing laws is essential.
The Decline of Mediterranean Great White Sharks
The Mediterranean Sea, a biodiversity hotspot, is home to a variety of species, including the majestic great white shark. However, recent studies indicate that these apex predators are on the brink of extinction due to a combination of overfishing and illegal fishing practices. U.S scientists collaborating with the Blue Marine Foundation uncovered disturbing evidence of great whites being targeted and sold in North African markets. This worrying trend highlights not only the dire state of great white shark populations but also the urgent need for effective conservation measures.
The significant decline of great white sharks in the Mediterranean is particularly alarming, as the International Union for the Conservation of Nature has categorized them as Critically Endangered. It is estimated that illegal fishing activities have led to the death of over 40 great white sharks in just a single year. This illegal trade, often overlooked due to complex fishing regulations in various Mediterranean countries, underscores the necessity for strict enforcement of shark protection laws and the collaboration among nations to ensure the survival of these endangered species.
The Role of Illegal Fishing in Shark Population Decline
Illegal fishing remains a critical challenge for the conservation of great white sharks in the Mediterranean. Despite international laws forbidding the capture and sale of these endangered species, illicit activities persist, threatening not only the sharks themselves but the entire health of marine ecosystems. The practice of selling caught sharks in local markets, particularly in North Africa, exemplifies the conflict between local livelihoods and marine conservation efforts. This alarming trend calls for a reevaluation of existing Mediterranean fishing regulations to address loopholes that allow such practices to continue.
Furthermore, it is crucial to recognize that illegal fishing does not occur in isolation. The economic pressures faced by local fishermen, particularly in impoverished regions, create a scenario where the return of endangered species to the ocean may be overlooked in favor of immediate survival needs. Communities that depend on fishing must be provided with viable alternatives and better oversight to prevent the exploitation of endangered shark species. Socioeconomic initiatives combined with stronger enforcement of shark protection laws can help mitigate this trend and promote sustainable fishing practices.
International Conservation Efforts and Regulations
To combat the decline of the Mediterranean great white shark population, international regulatory frameworks have been established to protect threatened species. Agreements made by the EU and Mediterranean nations prohibit the fishing, sale, and retention of these sharks. However, enforcement of these regulations remains inconsistent across the region, allowing illegal activities to flourish. Strengthening these regulations and ensuring compliance can play a pivotal role in the conservation of great white sharks and other endangered shark species.
In conjunction with stronger laws, awareness-raising campaigns are needed to educate local communities about the importance of shark conservation. The balance between human needs and wildlife preservation is delicate, and fostering a culture of conservation can help ensure that both local fishermen and marine biodiversity thrive. Collaborative efforts among governments, NGOs, and the fishing community can create a sustainable framework where both economic needs and marine life preservation co-exist harmoniously.
The Importance of Local Fishing Communities in Conservation
Local fishing communities play a crucial role in the conservation of shark species, particularly in regions like the Mediterranean. Many fishermen depend on fish catches for their livelihoods, which often leads to unintended capture of great white sharks and other protected species. By integrating conservation efforts with local economies, initiatives can be developed that promote sustainable fishing methods while providing fishers with alternative income sources. The challenge lies in educating these communities about the long-term benefits of preserving marine ecosystems, which ultimately support their livelihoods.
Additionally, involving local fishers in conservation efforts can help create a sense of ownership and responsibility for the marine resources they rely on. Initiatives that reward sustainable fishing practices can motivate families to refrain from illegal fishing and instead contribute to the recovery of endangered shark populations. Collaborating with organizations like Blue Marine can inspire innovative approaches to marine conservation and foster community-driven solutions that guarantee both food security and shark protection.
The Role of Science in Tracking Shark Populations
Scientific research plays a vital role in understanding and protecting endangered species like the Mediterranean great white shark. Through advancements in technology, researchers are now able to track the movement and behavior of these sharks, providing invaluable data that can inform conservation strategies. By placing satellite tags on sharks, scientists aim to monitor their populations and identify critical habitats that need protection. Unfortunately, the lack of sightings of great whites during these research endeavors highlights the severity of their decline and the urgency for increased conservation actions.
The utilization of underwater cameras and DNA sampling also contributes to our understanding of shark demographics and their interactions within marine ecosystems. Such scientific endeavors not only help clarify the current status of endangered shark species but also strengthen the case for robust protections against illegal fishing. Continuous monitoring, research, and collaboration with local fisheries can ensure that effective conservation measures are tailored to the specific challenges faced by Mediterranean great white sharks.
Education and Awareness for Shark Conservation
Raising awareness about the plight of great white sharks in the Mediterranean is critical to ensuring their survival. Education plays an essential role in shifting public perception of sharks from fearsome predators to vital components of marine ecosystems. By disseminating information about their ecological importance and the dangers they face from illegal fishing, communities can become advocates for conservation efforts. Educational programs targeting local fishermen and fishing communities can empower them to make informed decisions that benefit both their livelihoods and the ocean’s health.
Moreover, media outlets have a significant part to play in shark conservation. By covering stories about the illegal fishing of great whites and the effectiveness of conservation initiatives, journalists can compel governments and organizations to prioritize shark protection laws. The visibility brought by such reporting can mobilize community action and reinforce the commitment to preserving not only great white sharks but also the diverse marine life that accompanies them. Public awareness campaigns, bolstered by scientific data, will be fundamental in shaping a future where sharks thrive once again.
Challenges in Enforcing Shark Protection Laws
Despite international agreements aimed at protecting great white sharks, enforcement remains one of the biggest hurdles in preventing their decline. Monitoring fishing activities and reporting violations takes considerable resources and cooperation among Mediterranean countries. The complexity of regulations, coupled with varying levels of commitment to enforcement, often leads to exploitation and illegal fishing practices. Streamlining and harmonizing these laws can bridge gaps in regulation and create a more effective framework for protecting endangered shark species in the region.
Another challenge lies in addressing the gap between legislation and local fishing practices. Many fishers, due to lack of awareness or resources, continue operating outside legal requirements, capturing protected shark species. Enhancing communication between conservationists, legal authorities, and local fishermen can help clarify the importance of compliance and the benefits of sustainable fishing practices. Stronger community engagement in conservation initiatives will be essential to establish a foundation of shared responsibility that enhances compliance with shark protection laws.
Collaborative Efforts for Future Conservation
The future of Mediterranean great white sharks rests in the hands of collaborative conservation efforts. By working together, governments, NGOs, and local fishing communities can create unified strategies to protect these endangered marine species. International collaborations can leverage resources for research, raise awareness, and strengthen enforcement of existing protections. Only through shared responsibility and coordinated action can we hope to reverse the decline of great white sharks and ensure their survival in the Mediterranean for generations to come.
Initiatives that foster partnerships can lead to innovative solutions tailored to the unique dynamics of Mediterranean fishing communities. These efforts should include stakeholder input, addressing the needs and concerns of all parties involved in fishing while reinforcing the importance of biodiversity conservation. As the Mediterranean region faces increasing environmental challenges, building resilient frameworks that can adapt to new conditions will be paramount for the survival of species like the great white shark.
The Significance of Marine Biodiversity in Ecosystem Health
Marine biodiversity, including the presence of great white sharks, is crucial for maintaining the health of ocean ecosystems. Sharks are apex predators that help regulate fish populations, thus ensuring a balanced and thriving marine environment. The decline of great whites and other shark species can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, leading to overpopulation of certain fish and a decline in overall ocean health. Protecting great white sharks is not only about saving a single species; it is about safeguarding the biodiversity that supports the entire marine ecosystem.
The health of the Mediterranean Sea hinges on the complex interactions between species, making the conservation of sharks vital. By preserving great white sharks, we also protect the myriad of species that cohabitate their habitats. Promoting awareness about the interconnectedness of marine life can help garner support for broader conservation efforts, contributing to the preservation of biodiversity in the Mediterranean and beyond. Ultimately, investing in shark protection is an investment in the overall viability of our oceans.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the conservation status of Mediterranean great white sharks?
The Mediterranean great white shark population is classified as Critically Endangered by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature. This severe classification highlights the urgent need for effective conservation measures in the region to protect these endangered shark species.
How does illegal fishing affect Mediterranean great white sharks?
Illegal fishing poses a significant threat to Mediterranean great white sharks, contributing to their decline. Research has shown that over 40 individuals were killed in just one year in North African waters, underscoring the impact of illegal fishing practices on this endangered species.
What are the fishing regulations for great white sharks in the Mediterranean?
Mediterranean fishing regulations protect great white sharks under international law, making it illegal to fish for or sell them. However, enforcement of these regulations is inconsistent, allowing illegal fishing activities to persist and jeopardizing the survival of this critically endangered species.
What measures are being taken to protect great white sharks in the Mediterranean?
Efforts to protect Mediterranean great white sharks include monitoring fishing ports and seeking international collaboration to enhance shark protection laws. Conservationists and researchers are working together to document illegal fishing activities and promote awareness about the endangered status of these sharks.
Why are Mediterranean great white sharks considered endangered?
Mediterranean great white sharks are considered endangered due to their declining populations, primarily driven by illegal fishing and industrial fishing practices. With their habitat heavily exploited, these sharks face a critical threat of extinction in the near future.
How can the public help in the conservation of Mediterranean great white sharks?
The public can support the conservation of Mediterranean great white sharks by spreading awareness about the importance of shark protection laws, advocating against illegal fishing, and supporting organizations focused on marine conservation efforts in the region.
What role do Mediterranean countries play in protecting great white sharks?
Mediterranean countries play a crucial role in protecting great white sharks by adhering to signed international agreements that prohibit the retention and sale of endangered species. Collaboration among these nations is essential for enforcing shark protection laws and ensuring the survival of these vulnerable populations.
What impact does the fishing industry have on great white shark populations in the Mediterranean?
The fishing industry significantly impacts great white shark populations in the Mediterranean through overfishing and illegal catches. As one of the most fished waters globally, the Mediterranean puts immense pressure on shark populations, contributing to their critical endangerment.
What is being done to monitor the great white shark population in the Mediterranean?
Researchers are actively monitoring the great white shark population in the Mediterranean, including satellite tagging efforts to track their movements. These scientific initiatives aim to gain valuable data for better understanding and protecting these endangered sharks.
What challenges do Mediterranean great white sharks face aside from illegal fishing?
Aside from illegal fishing, Mediterranean great white sharks face challenges such as habitat degradation, lack of awareness about their conservation needs, and the complexities of international fishing regulations, which hinder effective protection and recovery strategies.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Mediterranean Great White Sharks | Great white sharks in the Mediterranean Sea are facing extinction due to illegal fishing and human activities. |
Summary
Mediterranean great white sharks are critically endangered, with population declines attributed to illegal fishing practices and habitat degradation. Despite being protected under international law, these sharks are still being captured and sold in North African fish markets. Conservationists are working to study and protect the remaining populations, underscoring the urgent need for collaborative efforts to safeguard these majestic predators for future generations.