Listen to this article
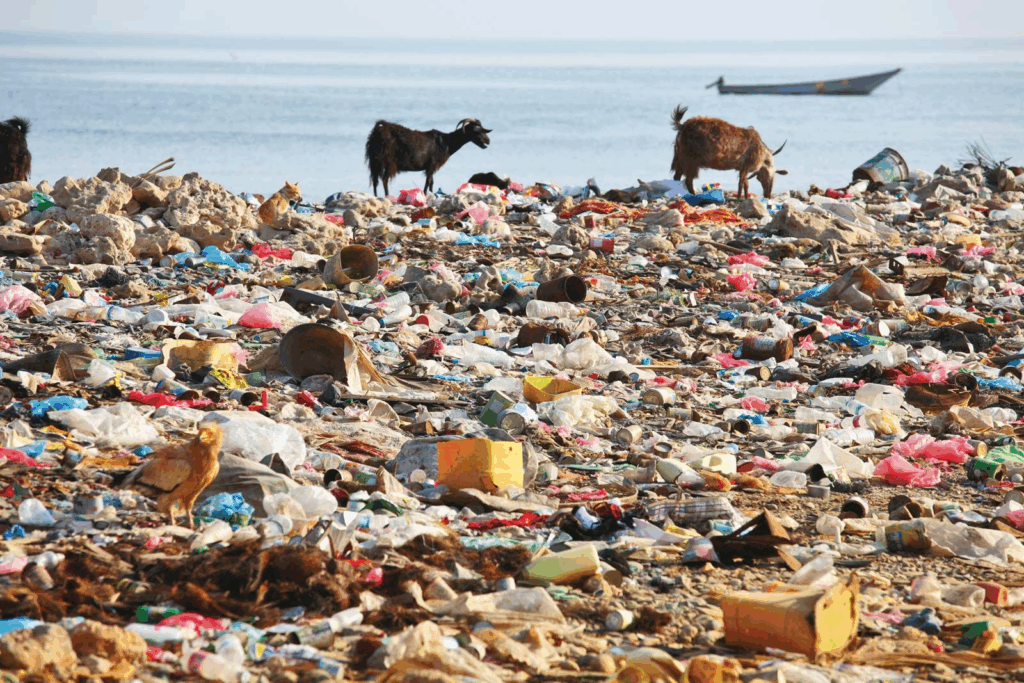
Plastic pollution poses a severe threat to marine wildlife, affecting countless species from seabirds to sea turtles. Recent studies have revealed alarming statistics about plastic ingestion, with seabirds facing a staggering 90% mortality rate after swallowing as few as 23 pieces of plastic. This environmental impact extends beyond birds; sea mammals and turtles also suffer devastating consequences from consuming plastic debris. The pervasive presence of plastic in our oceans not only endangers marine animals but also disrupts entire ecosystems, making ocean conservation efforts more urgent than ever. As we strive to mitigate this crisis, it’s crucial to understand the connection between our daily plastic use and the health of our oceans.
The issue of plastic waste is increasingly recognized as a critical environmental challenge, impacting various forms of aquatic life. From the dangers posed by unintentional plastic consumption in birds and marine mammals to the broader repercussions on ecosystems, plastic pollution represents a grave concern. Research has illustrated how species such as seabirds often mistake plastic for food, leading to dire consequences like nutrient blockage and potential death. To address this ongoing crisis of synthetic refuse, it’s essential to employ more sustainable practices and enhance public awareness. Therefore, focusing on clean-up initiatives and reducing plastic manufacturing can significantly contribute to the protection of ocean biodiversity.
The Alarming Effects of Plastic Pollution on Marine Wildlife
Plastic pollution has emerged as one of the most significant threats facing marine wildlife today. Evidence gathered from extensive scientific research, including the analysis of 10,000 marine animal autopsies, highlights the alarming reality that even small quantities of plastic can lead to fatal consequences. The harsh truth is that seabirds are particularly vulnerable, with a staggering 90% risk of death after ingesting just 23 pieces of plastic. Such data underscores the urgency for ocean conservation efforts that address the pervasive issue of plastic waste in our seas.
Furthermore, marine mammals, including seals and sea lions, exhibit a similarly high risk, with lethal thresholds set at nearly 29 pieces of plastic ingestion. The types of plastic ingested also play a critical role in mortality rates, as specific materials are more toxic than others. Addressing plastic pollution is not merely a matter of aesthetics; it is crucial for the survival of countless marine species. Without immediate intervention, the continuing rise in plastic waste jeopardizes the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Seabirds and Plastic: A Deadly Combination
Seabirds face uniquely grave risks associated with plastic ingestion, resulting in severe injury and even death. The most recent research indicates that these birds can die from consuming just a few pieces of plastic debris, which they often mistake for food. Notably, rubber fragments have been identified as particularly hazardous for seabirds. As such, it becomes imperative to educate the public on the dangers posed by plastic pollution to our avian friends.
The predilection of seabirds to ingest plastic can lead to devastating repercussions not only for individual birds but also for the entire ecosystem. The continual accumulation of plastic debris impacts seabird populations, potentially disrupting their breeding and feeding patterns. Conservation strategies focusing on reducing marine plastic waste are essential, as saving seabirds means preserving biodiversity and the health of marine habitats worldwide.
Plastic Ingestion Among Sea Turtles: Risks and Realities
Sea turtles are another group significantly affected by plastic pollution. Recent studies reveal that these creatures may need to ingest up to 405 pieces of plastic to reach similar mortality rates observed in seabirds and marine mammals. However, this figure should not diminish the seriousness of the threat; each piece can cause internal injuries, impede digestion, and lead to long-term health complications, making plastic ingestion a critical issue for sea turtle conservation.
Misidentifying plastic bags as jellyfish is a common behavior among turtles, leading to tragic consequences. The findings from global research highlight the urgent need for effective conservation measures. Solutions involve not only reducing plastic production and improving waste management systems but also promoting public awareness about the dangers posed by plastic to sensitive species like sea turtles. Protecting these magnificent creatures requires a unified effort in tackling the underlying causes of plastic pollution.
Understanding the Environmental Impact of Marine Plastic Pollution
The environmental impact of plastic pollution on marine ecosystems is profound and multifaceted. As millions of tons of plastic enter the oceans each year, the resulting ecological disruption is felt across numerous species, altering habitats and food chains. The potential for plastic to transport harmful chemicals and microplastics magnifies the threat to marine life, leading to intricate challenges in ocean conservation that necessitate immediate and vigorous action.
Moreover, the presence of plastic in marine environments presents significant risks for both wildlife and human health. As smaller organisms consume microplastics, they inadvertently enter the food chain, posing indirect risks to larger predators, including humans. The wide-reaching consequences of marine plastic pollution make it imperative for societies to prioritize actions aimed at reducing plastic waste and developing effective ocean cleanup initiatives. Emphasizing sustainable practices is key to protecting marine ecosystems and maintaining the health of our oceans.
Promoting Ocean Conservation to Combat Plastic Pollution
Ocean conservation efforts must take center stage in the fight against plastic pollution. Comprehensive strategies involving community engagement, international cooperation, and innovative waste management solutions are integral to reducing plastic waste entering marine ecosystems. Educating the public on the impact of plastic pollution on marine wildlife fosters greater involvement in conservation efforts, enhancing the efficacy of initiatives designed to protect vulnerable species.
Collaboration between governments, non-profit organizations, and local communities is essential in creating meaningful change. Initiatives that focus on beach cleanups, community recycling programs, and policies aimed at reducing single-use plastics can significantly mitigate the flow of debris into the ocean. Uniting efforts across diverse sectors empowers communities to preserve marine biodiversity and protect vital ocean habitats, securing a healthier future for both marine life and humanity.
The Role of Research in Combating Plastic Pollution
Scientific research serves as the backbone of efforts to combat plastic pollution. Studies, such as the one analyzing thousands of marine animal autopsies, provide critical data that informs policy decisions and conservation strategies. With clear evidence of the direct correlation between plastic ingestion and mortality rates among various marine species, researchers can effectively advocate for measures that address plastic pollution comprehensively.
Further research into the types of plastics that pose the greatest risks allows for targeted interventions. By understanding which materials are most harmful to marine wildlife, conservationists can tailor their approaches to address the specific challenges faced by different species. This data-driven perspective not only highlights the pressing need for immediate action but also inspires innovative solutions aimed at reducing plastic footprints and promoting healthier ocean ecosystems.
Innovative Solutions to Mitigate Plastic Waste
Mitigating plastic pollution requires innovative solutions that go beyond traditional waste management approaches. Emerging technologies such as biodegradable plastics and recycling innovations are pivotal in reshaping the future of plastic production and disposal. These advancements, coupled with increased public awareness, stand to redefine our relationship with plastic and its role in society.
Moreover, proactive measures like community-focused initiatives promoting the use of alternatives to single-use plastics can have a substantial impact. By fostering a culture of sustainability and responsible consumption, society can collectively reduce plastic waste and its adverse effects on marine wildlife. The integration of sustainable practices into daily life is crucial for achieving lasting change and ensuring the well-being of our oceans and the myriad of species that inhabit them.
The Importance of Public Awareness in Plastic Pollution
Public awareness plays a crucial role in effectively addressing the problem of plastic pollution. Increasing knowledge about the impacts of plastic on marine wildlife, particularly among young people, can inspire a new generation to be stewards of the environment. Educational campaigns that highlight the dangers of plastic ingestion and the benefits of conservation efforts are essential in mobilizing community action towards ocean conservation.
Encouraging responsible practices, such as reducing plastic consumption and participating in cleanup events, empowers individuals to make impactful changes. When communities understand the detrimental effects of plastic waste on marine ecosystems, they are more likely to advocate for and adopt sustainable practices in everyday life. Proactive public engagement can significantly contribute to the ongoing battle against plastic pollution and foster a culture of environmental stewardship.
Collaborative Efforts Against Plastic Pollution
Collaboration across various sectors is a powerful driver in the fight against plastic pollution. Government agencies, non-profit organizations, and the private sector can work together to implement policies and initiatives aimed at reducing plastic waste. By combining resources and expertise, these collaborations can create comprehensive strategies that address the issue on multiple fronts, from production to disposal.
In addition to policy initiatives, partnerships with local communities can amplify the impact of ocean conservation efforts. Engaging citizens in the conversation about plastic pollution fosters a sense of ownership and accountability for their local environments. Through collaborative cleanup efforts and educational programs, communities can come together to tackle the pressing issue of plastic pollution, ultimately leading to healthier oceans and thriving marine wildlife.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does plastic pollution affect marine wildlife?
Plastic pollution poses a significant threat to marine wildlife, leading to injury, poisoning, and death. Many animals, including seabirds and sea turtles, mistakenly ingest plastic, which can accumulate in their digestive systems and cause fatal blockages or poisoning. The study highlights that even small amounts of plastic can have lethal consequences for various marine species.
What is the impact of plastic ingestion on seabirds?
Seabirds are severely impacted by plastic ingestion, with research showing that swallowing just 23 pieces of plastic can lead to a 90% mortality rate. Plastics can cause internal injuries, blockages, and exposure to toxic substances, ultimately jeopardizing seabird populations and their ecological roles in marine ecosystems.
Why is plastic pollution dangerous for sea turtles?
Plastic pollution presents dangerous risks for sea turtles, which can mistake plastic bags for jellyfish. The research indicates that sea turtles face lethal threats from ingesting approximately 405 pieces of plastic. This not only endangers individual turtles but also threatens the overall balance of marine ecosystems.
What is the environmental impact of plastic pollution on marine mammals?
The environmental impact of plastic pollution on marine mammals is profound, with studies revealing that ingesting around 29 pieces of plastic can be fatal for these animals. Different types of plastics pose varying risks; soft plastics and fishing debris are particularly hazardous for marine mammals like seals and dolphins.
How can ocean conservation efforts address plastic pollution?
To effectively tackle plastic pollution, ocean conservation efforts must focus on reducing plastic production, enhancing collection and recycling systems, and conducting cleanup initiatives. Research like that conducted by Ocean Conservancy provides crucial data that can inform policies and strategies aimed at protecting marine wildlife from the deleterious effects of plastic.
What should be done to prevent the fatal effects of plastic pollution on marine wildlife?
Preventing the fatal effects of plastic pollution on marine wildlife requires stringent measures, including reducing plastic waste, improving waste management, and increasing public awareness about the dangers of plastic ingestion among marine creatures. Education and policy changes can help minimize plastic use and protect vulnerable species.
What role do seabirds play in understanding plastic pollution?
Seabirds serve as critical indicators of plastic pollution levels in marine environments. Their susceptibility to plastic ingestion allows scientists to assess the broader impact of plastic waste on ocean health and the risks faced by various marine species, guiding conservation efforts and policy development.
What are the consequences of plastic ingestion for marine ecosystems?
Plastic ingestion has dire consequences for marine ecosystems, including population declines in key species such as seabirds, sea turtles, and marine mammals. This can disrupt food chains and ecosystem balance, as the health of these animals is essential for the overall function of marine environments.
| Species | Risk Level (pieces of plastic ingested) | Type of Plastic | Percentage Affected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seabirds | 23 pieces | Rubber | 33% affected |
| Marine Mammals (e.g., dolphins) | 29 pieces | Soft plastics, fishing debris | 10% affected |
| Sea Turtles | 405 pieces | Hard and soft plastics | 50% affected |
Summary
Plastic pollution poses a significant existential threat to ocean wildlife, with alarming effects highlighted in recent studies. Researchers have identified critical ingestion levels of plastic that can lead to devastating outcomes for various marine species. Specifically, seabirds face a high mortality risk after consuming merely 23 pieces of plastic, while marine mammals and sea turtles are also significantly affected. The findings emphasize the urgent need to tackle plastic pollution through reductions in plastic production and enhanced recycling efforts, as well as cleanup initiatives to protect vulnerable marine ecosystems.