Listen to this article
Recent police funding changes are set to reshape the landscape of law enforcement in England and Wales. The Home Office’s decision to eliminate the Officer Maintenance Grant, which incentivized police departments to uphold officer headcount targets, marks a significant shift in funding strategy. Instead, this funding will now focus on enhancing neighborhood policing, aiming to increase the presence of dedicated officers in local communities. Critics argue that previous funding schemes have led to too many officers relegated to support roles rather than engaging directly with citizens. As police officer numbers decline amidst these changes, the emphasis on more community-focused strategies signals a pivotal moment for public safety and accountability.
In a transformative era for law enforcement finance, the recent alterations to police funding prioritize community relations and local engagement over traditional metrics of officer deployment. The Home Office’s shift away from a grant system that rewarded high officer counts points to a broader reallocation of resources aimed at bolstering community policing initiatives. By promoting dedicated officers who are integrated into neighborhood dynamics, the government seeks to address the pressing issues facing public safety today. As this reimaging of policing unfolds, the challenges of staffing and resource allocation remain at the forefront, beckoning a discussion about the essential skills needed in modern crime prevention.
Understanding Police Funding Changes: Impact on Community Policing
Recent changes to police funding, particularly the discontinuation of the Officer Maintenance Grant, are poised to redefine community policing efforts across England and Wales. The Home Office’s initiative to shift funding from maintaining officer headcount to dedicated neighborhood officers aims to bolster the presence of police in communities. This transition underscores a growing acknowledgment that mere numbers are insufficient; the quality and effectiveness of policing are paramount. By re-evaluating funding strategies, the government hopes to ensure that officers are actively engaged in the neighborhoods they serve, thereby fostering trust and collaboration between law enforcement and the community.
However, critics argue that without proper financial backing, the ambitious target of integrating 13,000 additional officers into neighborhood policing roles by 2029 is at risk. The proposal reflects a balancing act between maintaining officer counts and providing necessary resources for specialized roles. Community policing is essential not just for crime prevention, but also for addressing the root causes of criminal behavior, which often involves collaboration between various community stakeholders. As the landscape of crime evolves, so too must the strategies adopted to combat it, necessitating a reevaluation of funding priorities to support them.
The Role of Neighborhood Policing in Crime Prevention
Neighborhood policing has emerged as a critical component in modern law enforcement strategies, focusing on building relationships between officers and community members. This grassroots approach allows police officers to engage directly with residents, helping to identify and address local issues promptly and effectively. With the government’s commitment to generating funding aimed at increasing neighborhood officer numbers, there’s potential for significant improvements in community safety and crime prevention. This personalized approach not only serves to deter crime but also fosters a sense of community belonging and accountability.
Moreover, as crime patterns shift—particularly with an increase in online offenses—neighborhood policing needs to adapt. Enhancing police presence in communities goes hand in hand with employing specialists, such as cybercrime analysts, to address contemporary challenges. Therefore, while neighborhood officers play a crucial role in localized crime prevention, the integration of diversified skills within these units will be vital for a comprehensive public safety strategy. Effective neighborhood policing is about more than assigning officers; it is about creating a responsive, multi-faceted law enforcement approach that can address both traditional and emerging crime.
The Consequences of Reducing Police Officer Numbers
A significant concern arising from the ongoing changes in police funding is the potential reduction in officer numbers, which would mark a reversal in progress made since 2019. Over the years, the removal of financial support for officer maintenance threatens to destabilize police forces across England and Wales. The warnings issued by police officials about the difficulties in meeting future recruitment targets highlight the serious implications of budget constraints. If police officer populations dwindle, the effectiveness of local policing initiatives and community engagement could suffer.
Furthermore, as suggested by critics, the implications of relying on back-office roles for officers will exacerbate the problem. It raises an alarm about prioritizing administrative duties over preventative community policing activities. Without a stable influx of officers into active community roles, the societal benefits of policing will diminish, leading to a potential increase in fear of crime among residents. The success of community policing efforts hinges on adequate funding, and any reduction in officer numbers could undo progress made toward creating safer neighborhoods.
Understanding the Officer Maintenance Grant and its Discontinuation
The Officer Maintenance Grant was introduced under the Conservative government to meet considerable recruitment ambitions with a promise to hire 20,000 new officers by 2023. However, the recent announcement of its discontinuation raises questions about the sustainability of police funding. With the transition to neighborhood officer funding, there is a clear shift away from the previous model that prioritized headcount to one that values active community engagement. This shift signals a recognition that simply having more officers does not intrinsically lead to improved public safety or community trust.
Despite the stated intentions behind this funding change, there remain significant concerns regarding how police forces can adapt. As historical data shows a trend of increasing officer numbers leading to back-office placements, the concern emerges that neighborhood policing efforts may not be adequately resourced. If the funding does not match the demands of active neighborhood policing, the ultimate goal of enhancing public safety may face setbacks. Therefore, while the concept of dedicated funding for community officers is promising, its implementation will be crucial for sustaining effective policing.
The Future of Neighborhood Policing Initiatives
With the government’s Neighbourhood Policing Guarantee promising additional officers in community roles, the response from police and the public will be critical in shaping the future of local law enforcement strategies. The plan outlines a comprehensive approach aimed at integrating officers directly into neighborhood communities, addressing crime, and enhancing public safety from a local perspective. Importantly, the effectiveness of such an initiative hinges on the government’s commitment to adequately fund these roles to ensure that officers possess the resources necessary to succeed.
Moreover, as societal needs continue to evolve, neighborhood policing must also adapt to meet contemporary challenges. Establishing clear accountability and visibility for police officers within neighborhoods can strengthen community ties and ultimately foster safer environments. While the challenge remains to fulfill recruitment goals amid financial constraints, the government’s focus can pivot toward ensuring a robust framework that supports local officers with the tools, training, and capacity needed to effectively combat crime and enhance community well-being.
Incorporating Community Perspectives in Policeman Recruitment
As the conversation around police officer numbers and funding changes unfolds, it becomes increasingly apparent that community perspectives should be integral to recruitment strategies. Engaging local residents in the decision-making processes around policing fosters transparency and encourages community members to take active roles in their safety. This collaborative approach can not only improve trust between law enforcement and communities but also ensure that the recruitment of officers reflects the diversity and needs of the populations they serve.
For effective neighborhood policing, it is crucial to assess community priorities and adapt recruitment methods accordingly. The recent changes in police funding allow an opportunity to refocus efforts on attracting candidates who are not just skilled officers but also community-oriented individuals who understand the specific challenges faced by their neighborhoods. By fostering a culture of inclusivity and responsiveness within police forces, recruitment strategies can lead to a more connected and supportive policing environment that reflects the community’s values.
The Financial Implications of Police Funding Strategies
Changes in police funding strategies carry significant financial implications for law enforcement forces across England and Wales. For many forces, the shift from a centralized grant like the Officer Maintenance Grant to funding focused on community-based policing means they must navigate budget constraints carefully. Reduced funding, paired with the challenge of meeting officer recruitment targets, may limit the current capabilities of policing initiatives, leading to tough financial decisions on which units to retain and which to cut.
Moreover, the argument put forth by critics about underfunding police officers amid inflationary pressures sets the stage for a critical discussion on sustainable policing finance. Departments may struggle to fund specialized units essential for modern policing if base officer numbers are compromised. For effective neighborhood policing to be achievable, financial strategies must evolve to ensure that police departments can manage both frontline presence and specialized skill needs efficiently, allowing for a well-rounded approach to public safety.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Neighborhood Officer Roles
The plan to embed more neighborhood officers into local communities raises questions about the effectiveness of their roles in combating crime and enhancing safety. By focusing on neighborhood policing, police forces hope to create identifiable local officers who are trusted figures within their communities. Evaluating the outcomes of this strategy will be crucial to ascertain whether the reduced reliance on back-office duties improves community engagement and overall crime rates. Metrics such as response times, crime statistics, and community feedback will play essential roles in this evaluation.
Additionally, the success of this initiative can also hinge on the continued professional development of neighborhood officers. Ensuring that police officers receive ongoing training in community relations, conflict resolution, and crime prevention strategies will fortify their ability to positively impact communities. Thus, while the goal of increasing presence and visibility in neighborhoods is laudable, its execution must focus on the holistic development of officers dedicated to community service and protection.
Addressing Public Concerns About Safety and Accountability
Public concerns regarding safety and police accountability remain paramount in light of the proposed changes to funding and officer distributions. As neighborhoods await the promised increase in dedicated neighborhood officers, residents want assurances that their safety is prioritized and that officers are well-equipped to engage with the community. This heightened sense of scrutiny makes it essential for police departments to be transparent about their strategies and results in addressing crime.
Moreover, the integration of community feedback into policing strategies can enhance public accountability and trust. Initiatives to solicit input from local residents can create pathways for constructive dialogue, helping officers better understand community concerns while fostering a collaborative environment. When the public perceives that their police force is responsive and accountable, it enhances community relations and cooperation, paving the way for a safer, more secure neighborhood environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key changes in police funding related to neighborhood policing?
The Home Office is discontinuing the Officer Maintenance Grant, which incentivized police forces to maintain officer headcount targets, and replacing it with dedicated funding for neighborhood policing. This shift aims to bolster community policing efforts and ensure more officers are actively serving on the front lines.
How will the discontinuation of the Officer Maintenance Grant affect police officer numbers?
The discontinuation of the Officer Maintenance Grant is expected to impact police officer numbers as funds will be redirected to support neighborhood policing. However, there are concerns that this change may not sufficiently address the current decline in officer numbers, which fell from March 2024 to March 2025.
What is the government’s plan to enhance neighborhood policing by 2029?
The government has announced the Neighbourhood Policing Guarantee, which aims to deploy an additional 13,000 officers into neighborhood policing roles by 2029. This initiative focuses on establishing identifiable local officers to address community concerns and improve overall public safety.
What challenges do police forces face with the new funding structure for neighborhood policing?
Police forces face significant challenges due to budget cuts and funding limitations under the new neighborhood policing framework. The Police Federation has voiced concerns over insufficient funding amid rising inflation, which may lead to tough decisions about staff reductions and resource allocation.
How has previous police funding impacted community policing initiatives?
Past police funding decisions, particularly the Officer Maintenance Grant, have resulted in numerous officers allocated to back-office roles rather than community policing duties. Critics have argued that this has undermined the effectiveness of neighborhood policing initiatives, making it crucial to refocus resources on frontline officers.
What has been the public response to police funding changes affecting officer numbers?
The public response has been mixed, with calls for more police officers on the streets and concerns about safety. The Conservative opposition has criticized the Labour government’s funding proposals, claiming they are insufficient to fulfill promises for hiring additional officers and enhancing community safety.
What is the significance of the £18.4 billion investment in police forces?
The announced £18.4 billion investment in police forces is intended to support a range of initiatives, including enhancing neighborhood policing. This funding is seen as crucial for addressing both current staffing challenges and improving overall community safety by increasing visible police presence.
How does the Home Office’s new funding aim to transition officers into community roles?
The Home Office’s new funding initiative for neighborhood policing will replace the current Officer Maintenance Grant, aiming to transition more desk-based officers into community roles. This approach intends to ensure that police forces have the necessary personnel actively engaging with their communities.
What impact have budget cuts had on police recruitment and retention?
Budget cuts have significantly impacted police recruitment and retention, leading to job losses and a reduction in officer numbers. The Police Federation has highlighted that these cuts hinder the ability to achieve targets for increasing neighborhood officers, contributing to a challenging environment for maintaining public safety.
How are police forces expected to prove their officer numbers to access funding?
To access the dedicated funding from the Home Office, police forces must demonstrate they have maintained their officer numbers. This requirement ensures accountability and directs resources towards forces that meet specific staffing benchmarks.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Elimination of Officer Maintenance Grant | The Home Office is discontinuing the grant that funds police forces for meeting officer headcount targets. |
| Replacement with Neighborhood Officer Funding | Funding will now prioritize dedicated neighborhood officers instead of merely increasing headcounts. |
| Achievements of the Grant | Established in 2019, aimed to recruit an additional 20,000 officers by 2023, which was achieved. |
| Criticism of Back-Office Assignments | The Labour government argues the grant led to officers being assigned to non-frontline roles. |
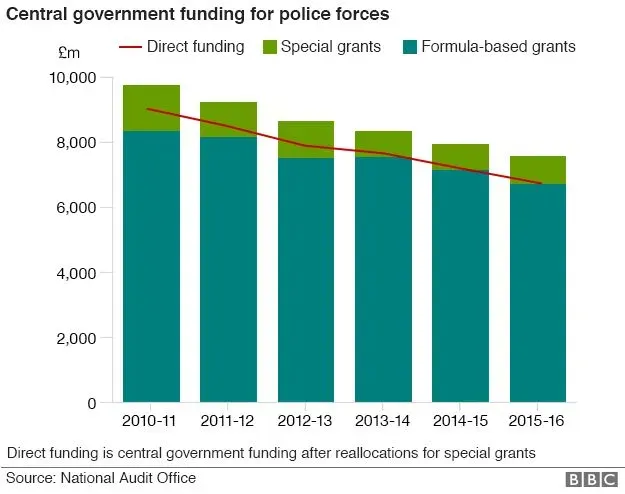
| Decline in Officer Numbers | Total officers decreased from March 2024 to March 2025 for the first time since 2018. |
| Funding Concerns | Critics highlight that insufficient funding may hinder recruitment of additional officers. |
| Support for Neighborhood Policing | Government’s Neighbourhood Policing Guarantee aims for 13,000 additional neighborhood officers by 2029. |
| Investment in Police Forces | Home Secretary Shabana Mahmood plans to announce £18.4 billion investment to support police. |
| Need for Specialist Skills | Emphasis on the need for flexibility to recruit necessary specialists amid officer number goals. |
Summary
Police funding changes are set to reshape the structure and effectiveness of law enforcement in England and Wales. With the discontinuation of the Officer Maintenance Grant, the expectation is for a strategic shift towards strengthening neighborhood policing. The government’s drive to replace this grant signifies a commitment to enhance community safety by repositioning officers where they are needed most. As the landscape of crime evolves, ensuring the right balance of personnel, alongside adequate funding, becomes crucial to meet the demands of modern policing.