Listen to this article
The Gaza peace plan put forth by the Trump administration aims to restore stability and peace in the war-torn region, marking a pivotal step in the long-standing conflict between Israel and Hamas. Spearheaded by prominent figures, including Secretary of State Marco Rubio and former UK Prime Minister Tony Blair, this initiative seeks to ensure effective governance and Gaza reconstruction. The involvement of an international stabilization force underscores the urgent need for a durable ceasefire while allowing humanitarian aid to flow freely. Through this plan, the Trump administration hopes to engage various stakeholders and establish a pathway to sustainable Middle East peace. As efforts unfold, the complexities of post-war Gaza governance will be monitored closely by both local and international entities to prevent further escalation.
The initiatives surrounding the resolution of conflict in Gaza have gained renewed attention under the Trump administration’s proposal for a peace accord. This strategic plan not only emphasizes the roles of key international leaders but also highlights the critical need for reconstruction efforts and governance in the area. With a focus on establishing a humanitarian response coupled with security measures, the proposal aims to foster cooperative engagement among various factions and global powers alike. As discussions surrounding a ceasefire and reconstruction progress, the political landscape will be heavily influenced by the actions taken to stabilize the region while addressing the underlying causes of the conflict. This multifaceted approach embodies a significant commitment to achieving lasting peace and security within the often tumultuous geopolitical environment of the Middle East.
The Trump Administration’s Gaza Peace Plan
The Trump administration has unveiled its ambitious Gaza peace plan, appointing prominent figures like Secretary of State Marco Rubio and former UK Prime Minister Tony Blair to its Board of Peace for Gaza. This governance initiative, designed to bring stability and reconstruction to the war-torn region, reflects a broader strategy aimed at resolving the long-standing conflict between Israel and Hamas. By including key players from the international community, the administration seeks to leverage diplomatic influence while prioritizing humanitarian aid and rebuilding efforts across the Gaza Strip.
Under the proposed Gaza peace plan, an International Stabilization Force (ISF) will oversee the training of local Palestinian police forces, ensuring that security precedes further developmental initiatives. Led by US Major General Jasper Jeffers, the ISF is expected to mitigate violence and create an atmosphere conducive to dialogue and reconstruction. As the plan progresses, the hope is that it will not only reconcile hostilities but also foster economic growth, paving the way for long-term peace in the region.
Key Players in the Gaza Reconstruction Effort
The Gaza reconstruction effort is being spearheaded by an influential board comprising global leaders such as Ajay Banga of the World Bank and Robert Gabriel, the US National Security Adviser. Each board member has been assigned significant roles that reflect their expertise and past experiences in governance and international relations. This diverse collective brings together a wealth of knowledge and resources that are critical for implementing effective strategies aimed at stabilizing Gaza and addressing the humanitarian crisis faced by its residents.
Additionally, the National Committee for the Administration of Gaza (NCAG) has been established to oversee the daily operations of the region post-conflict. With Ali Shaath as its leader, this Palestinian technocratic committee is tasked with ensuring that governance in Gaza aligns with the broader objectives set out by the Board of Peace. By fostering local leadership while incorporating international oversight, the reconstruction plan aims to create a self-sustaining governance structure that can withstand external challenges and foster peace.
Controversies Surrounding the Hamas Ceasefire
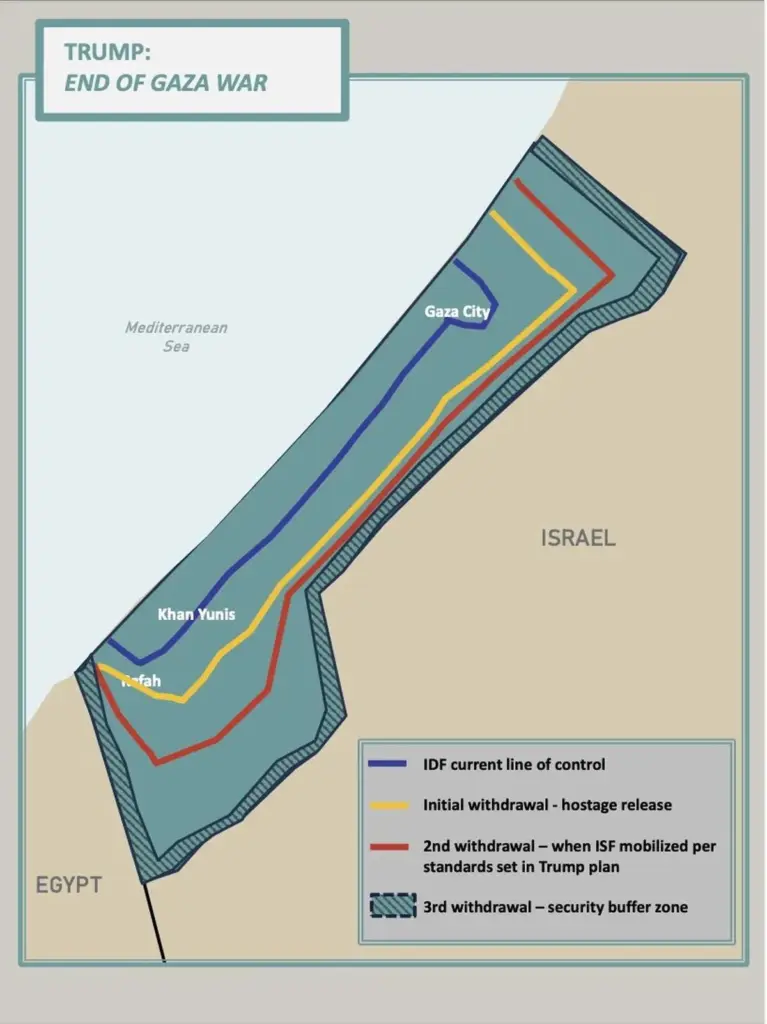
The fragile ceasefire between Hamas and Israel has drawn both skepticism and hope from international observers. Arranged in October, the truce included critical elements like a hostage exchange and the partial withdrawal of Israeli forces, yet it remains marred by ongoing accusations of violations from both sides. The complexities of enforcing such agreements while treating the humanitarian needs effectively pose significant challenges, and there are fears that setbacks will reignite hostilities and undermine the reconstruction efforts for Gaza.
Hamas’s compliance with the ceasefire terms is viewed as imperative for maintaining stability in the region. The US has clearly outlined expectations, emphasizing the need for disarmament and the return of hostages. However, with nearly 450 Palestinian fatalities reported from ongoing Israeli strikes since the ceasefire’s inception, the situation continues to be unstable. Achieving a comprehensive peace agreement will require persistent engagement from both sides alongside international mediation to ensure adherence to the ceasefire and ongoing diplomatic dialogues.
Role of the International Community in Gaza Peace
The role of the international community has never been more crucial in the context of Gaza’s peace and reconstruction efforts. With global powers like the US and UK representing significant interests, their involvement through boards such as the one recently established under the Trump administration highlights a multifaceted approach to peacemaking in the Middle East. The anticipated International Stabilization Force, alongside constructive measures from entities like the World Bank, underscores the need for collective action in addressing the immediate aftermath of conflict while planning for a sustainable future.
Moreover, the engagement from the Quartet of international powers—the US, EU, Russia, and the UN—through its representatives adds another layer of oversight and support for the ongoing peace initiatives. As every member of this committee brings unique strengths and perspectives, collaboration between these countries and local governance will be critical in securing a lasting peace. Investing in infrastructure and economic opportunities must go hand in hand with political stability to foster resilience among the Palestinian population.
Challenges in Gaza’s Humanitarian Conditions
Gaza’s humanitarian conditions remain dire and continue to be a significant concern amid ongoing reconstruction efforts. Reports of widespread devastation following the recent conflict highlight the urgent need for essential supplies, including medical assistance, food, and clean water to people affected. The United Nations has repeatedly emphasized the necessity for uninterrupted aid flow to alleviate the suffering of over 2 million residents. However, bureaucratic and logistical challenges often hinder access to those most in need, stretching resources to their limits.
Additionally, the humanitarian landscape is complicated by the geopolitical dynamics surrounding the Gaza Strip. For instance, the ongoing tensions between Israel and Hamas must be navigated carefully to ensure that aid workers can operate without risk and that supplies reach the intended recipients. Addressing these humanitarian challenges is not merely about stopping the bleeding; it requires a long-term commitment to rebuilding infrastructure and ensuring that human rights and dignity are prioritized at every level of governance and aid delivery.
Long-term Vision for Gaza’s Stability
The long-term vision for Gaza’s stability hinges on a collaborative framework that encourages both local participation and international support. As the Trump administration’s Board of Peace focuses on governance and reconstruction, aligning efforts with the priorities of the Palestinian people will be paramount. This vision is not just about rebuilding physical structures but also fostering social cohesion and economic development that can uplift communities and restore hope among the populace. By integrating community voices into the development process, the likelihood of achieving lasting peace increases considerably.
Investment in education, job creation, and infrastructure, coupled with consistent diplomatic pressure for compliance with peace agreements, will be crucial for ensuring that the hard-won gains are not easily reversed. The process is inherently delicate, as any missteps can lead to a recent history of violence repeating itself. Therefore, a clear roadmap charting the course for Gaza’s future, which includes measurable goals and accountability for all parties involved, is essential in shaping a viable pathway for stability.
The Importance of Governance in Post-War Gaza
Effective governance post-war will play a critical role in the success of Gaza’s reconstruction efforts. The establishment of the National Committee for the Administration of Gaza (NCAG) is a step towards creating a stable administrative structure necessary for rebuilding. With a focus on transparency and accountability, the committee must navigate complex political dynamics while addressing immediate needs such as education, health, and security. Having capable local leadership supported by international oversight can promote citizens’ trust in the governance process and foster collaboration across all sectors.
Moreover, establishing strong governance frameworks will also be essential for attracting international investments and support, which are necessary for rebuilding shattered infrastructure and providing essential services. The international community must consider constructive engagement with local governance to facilitate this process, ensuring that policies reflect the needs of the people while aligning with broader security objectives. By prioritizing governance as a foundation for peace, there is potential for a transformative and sustainable future for Gaza.
Security Concerns in the Gaza Strip
Security in the Gaza Strip is one of the most pressing issues following the ceasefire agreement. The ongoing threat from armed groups and the need for a strong, vetted local police force have been highlighted in the Trump administration’s Gaza peace plan. The deployment of the International Stabilization Force (ISF) under Major General Jasper Jeffers aims to build a framework of safety that is essential for successful reconstruction efforts. Ensuring security is not merely about military presence but entails a comprehensive approach that includes community policing and engaging local populations in maintaining peace.
While the plan targets establishing a terror-free environment, the historical context of violence and retaliation complicates these efforts. Both Hamas and Israel must navigate their security dilemmas to avoid escalation. Moreover, robust dialogues around disarmament and civilian protection are vital for sustainable peace. A concerted effort to engage in open discussions focused on security concerns while respecting human rights will be pivotal in shaping a secure and peaceful Gaza.
Economic Recovery Initiatives for Gaza
Economic recovery initiatives are critical for the long-term stability of Gaza, as rebuilding the economy can significantly impact the lives of its residents. The involvement of international financial institutions like the World Bank suggests a commitment to not only addressing immediate needs but also investing in sustainable growth. By focusing on crucial sectors such as agriculture, technology, and education, recovery initiatives can lead to job creation and infrastructure development that equips Gazans with the means to rebuild their lives.
Additionally, cooperation among various political and economic entities will be essential in achieving economic recovery. Encouraging private sector investments while ensuring access to resources will enhance local capacities to drive economic growth. The reconstruction process should aim to empower communities by promoting entrepreneurship and inclusive development models that consider the unique socio-economic factors within Gaza. This approach has the potential not only to improve living standards but also to fortify the groundwork for peaceful coexistence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Gaza peace plan proposed by the Trump administration?
The Gaza peace plan proposed by the Trump administration is a comprehensive framework aimed at ending the longstanding conflict between Israel and Hamas. Central to this plan is the establishment of a ‘Board of Peace,’ which includes notable figures such as US Secretary of State Marco Rubio and former UK Prime Minister Tony Blair. This board is designed to oversee the reconstruction and stabilization of Gaza, following a ceasefire agreement between Hamas and Israel. The plan outlines goals for governance, security, and humanitarian aid within the region.
Who are the key members of the Gaza peace plan’s ‘Board of Peace’?
The ‘Board of Peace’ for the Gaza peace plan includes prominent members such as US Secretary of State Marco Rubio, former UK Prime Minister Tony Blair, US National Security Adviser Robert Gabriel, and Major General Jasper Jeffers, who will lead the International Stabilization Force. The board plays a crucial role in managing Gaza’s reconstruction and overseeing efforts to maintain peace and stability in the area after the conflict.
What role does the International Stabilization Force play in the Gaza peace plan?
The International Stabilization Force, as part of the Gaza peace plan, is tasked with training and supporting Palestinian police forces to ensure security and preserve peace in Gaza. Led by US Major General Jasper Jeffers, this force aims to establish a terror-free environment essential for the successful reconstruction of the region. Its deployment is a critical component of the plan to stabilize Gaza post-conflict.
How does the Gaza ceasefire fit into the overall peace plan?
The Gaza ceasefire is a pivotal element of the peace plan initiated by the Trump administration. Established in October, this ceasefire accompanied a hostage exchange and a partial withdrawal of Israeli forces. It marked the first phase of the peace process, creating a necessary environment for subsequent phases, which aim to address Gaza’s reconstruction and the demilitarization of Hamas. However, ongoing violations from both sides raise concerns about the ceasefire’s sustainability.
What are the expected outcomes of the Gaza reconstruction efforts under the peace plan?
The expected outcomes of the Gaza reconstruction efforts under the peace plan include rebuilding infrastructure, restoring essential services, and improving humanitarian conditions for the 2.1 million residents of Gaza. This plan emphasizes the need for international support and oversight to ensure the effective governance of post-war Gaza. Additionally, it aims to create a stable and secure environment free from Hamas’ military influence, setting the groundwork for lasting peace in the region.
What challenges does the Gaza peace plan face in its implementation?
The Gaza peace plan faces numerous challenges, including the fragile nature of the current ceasefire, ongoing hostilities, and the need for Hamas’ full compliance with disarmament obligations. Additionally, humanitarian conditions in Gaza remain dire, complicating the reconstruction process. International collaboration will be essential, but mistrust between parties may hinder effective implementation of the plan’s objectives, including the establishment of a stable governance structure.
How does the Trump administration envision long-term stabilization in Gaza?
The Trump administration envisions long-term stabilization in Gaza through a combination of reconstruction efforts, governance reforms, and the establishment of security measures facilitated by the International Stabilization Force. The involvement of notable leaders in the ‘Board of Peace’ is meant to ensure a strategic approach to resolving underlying issues and fostering cooperation among local authorities. This coordinated effort aims to create an environment conducive to peace and prosperity for Gazans.
What impact did the October conflict have on the Gaza peace plan’s timeline?
The conflict in Gaza, ignited in October 2023, significantly impacted the peace plan’s timeline by necessitating an immediate ceasefire and humanitarian aid measures. The violence resulted in substantial loss of life and heightened tensions, prompting the urgent establishment of the ‘Board of Peace’ to oversee reconstruction efforts and implement the peace plan. While initial phases have commenced, ongoing violence complicates the transition to subsequent phases focused on governance and demilitarization.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Formation of the Board of Peace | Trump appointed US Secretary of State Marco Rubio and former UK Prime Minister Tony Blair as founding members. |
| Executive Board Members | Includes Jared Kushner, Steve Witkoff, Marc Rowan, Ajay Banga, and Robert Gabriel. |
| Chairman of the Board | Donald Trump serves as the chairman, emphasizing its unprecedented prestige. |
| National Committee for the Administration of Gaza (NCAG) | A 15-member committee to manage post-war governance in Gaza, led by Ali Shaath. |
| International Stabilization Force (ISF) | To be deployed in Gaza to train Palestinian police, led by US Major General Jasper Jeffers. |
| Ceasefire and Reconstruction Phases | Phase one includes a ceasefire; phase two involves reconstruction and demilitarization of Gaza. |
| Current Situation | Ongoing violence with casualties, humanitarian needs highlighted by the UN due to dire conditions. |
Summary
The Gaza peace plan sets forth a comprehensive approach to resolving ongoing conflicts in the region. With key figures like Marco Rubio and Tony Blair at the helm, the Board of Peace aims to coordinate efforts for Gaza’s stabilization and reconstruction. This initiative includes establishing the International Stabilization Force to ensure security and manage governance through the newly formed NCAG. Despite these efforts, the situation remains precarious, with ongoing violence and critical humanitarian needs to address.