Listen to this article
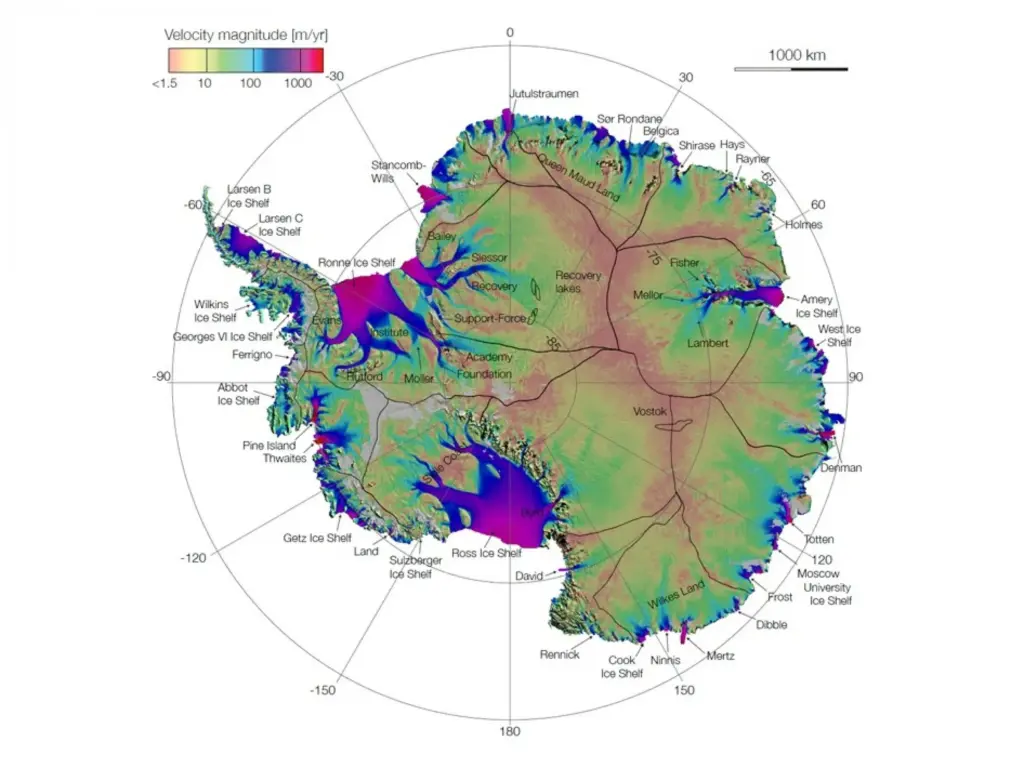
Antarctica’s ice mapping has revolutionized our understanding of the hidden landscape beneath the continent’s vast ice sheets. Recent research, leveraging satellite technology and glacier movements, reveals a detailed picture of Antarctic topography that has remained obscured for centuries. This groundbreaking mapping effort has unveiled thousands of subglacial features, including previously unknown hills and ridges, which provide essential insights into glacier dynamics and their interactions with climate change impacts. As our knowledge of these intricate ice formations expands, we can better anticipate the effects of global warming on sea levels and the future of polar environments. This descriptive portrait of Antarctica not only enhances scientific exploration but also raises awareness about the critical importance of preserving this fragile ecosystem.
The exploration of Antarctica’s icy depths through innovative mapping techniques represents a significant advancement in glacial studies. By uncovering the sub-surface terrain of this remote continent, scientists are gaining crucial insights into the complex dynamics of ice behavior and the intricate natural features that lie hidden beneath. The detailed profiles of glacier movements, combined with the understanding of temperature changes and environmental shifts, shed light on the interactions between ice and the underlying landforms. This discovery is vital in predicting how vital Antarctic ecosystems will respond to ongoing climate change and its subsequent impacts. Enhanced knowledge of these subglacial landscapes is key to understanding the future of our planet’s climate.
Unveiling Antarctica’s Ice Mapping
A game-changing new map detailing the Antarctic subglacial landscape has emerged, revealing intricate topographical features hidden beneath the ice. Researchers, utilizing advanced satellite data and in-depth analyses of glacier movements, have uncovered an astonishing array of thousands of hills and ridges that define the continent’s underbelly. This comprehensive mapping effort not only enhances our understanding of Antarctic topography but also offers significant implications for the study of ice dynamics in a rapidly changing climate.
The mapping process involved innovative techniques that combined satellite imagery with physics-based models. By understanding how ice flows, scientists were able to infer the underlying geological features, revealing a clear picture of Antarctica’s mysterious subglacial realms. This new data set allows for a high-definition perspective of previously unknown structures, making it an invaluable resource in climate research, especially concerning the interactions between ice and climate change impacts.
Antarctica’s Topography and Subglacial Features
Understanding Antarctica’s topography is essential for predicting future glacial movements and the broader implications for global sea-level rise. The newly uncovered subglacial features provide insights into how these immense ice masses behave and how they might respond to climate change. The detailed contours and depths mapped also suggest regions that may be more vulnerable to melting, as warmer temperatures continue to exert their influence on the continent.
Furthermore, the structural complexities determined through this mapping, from deep channels to hidden mountain ranges, play a critical role in ice dynamics. These features affect how glaciers flow, interact, and ultimately melt into the surrounding ocean, contributing to the ongoing conversation about climate resilience and adaptation strategies. Enhanced knowledge of these subglacial characteristics is indispensable for accurately modeling potential future scenarios concerning both regional and global environmental changes.
The Role of Glacier Movements in Climate Change
Glacier movements are a fundamental aspect of studying Antarctica’s response to climate change. The recently updated mapping emphasizes the importance of these movements, revealing how the underlying topography influences the speed and direction of glacial flow. Researchers have been particularly attentive to the effects of climate change on these dynamics, as changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can dramatically alter ice behavior.
Additionally, the interplay between subglacial features and glacier movements can create critical feedback mechanisms. As glaciers glide over various terrains, they may experience acceleration due to the presence of deep channels or smooth ridges, potentially leading to enhanced melting rates. Understanding these interactions is crucial for developing accurate predictions regarding sea-level rise, as melting glaciers directly contribute to ocean levels rising around the world.
Impact of Climate Change on Antarctica’s Ice Dynamics
The implications of climate change on Antarctica’s ice dynamics cannot be overstated. With melting glaciers contributing significantly to sea-level rise, researchers are racing against time to understand the underlying mechanisms that drive these transformations. The newly uncovered subglacial topography helps paint a clearer picture of how these ice masses are likely to respond to increasing temperatures, providing vital information that can influence policy and conservation efforts.
Moreover, the physics of ice flow, informed by the new mapping details, offers insights into how climate change could reshape the Antarctic landscape. Understanding the potential alterations in glacier movements prompted by warming conditions can lead to better forecasting models, equipping scientists with the necessary data to address pressing environmental challenges in an era of climate uncertainty.
Exploring the Future of Antarctic Research
The future of Antarctic research is poised for significant advancements thanks to the latest discoveries in ice mapping. As more detailed topographical information becomes available, researchers can refine their models and hypotheses regarding glacial behavior and the broader impacts of climate change. The new mapping not only marks a technological leap in how scientists gather and analyze earth data but also emphasizes the urgent need for continued exploration and study of the Antarctic region.
With the ability to visualize previously hidden subglacial features, scientists can now focus on uncharted territories that could reveal crucial data about past climate events and their relevance to current global patterns. This enriched understanding is imperative for climate action and for shaping the initiatives aimed at mitigating adverse outcomes associated with climate change.
Significance of Antarctic Ice Mapping in Climate Modeling
The role of Antarctic ice mapping in climate modeling is of immense significance. By uncovering detailed subglacial landscapes, scientists can enhance existing climate models that predict future ice dynamics and sea-level changes. The accuracy of these models is crucial for understanding potential scenarios resulting from climate change, as the rate of ice melt directly correlates with global sea-level rise.
Furthermore, the mapping facilitates a more profound comprehension of iceberg calving processes and melting rates. With this information, researchers can evaluate how changes in the ice sheet’s stability may affect adjacent ecosystems and coastal communities, reinforcing the importance of integrated climate research efforts that account for these interdependencies.
Understanding Subglacial Basins and Their Influence
Subglacial basins represent significant components of Antarctica’s geological and hydrological systems. The recent mapping has exposed the complex nature of these features, which can influence not only glacier dynamics but also the stability of the ice sheet itself. These basins may act as reservoirs of meltwater, impacting flow patterns and potentially leading to accelerated glacial retreat.
Additionally, the discovery of extensive subglacial channels and depressions offers new insights into how water interacts with ice sheet dynamics. This relationship is essential for predicting future changes in glacier behavior as the climate continues to warm, given that subglacial water can either promote stability or contribute to instability in glacial systems.
The Role of Advanced Technology in Ice Mapping
Advancements in technology play a pivotal role in the progress of ice mapping in Antarctica. Researchers have leveraged high-resolution satellite imagery and sophisticated data analysis techniques to obtain unparalleled views of the frozen continent and its concealed landscapes. These technologies facilitate the collection of vast amounts of data, enabling scientists to build accurate models of Antarctica’s topography and ice flow dynamics.
Such technological innovations are critical to overcoming the challenges presented by the extreme conditions in Antarctica. With each breakthrough, researchers gain deeper insights into the subglacial features that shape glacial movement and, consequently, the implications for climate change. The integration of technology with traditional research methods creates a powerful synergy that propels forward the understanding of this vital region.
Antarctica’s Hidden Mountain Ranges and Their Significance
The identification of previously unknown mountain ranges in Antarctica has significant implications for our understanding of the continent’s geology and ice dynamics. These hidden formations can influence the flow of glaciers, with steep slopes and elevated ridges potentially acting as barriers that impact how ice moves across the landscape. This newfound knowledge allows for a more comprehensive understanding of how these challenges may be affected by a warming climate.
Moreover, the potential for these mountain ranges to host unique ecosystems is an area of growing interest. As researchers explore these untouched areas, they may uncover new species and habitats that have remained isolated from external influences. The preservation of these regions and the study of their complexities are crucial for understanding broader ecological connectivity in the face of climate change.
Frequently Asked Questions
What recent advances have been made in Antarctica’s ice mapping?
Recent advancements in Antarctica’s ice mapping include the creation of a detailed new map revealing the landscape underneath the ice using satellite data and studies of glacier movements. This breakthrough identifies thousands of previously unknown subglacial features, significantly enhancing the understanding of Antarctica’s topography.
How does Antarctic topography influence glacier movements?
Antarctic topography plays a critical role in influencing glacier movements. The detailed mapping has clarified how the landscape underneath the ice interacts with ice dynamics, affecting the speed and direction of glaciation. As glaciers move over varied subglacial features, their dynamics can lead to differences in melt rates and contributions to sea-level rise.
What are the implications of Antarctica’s ice mapping for climate change research?
The implications of Antarctica’s ice mapping for climate change research are profound. By providing a clearer picture of ice dynamics and the interactions with the underlying topography, this mapping contributes significantly to understanding how Antarctica might respond to climate change, including the potential acceleration of glacier movements and melting rates.
What new subglacial features have been identified in Antarctica’s ice mapping?
The latest ice mapping of Antarctica has identified thousands of new subglacial features, including previously unknown hills, ridges, and deep channels such as the one located in the Maud Subglacial Basin. These features are crucial for understanding the terrain’s influence on glacier dynamics and ice movements.
How does the new detailed map compare to previous ice mapping efforts in Antarctica?
The new detailed map represents a significant upgrade over previous ice mapping efforts in Antarctica, often described as moving from a grainy, pixelated image to a high-definition digital representation. It integrates advanced satellite data with physics-based analysis, resulting in a comprehensive view of the Antarctic ice dynamics and subglacial landscape.
Why is understanding the ice dynamics beneath Antarctica important?
Understanding the ice dynamics beneath Antarctica is vital because it informs predictions about glacier movements and melt rates, which are crucial in assessing the potential for global sea-level rise. The newly mapped features influence how ice flows, making it an essential aspect of climate change impact studies.
What role does satellite data play in mapping Antarctica’s ice?
Satellite data plays a pivotal role in mapping Antarctica’s ice by providing high-resolution images and measurements of surface features, which researchers use to infer the landscape underneath. This data, combined with physics-based models of ice flow, enhances the understanding of Antarctic topography and its effects on glacier movements.
How can this new mapping of Antarctica’s ice affect future scientific studies?
The new mapping of Antarctica’s ice can significantly impact future scientific studies by filling knowledge gaps about subglacial terrain and ice dynamics. This improved understanding will enhance predictive models of how Antarctica’s glaciers will react to climate change, aiding in global climate assessments.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Mapping Discovery | A new map reveals Antarctica’s landscape beneath the ice in unprecedented detail, enhancing understanding of the frozen continent. |
| Research Methodology | Combines satellite data with glacier movements, uncovering thousands of previously unknown hills and ridges. |
| Significant Findings | Identified a deep channel in the Maud Subglacial Basin, 50 meters deep, 6 km wide, and 400 km long. |
| Importance | Improves models for predicting how Antarctica will respond to climate change and contributes to understanding global sea-level rise. |
| Study Publication | Findings published in the journal Science, highlighting the need for further research despite uncertainties. |
Summary
Antarctica’s ice mapping is a groundbreaking advancement in understanding the hidden landscape beneath the continent’s icy surface. The new detailed map provides vital insights into the geological features that influence glacier dynamics and melting processes. As climate change continues to impact our planet, understanding these dynamics is crucial for predicting future sea-level rise and the overall effects on global ecosystems.